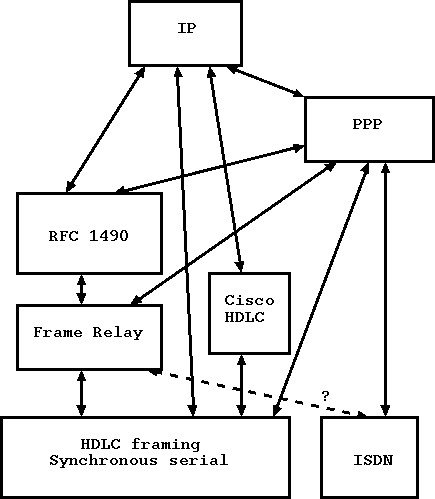
Рисунок 1: Способы передачи IP поверх последовательных синхронных и ISDN WAN соединений
| Архив документации на OpenNet.ru / Раздел "Сети, протоколы, сервисы" | (Для печати) |
Представьте следующую ситуацию: вы разрабатываете маршрутизатор TCP/IP основанный на FreeBSD. Продукт должен поддерживать синхронные последовательные WAN-линии, то есть выделенные цифровые каналы, работающие на скоростях до T1, где используется инкапсуляция HDLC. Вы должны поддерживать следующие протоколы для передачи IP пакетов через кабель:
На Рисунке 1 показаны все возможные комбинации:

Рисунок 1: Способы передачи IP поверх последовательных синхронных и ISDN WAN соединений
Эта ситуация была показана Джулианом Элисчером (Julian Elischer) <julian@freebsd.org> и мной в 1996 когда мы работали в компании Whistle InterJet. В то время во FreeBSD имелась очень ограниченная поддержка последовательного синхронного оборудования и протоколов. Мы думали использовать OEMing от Emerging Technologies, но вместо этого решили реализовать это сами.
Ответом был netgraph. Netgraph это сетевая подсистема в ядре, следующая принципу UNIX достижения мощности посредством комбинации простых инструментов, каждый их которых предназначен для выполнения одной, вполне определенной задачи. Основная идея проста: есть узлы (nodes) (инструменты) и ребра (edges) которые соединяют пару узлов (отсюда и "граф" в "netgraph"). Пакеты данных идут в двух направлениях вдоль ребер от узла к узлу. Когда узел получает пакет данных, он обрабатывает его, и затем (обычно) отправляет его другому узлу. Обработка может быть простейшим добавлением/удалением заголовков или может быть более сложной или включает другие компоненты системы. Netgraph напоминает потоки (Streams) в System V, но он разработан более гибким и производительным.
Netgraph оказался очень полезным для работы в сети, и сейчас он используется в Whistle InterJet для всех указанных выше комбинаций протоколов (за исключением frame relay поверх ISDN), плюс обычный PPP поверх асинхронных последовательных (таких как модемы и терминальные адаптеры) и PPTP, которые включают шифрование. Во всех этих протоколах данные полностью обрабатываются в ядре. В случае PPP, пакеты согласования (negotiation) обрабатываются отдельно в пользовательском режиме (смотрите порт FreeBSD для mpd).
Глядя на рисунок выше, очевидно, что должны быть узлы и ребра. Менее очевиден факт, что узел может иметь определенное число подключений к другим узлам. Например, вполне возможно иметь одновременно IP, IPX, и PPP в инкапсуляции RFC 1490; конечно, мультиплексирование это та задача, для которой и нужен RFC 1490. В этом случае нужно три ребра подключить к узлу RFC 1490, одно для каждого стека протоколов. Нет требований, чтобы данные следовали строго в определенном направлении, и нет ограничений на действия, которые узел выполняет с пакетом. Узел может быть источником/потребителем данным, например, если он связан с аппаратной частью, или он может просто добавлять/удалять заголовки, мультиплексировать и т. п.
Узлы netgraph существуют в ядре и полупостоянно. Обычно узел существует пока он подключен, к какому либо другому узлу, однако некоторые узлы постоянные, например, узлы, связанные с аппаратной частью; когда число ребер уменьшается до нуля, аппаратное устройство выключается. Поскольку узлы существуют в ядре, они не связаны с каким либо определенным процессом.
Эта картина все еще слишком упрощенная. В реальной жизни узел нужно конфигурировать, запрашивать его состояние и т. д. Например, PPP сложный протокол, с большим количеством опций. Для этого в netgraph определены управляющие сообщения (control messages). Управляющее сообщение это "внешние управление". Вместо следования от узла к узлу как пакеты данных, управляющие сообщения посылаются асинхронно и непосредственно от одного узла к другому. Два узла могут быть не связаны (даже через другие узлы). Для обеспечения этого в netgraph существует простая схема адресации по которой узел можно идентифицировать, используя простую ASCII-строчку.
Управляющие сообщения это просто структуры Си с фиксированным заголовком (структура ng_mesg)
и переменной областью данных. Есть несколько управляющих сообщений, которые все узлы должны понимать;
они называются общие управляющие сообщения (generic control messages) и реализованы в базовой системе.
Например, узлу можно указать разрушить себя или создать/разрушить ребро. Узлы могут также иметь свои собственные управляющие сообщения, зависящие от типа. Каждый тип узла, определяющий свои собственные управляющие сообщения должен иметь уникальное значение typecookie. Комбинация полей typecookie и command в заголовке управляющего сообщения определяет, как его интерпретировать.
На управляющие сообщения часто идут ответы в виде ответного контрольного сообщения (reply control message). Например, чтоб узнать состояние узла или статистику вы можете послать управляющее сообщение "get status"; он затем пошлет вам ответ (который идентифицируется значением token, скопированным из исходного запроса) содержащий запрошенную информацию в поле данных. Заголовок ответного управляющего сообщения обычно такой же, как исходный заголовок, но выставлен флаг reply flag
Netgraph предоставляет способ преобразования этих структур в строки ASCII и обратно для упрощения взаимодействия с человеком.
В netgraph, ребра на самом деле не существуют сами по себе. Вместо этого ребро это просто комбинация двух крючков (hooks), по одному от каждого узла. Крючок узла определяет как узел может быть подключен. Каждый крючок имеет уникальное, статически определенное имя, которое часто отражает его цель. Имя имеет значение только в контексте данного узла; два узла могут иметь крючки с одинаковым названием.
Например, рассмотрим узел Cisco. Cisco HDLC это очень простая схема мультиплексирования протоколов посредством дополнения каждого кадра спереди полем Ethertype перед передачей на физический уровень. Cisco HDLC поддерживает одновременную передачу IP, IPX, AppleTalk, и т. д.
Таким образом, узел netgraph для Cisco HDLC (см ng_cisco(8)) определяет крючки, называемые inet, atalk, and ipx.
Эти крючки предназначены для подключения к соответствующим вышележащим стекам протоколов.
Он так же определяет крючок, называемый downstream который подключается к нижележащему уровню, например узлу, связанному с синхронной последовательной платой. К пакетам, получаемым через крючки inet, atalk, и ipx добавляется два байта заголовка, и затем они отправляются через крючок downstream. Наоборот, из пакетов полученных через downstream удаляется заголовок, и они отправляются вверх через крючок, соответствующий протоколу. Узел так же обрабатывает периодические пакеты "tickle" и запросы, определенные протоколом Cisco HDLC.
Крючки всегда либо подключены, либо не подключены; операция подключения или отключения пары крючков атомарная. Когда пакет посылается через крючок, которые не подключен, он отбрасывается.
Некоторые типы узлов достаточно очевидны, такие как Cisco HDLC. Другие менее очевидны, но предоставляют некоторые интересные функции, например, возможность обращаться непосредственно к устройству или открытому сокету внутри ядра.
Несколько примеров типов узлов, реализованных на настоящий момент во FreeBSD. Все эти типы узлов описаны в соответствующих страницах справочного руководства man.
ng_echo(8)ng_disc(8)ng_tee(8)tee(1). Он копирует данные проходящие через него в любом направлении ("right" или "left"), и полезен для отладки. Пакеты, получаемые через "right" посылаются через "left" и копия шлется через "right2left"; аналогично для пакетов идущих от "left" к "right".
Пакеты, получаемые через "right2left" посылаются через "left" и пакеты получаемы через "left2right", отправляются через "right".
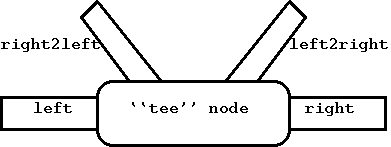
Рисунок 2: Тип узла tee
ng_iface(8)ifconfig -a. Вы можете прописать на этом интерфейсе адрес, как на другом PPP интерфейсе, пинговать удаленную сторону, и т. д. Конечно, узел должен быть подключен к чему либо, иначе пакеты ping будут выходить через крючок inet и исчезать.
К сожалению, FreeBSD в настоящий момент не поддерживает удаление интерфейсов, т. о. однажды создав узел ng_iface(8) он будет существовать до следующей перезагрузки (однако это будет скоро исправлено).
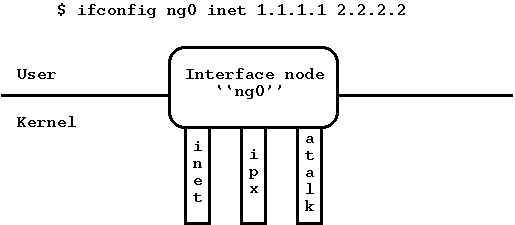
Рисунок 3: Тип узла interface
ng_tty(8)tty(4)). Вы создаете узел установкой дисциплины линии NETGRAPHDISC на последовательной линии. Узел имеет одни крючок называемый "hook". Пакеты, получаемые через "hook" передаются (как последовательные байты) через соответствующее последовательное устройство; данные, получаемые от устройства, формируются в пакеты и посылаются через "hook". Нормальное чтение и запись в последовательную линию блокируются. 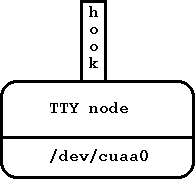
Рисунок 4: Тип узла TTY
ng_socket(8)PF_NETGRAPH. Узел создается, когда программа пользовательского режима создает соответствующий сокет через системный вызов socket(2). Один сокет используется для передачи и получения пакетов данных, а второй для контрольных сообщений. Этот узел поддерживает крючки с произвольными именами, например "hook1", "hook2" и т. д. 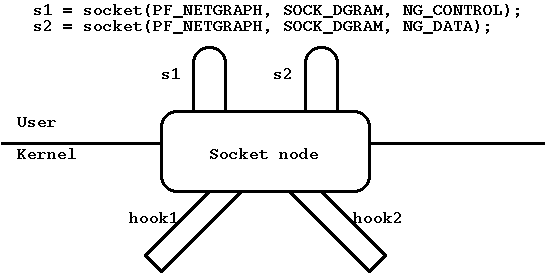
Рисунок 5: Тип узла socket
ng_bpf(8)bpf(4).ng_ksocket(8)ng_socket(8). Каждый узел одновременно является сокетом, полностью расположенном в ядре. Данные, получаемые узлом, записываются в сокет и наоборот. Нормальные bind(2), connect(2), и т. д. операции осуществимы вместо контрольных сообщений. Этот тип узла полезен для туннелирования пакетов через сокет (например, туннелирование IP поверх UDP).ng_ether(8)options NETGRAPH, то каждый интерфейс Ethernet так же является узлом netgraph с таким же именем как интерфейс. Каждый узел имеет два крючка "orphans" и "divert"; только один крючок может быть подключен одновременно. Если "orphans" подключен, то устройство продолжает работать нормально, за исключением того, что все пакеты Ethernet с неизвестным или неподдерживаемым типом, доставляются через этот крючок (в нормальном режиме эти пакеты просто отбрасываются). Когда крючок "divert" подключен то все входящие пакеты доставляются через этот крючок. Пакет полученный через любой из этих крючков передается в кабель. Все пакеты "сырые" кадры Ethernet со стандартным 14-байтным заголовком (но без контрольной суммы). Этот тип узла полезен, например для PPP поверх Ethernet (PPPoE).ar(4) and sr(4)options NETGRAPH, то драйвера ar(4) и sr(4) перестанут работать в нормальном режиме и вместо этого будут работать как постоянные узлы netgraph (с таким же именем как название устройства). Сырые кадры HDLC могут быть прочитаны и записаны через крючок "rawdata".
В некоторых случаях пакеты данных могут иметь связанную метаинформацию которую нужно передать вместе с пакетом. Хотя это редко используется, netgraph предоставляет механизм, чтоб сделать это. Пример метаинформации - приоритеты: некоторые пакеты могут иметь более высокий приоритет чем другие. Типы узлов могут определять свою собственную, специфичную метаинформацию, и netgraph для этой цели определяет структуру ng_meta. Мета информация не воспринимается базовой системой netgraph
Каждый узел netgraph адресуем через строку ASCII, называемую адрес узла (node address) или путь (path). Адрес узла используется только для отправки контрольных сообщений.
Многие узлы имеют имена. Например, узел, ассоциированный с устройством будет обычно иметь такое же имя как устройство. Когда узел имеет имя, он всегда может быть адресован, используя абсолютный адрес, состоящий из имени устройства и двоеточия. Например, если вы создали интерфейсный узел, названный "ng0" его адрес будет "ng0:".
Если узел не имеет имени, вы можете составить его из уникального номера ID узла заключив его в квадратные скобки (каждый узел имеет уникальный номер ID). Таким образом, если узел ng0: умеет номер ID 1234, тогда "[1234]:" так же является адресом этого узла.
Наконец, адрес ".:" или "." всегда указывает на локальный узел (источник).
Относительная адресация так же возможно когда два узла соединены опосредовано. Относительный адрес использует имена последовательных крючков в пути от одного узла к другому. Рассмотрим рисунок:
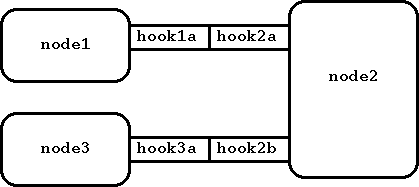
Рисунок 6: Простая конфигурация узлов
Если узел node1 хочет послать контрольное сообщение узлу node2, он может использовать адрес
".:hook1a" или просто "hook1a". Для обращения к узлу node3, он может использовать адрес ".:hook1a.hook2b" или просто "hook1a.hook2b".
Аналогично, узел node3 может обратиться к узлу node1, используя адрес ".:hook3a.hook2a" или просто "hook3a.hook2a".
Относительные и абсолютные адреса можно сочетать, например, "node1:hook1a.hook2b" будет указывать на узел node3.
Netgraph поставляется с утилитами командной строки и пользовательской библиотекой, которые позволяют взаимодействовать с системой ядра netgraph. Необходимы привилегии root для работы с netgraph из пользовательской режима.
Есть две утилиты командой строки для взаимодействия с netgraph, nghook(8)
и ngctl(8). nghook(8) очень проста: она подключается к любому неподключенному крючку любого узла и позволяет вам передавать и получать пакеты данных через стандартный ввод и стандартный вывод. Вывод может быть дополнительно декодирован в читаемый человеком формат hex/ASCII. В командной строке вы указываете абсолютный адрес узла и имя крючка.
Например, если ваше ядро собрано с options NETGRAPH и вы имеете сетевой интерфейс fxp0, следующая команда перенаправит все сетевые пакеты получаемые картой и выведет их через стандартный вывод в формате hex/ASCII:
nghook -a fxp0: divert
ngctl(8) более функциональная программа, которая позволяет вам делать практически все с netgraph из командной строки. Она работает в пакетном или интерактивном режиме, и поддерживает несколько команд, которые выполняют интересующую работу, в том числе:
connect Соединить пару крючков для объединения двух узлов list Вывести список всех узлов в системе mkpeer Создать узел и подключить его к существующему узлу msg Послать форматированное ASCII сообщение узлу name Назначит узлу имя rmhook Отключить два подключенных крючка show Показать информацию об узле shutdown Удалить/сбросить узел, разрушив все подключения status Получить статус узла в удобочитаемом виде types Показать типы установленных узлов quit Выйти из программы
Эти команды могут быть объединены в скрипт, который делает что-то полезное. Например, предположим, что у вас есть две частные сети, которые разделены, но обе подключены к интернету через машины с FreeBSD. Сеть A имеет внутренние адреса из диапазона 192.168.1.0/24 и внешний IP адрес 1.1.1.1, в то время как сеть B имеет адреса 192.168.2.0/24 и внешний адрес 2.2.2.2. Используя Netgraph, вы можете легко сделать UDP для IP трафика между двумя частными сетями. Пример скрипта, который это может сделать (его можно так же найти в /usr/share/examples/netgraph):
#!/bin/sh
# Этот скрипт устанавливает виртуальный канал точка-точка между двумя
# подсетями, используя UDP пакеты в качестве "глобального канала".
# Эти две подсети могут иметь адреса немаршрутизируемые между двумя
# файрволами.
# Определение локальной и удаленной внутренней сетей, также как и
# локального и удаленного внешних IP адресов и номера UDP порта,
# которые будут использованы для туннеля
#
LOC_INTERIOR_IP=192.168.1.1
LOC_EXTERIOR_IP=1.1.1.1
REM_INTERIOR_IP=192.168.2.1
REM_EXTERIOR_IP=2.2.2.2
REM_INSIDE_NET=192.168.2.0
UDP_TUNNEL_PORT=4028
# Создать интерфейсный узел "ng0", если его еще нету,
# если есть, просто убедиться, что он ни к чему не подключен
#
if ifconfig ng0 >/dev/null 2>&1; then
ifconfig ng0 inet down delete >/dev/null 2>&1
ngctl shutdown ng0:
else
ngctl mkpeer iface dummy inet
fi
# Присоединить UDP сокет к крюку "inet" интерфейсного узла использую
# узел типа ng_ksocket(8).
#
ngctl mkpeer ng0: ksocket inet inet/dgram/udp
# Присоединить UDP сокет к локальному внешнему IP и порту
#
ngctl msg ng0:inet bind inet/${LOC_EXTERIOR_IP}:${UDP_TUNNEL_PORT}
# Установить соединение с внешним IP и портом на удаленном сервере
#
ngctl msg ng0:inet connect inet/${REM_EXTERIOR_IP}:${UDP_TUNNEL_PORT}
# Настроить интерфейс точка-точка
#
ifconfig ng0 ${LOC_INTERIOR_IP} ${REM_INTERIOR_IP}
# Добавить маршрут к удаленной частной сети через туннель
#
route add ${REM_INSIDE_NET} ${REM_INTERIOR_IP}
Далее рассмотрим как можно работать с ngctl(8) в интерактивном режиме.
Пользовательский ввод выделен синим.
Запустим ngctl в интерактивном режиме. Будет показан список доступных команд...
$ ngctl Available commands: connect Connects hook <peerhook> of the node at <relpath> to <hook> debug Get/set debugging verbosity level help Show command summary or get more help on a specific command list Show information about all nodes mkpeer Create and connect a new node to the node at "path" msg Send a netgraph control message to the node at "path" name Assign name <name> to the node at <path> read Read and execute commands from a file rmhook Disconnect hook "hook" of the node at "path" show Show information about the node at <path> shutdown Shutdown the node at <path> status Get human readable status information from the node at <path> types Show information about all installed node types quit Exit program
ngctl создает при запуске узел типа ng_socket(8). Это наш локальный узел netgraph, который используется для взаимодействия с другими узлами в системе. Посмотрим на него. Мы видим, что ngctl назначил ему имя "ngctl652" и его тип "socket", номер ID 45 и он имеет ноль подключенных крючков, т. е. он не подключен к другим узлам.
+ show . Name: ngctl652 Type: socket ID: 00000045 Num hooks: 0
Теперь мы создадим узел "tee" и подключим его к локальному узлу. Мы подключим крючок "right" узла "tee" к крючку "myhook" на локальном узле. Мы можем использовать любое имя для нашего крючка, так как узел типа ng_socket(8) поддерживает крючки с произвольными именами. После этого снова посмотрим на наш локальный узел, чтобы убедиться, что он имеет безымянного соседа типа "tee".
+ help mkpeer Usage: mkpeer [path] <type> <hook> <peerhook> Summary: Create and connect a new node to the node at "path" Description: The mkpeer command atomically creates a new node of type "type" and connects it to the node at "path". The hooks used for the connection are "hook" on the original node and "peerhook" on the new node. If "path" is omitted then "." is assumed. + mkpeer . tee myhook right + show . Name: ngctl652 Type: socket ID: 00000045 Num hooks: 1 Local hook Peer name Peer type Peer ID Peer hook ---------- --------- --------- ------- --------- myhook <unnamed> tee 00000046 right
Аналогично, если мы посмотрим на вывод узла tee, мы увидим, что он подключен к нашему локальному узлу через крючок "right". Узел "tee" все еще безымянны, но мы можем его указать используя абсолютный адрес "[46]:" или относительный адрес ".:myhook" или "myhook"...
+ show .:myhook Name: <unnamed> Type: tee ID: 00000046 Num hooks: 1 Local hook Peer name Peer type Peer ID Peer hook ---------- --------- --------- ------- --------- right ngctl652 socket 00000045 myhook
Теперь назначим ему имя и убедимся, что можем по нему обратиться к этому узлу...
+ name .:myhook mytee + show mytee: Name: mytee Type: tee ID: 00000046 Num hooks: 1 Local hook Peer name Peer type Peer ID Peer hook ---------- --------- --------- ------- --------- right ngctl652 socket 00000045 myhook
Теперь подключим узел Cisco HDLC к другой стороне узла "tee" и снова проверим узел "tee". Мы подключимся к крючку "downstream" узла Cisco HDLC, как будто бы узел tee соответствует подключению к WAN. Cisco HDLC слева (крючек "left") от узла tee наш локальный узел справа (крючок "right") от узла tee...
+ mkpeer mytee: cisco left downstream + show mytee: Name: mytee Type: tee ID: 00000046 Num hooks: 2 Local hook Peer name Peer type Peer ID Peer hook ---------- --------- --------- ------- --------- left <unnamed> cisco 00000047 downstream right ngctl652 socket 00000045 myhook + Rec'd data packet on hook "myhook": 0000: 8f 00 80 35 00 00 00 02 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ...5............ 0010: ff ff 00 20 8c 08 40 00 ... ..@. + Rec'd data packet on hook "myhook": 0000: 8f 00 80 35 00 00 00 02 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ...5............ 0010: ff ff 00 20 b3 18 00 17 ... ....
Эй, что это такое?! Выглядит так, будто мы получаем какие то пакеты данных через наш крючок "myhook". Узел Cisco каждые 10 секунд посылает периодические пакеты keep-alive. Эти пакеты проходят через узел tee (слева направо от крючка "left" к крючку "right") и принимаются крючком "myhook", где ngctl показывает их в консоли.
Теперь посмотрим список всех узлов, существующих в системе. Заметим, что два наших интерфейса Ethernet так же показаны, поскольку это постоянные узлы и мы собирали ядро с options NETGRAPH...
+ list There are 5 total nodes: Name: <unnamed> Type: cisco ID: 00000047 Num hooks: 1 Name: mytee Type: tee ID: 00000046 Num hooks: 2 Name: ngctl652 Type: socket ID: 00000045 Num hooks: 1 Name: fxp1 Type: ether ID: 00000002 Num hooks: 0 Name: fxp0 Type: ether ID: 00000001 Num hooks: 0 + Rec'd data packet on hook "myhook": 0000: 8f 00 80 35 00 00 00 02 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ...5............ 0010: ff ff 00 22 4d 40 40 00 ..."M@@.
OK, давайте выключим (то есть удалим) узел Cisco HDLC, таким образом мы остановим получение данных...
+ shutdown mytee:left + show mytee: Name: mytee Type: tee ID: 00000046 Num hooks: 1 Local hook Peer name Peer type Peer ID Peer hook ---------- --------- --------- ------- --------- right ngctl652 socket 00000045 myhook
Теперь, давайте посмотрим статистику узла tee. Мы пошлем управляющее сообщение и немедленно получим ответ. Команда и ответ конвертируются в/из ASCII автоматически с помощью ngctl, так как управляющие сообщение это двоичная структура...
+ help msg
Usage: msg path command [args ... ]
Aliases: cmd
Summary: Send a netgraph control message to the node at "path"
Description:
The msg command constructs a netgraph control message from the
command name and ASCII arguments (if any) and sends that
message to the node. It does this by first asking the node to
convert the ASCII message into binary format, and re-sending the
result. The typecookie used for the message is assumed to be
the typecookie corresponding to the target node's type.
+ msg mytee: getstats
Rec'd response "getstats" (1) from "mytee:":
Args: { right={ outOctets=72 outFrames=3 } left={ inOctets=72 inFrames=3 }
left2right={ outOctets=72 outFrames=3 } }
Ответ это просто строковая версия структуры ng_tee_stats возвращаемой в ответном управляющем сообщении (Эта структура определена в ng_tee.h).
Мы видим, что три кадра (и 72 байта) прошли через узел слева направо. Каждый кадр был скопирован и отправлен через крючок "left2right" (но поскольку этот крючок не подключен эти кадры были отброшены).
OK, теперь проиграемся с узлом ng_ksocket(8)...
+ mkpeer ksocket myhook2 inet/stream/tcp + msg .:myhook2 connect inet/127.0.0.1:13 ngctl: send msg: Operation now in progress Rec'd data packet on hook "myhook": 0000: 54 75 65 20 46 65 62 20 20 31 20 31 31 3a 30 32 Tue Feb 1 11:02 0010: 3a 32 38 20 32 30 30 30 0d 0a :28 2000..
Мы создали в ядре TCP сокет, используя узел ng_ksocket(8), и подключили его к сервису "daytime" на локальной машине, который возвращает текущее время. Как мы узнали, что нужно использовать "inet/127.0.0.1:13" в качестве аргумента команды "connect"? Это описано в странице справочного руководства man ng_ksocket(8)
OK, поигрались и хватит...
+ quit
Существует так же пользовательская библиотека libnetgraph(3) для использования в программах netgraph. Она предоставляет много полезных вызовов, которые описаны в справочном руководстве man.
Пример использования их можно посмотреть в исходном коде /usr/src/usr.sbin/ngctl.
Как netgraph реализован? Одна из главных целей netgraph это скорость, поэтому он полностью работает в ядре. Другое конструктивное решение в том, что netgraph полностью функциональный. То есть пакеты не ставятся нигде в очередь при перемещении от узла к узлу. Вместо этого используется прямой вызов функций.
Пакеты данных это packet header mbuf'ы, в то время как мета-данные и управляющие сообщения Си-структуры расположенные в куче (используя malloc типа M_NETGRAPH).
Netgraph отчасти имеет объектно-ориентированную архитектуру. Каждый тип узла определен как массив указателей на методы, или функции Си, которые определяют специфическое поведение узлов данного типа. Каждый метод может быть оставлен NULL для того, чтобы оставить поведение по умолчанию.
Аналогично, есть несколько управляющих сообщений, которые понимают узлы всех типов и которые обрабатываются базовой системой (они называются общими управляющими сообщениями, generic control messages). Каждый тип узлов может дополнительно определять свои собственные управляющие сообщения. Управляющие сообщения всегда содержат typecookie и команду, которые вместе определяют, как интерпретировать это сообщение. Каждый тип узлов должен определить свое уникальное значение typecookie если предполагается, что он будет получать свои управляющие сообщения. Общие управляющие сообщения имеют предопределенные значения typecookie.
Netgraph использует подсчет ссылок для структур узлов и крючков. Каждый указатель на узел или крючок считается как одна ссылка. Если узел имеет имя, оно тоже считается ссылкой. Вся связанная с netgraph область памяти выделяется и освобождается используя malloc типа M_NETGRAPH.
Выполнение кода в ядре требует внимательной синхронизации. Узлы netgraph обычно выполняются через splnet() (см. spl(9)). Для большинства типов узлов не требуется дополнительного внимания. Некоторые узлы, однако, взаимодействуют с другими частями ядра, которые выполняются с другим приоритетом. Например, последовательный порт работает через spltty() и поэтому ng_tty(8) должен это учитывать. На этот случай в netgraph есть альтернативные вызовы передачи данных, которые обрабатывают все необходимые очереди авто-магически. (см. ng_queue_data() ниже).
Для реализации нового типа узлов, нужно сделать только две вещи:
ng_type. NETGRAPH_INIT(). Второй шаг простой, поэтому мы обратим внимание на первый шаг. Структура ng_type, из netgraph.h:
/*
* Structure of a node type
*/
struct ng_type {
u_int32_t version; /* должна совпадать с NG_VERSION */
const char *name; /* Уникальное имя типа */
modeventhand_t mod_event; /* Модуль обработки событий (не обязательно) */
ng_constructor_t *constructor; /* Конструктор узла */
ng_rcvmsg_t *rcvmsg; /* сюда поступают управляющие сообщения */
ng_shutdown_t *shutdown; /* сброс и освобождение ресурсов */
ng_newhook_t *newhook; /* первое сообщение о новом крючке */
ng_findhook_t *findhook; /* только если вы имеете несколько крючков */
ng_connect_t *connect; /* заключительное сообщение о новом крючке */
ng_rcvdata_t *rcvdata; /* сюда поступают данные */
ng_rcvdata_t *rcvdataq; /* или сюда, если через очередь */
ng_disconnect_t *disconnect; /* предупреждение об отключении */
const struct ng_cmdlist *cmdlist; /* команды, которые мы можем конвертировать */
/* R/W данные базового кода netgraph, НЕ ТРОГАТЬ! */
LIST_ENTRY(ng_type) types; /* связанный список всех типов */
int refs; /* число экземпляров */
};
Поле version должно совпадать с NG_VERSION. Это для избежания связывания несовместимых типов. Поле name уникальное имя типа узлов, например "tee". mod_event необязательный модуль обработки событий (когда узел загружается и выгружается) - похоже на статические инциализаторы в C++ или Java.
Далее идут методы типа узлов, описано подробнее ниже. cmdlist
предоставляет (дополнительно) информацию по конвертированию управляющих сообщений в/из ASCII (см. ниже), и оставшаяся часть используется только в базовом коде netgraph.
Каждый тип узлов должен реализовать методы, определенные в структуре ng_type. Каждый метод имеет реализацию по умолчанию, которая используется, если тип узлов не определяет данные метод.
int constructor(node_p *node);ng_make_node_common() и установив node->private если необходимо. Инициализация узла и выделение памяти для данного экземпляра
узла должно производиться здесь.
Сначала нужно вызвать ng_make_node_common(); он создаст узел и установит число указателей в 1.
Действие по умолчанию: Просто вызывает ng_make_node_common().
Когда переопределять: Если требуется специфичная для данного узла инициализация или выделение ресурсов.
int rcvmsg(node_p node, struct ng_mesg *msg,
const char *retaddr, struct ng_mesg **resp);retaddr.
Функция rcvmsg() ответственна за освобождение msg. Ответ, если есть,
может возвращен синхронно, если resp != NULL установкой *resp так,
чтоб он указывал на ответ. Общие управляющие сообщения (за исключением NGM_TEXT_STATUS)
обрабатываются базовой системой, и нет необходимости обрабатывать их здесь.
Действие по умолчанию: Обрабатывает все общие контрольные сообщения; иначе возвращает EINVAL.
Когда переопределять: Если вы определяете управляющие сообщения специфичные для данного типа, или если вы хотите реализовать управляющие сообщения определенные некоторыми другими типами узлов.
int shutdown(node_p node);ng_cutlinks(),
освободить всю частную память данного экземпляра узла, освободить присвоенное имя (если было) через ng_unname(), и освободить сам узел вызвав ng_unref() (этот вызов освобождает
ссылку добавленную в ng_make_node_common()). В случае постоянного узла, все крючки
должны быть отключены и связанное устройство (или что там) сбрасывается, но узел не должен удаляться
(т. е., используется только вызов ng_cutlinks()).
Действие по умолчанию: Вызвать ng_cutlinks(), ng_unname(), и ng_unref().
Когда переопределять: Когда вы должны отменить то, что вы сделали в конструкторе.
int newhook(node_p node, hook_p hook, const char *name);Если узлу нужна информация по данному крючку, этот метод должен инициализировать соответственно hook->private.
Действие по умолчанию: Ничего; подключение крючка всегда разрешено.
Когда переопределять: Всегда, если вы не планируете разрешать крючки с произвольными именами без инициализации и выделения ресурсов, и рассматривать все крючки одинаково при подключении.
hook_p findhook(node_p node, const char *name);Действие по умолчанию: Выполняет линейный поиск по списку крючков, подключенных к данному узлу.
Когда переопределять: Когда ваш узел поддерживает большое число одновременно подключенных крючков (скажем, больше чем 50).
int connect(hook_p hook);Действие по умолчанию: Ничего; подключение крючка принимается.
Когда переопределять: У меня никогда не было причин переопределять этот метод.
int rcvdata(hook_p hook, struct mbuf *m, meta_p meta);m == NULL (например, если посылается только meta),
таким образом, узлы должны учитывать эту возможность.
Действие по умолчанию: Отбросить пакет и метаинформацию.
Когда переопределять: Всегда, если вы не хотите игнорировать полученные пакеты.
int rcvdataq(hook_p hook, struct mbuf *m, meta_p meta);Замысел в том, что некоторые узлы могут захотеть посылать данные используя механизм очереди, вместо
функционального механизма. Это требует взаимодействия с типом узлов получателя, который должен
реализовать этот метод надлежащим образом для того, чтобы делать что-то отличное от rcvdata().
Действие по умолчанию: Вызвать метод rcvdata().
Когда переопределять: Никогда, если у вас нет причин рассматривать очередь входящих данных отдельно от данных без очереди.
int disconnect(hook_p hook);connect().
Хотя функция возвращает int, она должна в действительности возвращать void
поскольку возвращаемое значение игнорируется; отключение крючка не может быть блокировано узлом.
Функция должна проверять есть ли еще крючки (hook->node->numhooks == 0) и если был отключен последний крючок, вызывать ng_rmnode() для самоликвидации, если так надо. Это позволяет
избежать полностью неподключенных узлов, которые задерживаются в системе после завершения своей работы.
Действие по умолчанию: Ничего не делает.
Когда переопределять: Почти всегда.
int mod_event(module_t mod, int what, void *arg); what который может быть
либо MOD_LOAD либо MOD_UNLOAD. Параметр arg указатель на структуру
ng_type, определяющую тип узлов. Этот метод никогда не вызывается для
MOD_UNLOAD пока существуют узлы данного типа.
В настоящий момент только вызывается только со значение MOD_UNLOAD когда
вызывается kldunload(2). Однако в будущем выгрузка типа узлов может быть реализована как мера по "уборке мусора".
Действие по умолчанию: Ничего не делает. Если не переопределен, MOD_LOAD и MOD_UNLOAD нормально завершаются.
Когда переопределять: Если ваш тип нуждается в специфической инициализации или выделении
ресурсов при загрузке, или откате этого при выгрузке. Также, если ваш тип не поддерживает выгрузку (может быть из-за неразрушимых связей с другими частями ядра) возвращение ошибки в MOD_UNLOAD
предотвратит выгрузку типа.
Каждый тип узлов включает два заголовочных файла.
Заголовочный файл netgraph.h определяет базовые структуры netgraph (хороший объектно-ориентированный дизайн диктует, что определения структур ng_node и
ng_hook здесь фактически нет; вместо этого они должны быть скрыты внутри базового кода netgraph).
Структуры узлов освобождаются когда счетчик указателей уменьшается до нуля после вызова
ng_unref(). Если узел имеет имя, оно считается ссылкой; для удаления имени (и ссылка), вызывается
ng_unname(). Особенный интерес представляет структура ng_type, поскольку она должна быть предоставлена для каждого типа узлов.
Заголовочный файлng_message.h определяет структуры и макросы, имеющие отношение к обработке управляющие сообщений. В нем определена структура ng_mesg, с
которой начинается любое управляющее сообщение. Он также является "публичным заголовочным файлом" для всех
общих управляющих сообщений, которые имеют значение typecookie NGM_GENERIC_COOKIE.
Общие управляющие сообщения:
NGM_SHUTDOWNОтключает от целевого узла все крючки и удаляет узел (или сбрасывает его, если он постоянный) NGM_MKPEERСоздает новый узел и подключается к нему NGM_CONNECTПодключить крючок целевого узла к другому узлу NGM_NAMEНазначить имя целевому узлу NGM_RMHOOKОтключить целевой узел от другого узла NGM_NODEINFOПолучить информацию по целевому узлу NGM_LISTHOOKSПолучить список крючков, подключенных к данному узлу NGM_LISTNAMESПолучить список всех именованных узлов* NGM_LISTNODESПолучить список всех узлов, с именем и без имени* NGM_LISTTYPESПолучить список всех установленных типов узлов* NGM_TEXT_STATUSПолучить в удобочитаемом виде информацию о состоянии узла (может быть не реализовано) NGM_BINARY2ASCIIПреобразовать управляющее сообщение из двоичного вида в ASCII NGM_ASCII2BINARYпреобразовать управляющее сообщение из ASCII в двоичный вид * Не связано в каким либо конкретным узлом
Для большинства перечисленных команд в ng_message.h определены соответствующие структуры Си.
Заголовочные файлы netgraph.h и ng_message.h некоторые широко используемые функции и макросы:
int ng_send_data(hook_p hook, struct mbuf *m, meta_p meta); m и связанные метаданные meta
наружу через крючок hook и возвращает в error код ошибки.
Оба или один из параметров m и meta могут бытьNULL. В любом
случае, необходимо освободить m и meta при вызове этой функции, поэтому
переменные должны быть сброшены в NULL после вызова (это производится автоматически, если вместо функции вы используете макрос NG_SEND_DATA()). int ng_send_dataq(hook_p hook, struct mbuf *m, meta_p meta); ng_send_data(), за исключением того, что узел-получатель
получает данные через его метод rcvdataq() вместо rcvdata(). Если тип узлов
не переопределяет rcvdataq(), его вызов эквивалентен ng_send_data().int ng_queue_data(hook_p hook, struct mbuf *m, meta_p meta); ng_send_data(), за исключением того, что его безопасно
вызывать вне контекста splnet(). mbuf и метаинформация будут поставлены в очередь и доставлены позже, в splnet(). int ng_send_msg(node_p here, struct ng_mesg *msg, const char *address, struct ng_mesg **resp); msg от локального узла
here узлу с адресом address, который может быть абсолютным или относительным
адресом. Если resp не NULL, и получатель желает послать ответ синхронно, он
устанавливает указатель *resp на него. В этом случае вызывающий узел должен обработать и
освободить*resp.
int ng_queue_msg(node_p here, struct ng_mesg *msg, const char *address); ng_send_msg(), за исключением того, что его можно
вызывать вне контекста splnet(). Сообщение будет поставлено в очередь и доставлено
позже splnet(). Синхронный ответ невозможен.NG_SEND_DATA(error, hook, m, meta) ng_send_data(). Он просто вызывает
ng_send_data() и потом устанавливает m и meta в NULL.
Один или оба параметра m и meta могут быть NULL, но они должны
быть переменными (они не могут быть константой NULL из-за природы работы макроса). NG_SEND_DATAQ(error, hook, m, meta) ng_send_dataq(). Он просто вызывает
ng_send_dataq() и потом устанавливает m и meta в NULL.
Один или оба параметра m и meta могут быть NULL, но они должны
быть переменными (они не могут быть константой NULL из-за природы работы макроса).NG_FREE_DATA(m, meta) m и meta и устанавливают в NULL.
Один или оба параметра m и meta могут быть NULL, но они должны
быть переменными (они не могут быть константой NULL из-за природы работы макроса).NG_FREE_META(meta) meta и устанавливает в NULL. Параметр
meta может иметь значение NULL, он должен быть переменной (он не может
быть константой NULL из-за природы работы макроса). NG_MKRESPONSE(rsp, msg, len, how) msg. Этот ответ имеет len байт места для аргументов (len
должна быть нулевой, если аргументов нет).msg должен быть указателем на существующую
структуру ng_mesg в то время как rspдолжен иметь тип ng_mesg *. how это M_WAITили M_NOWAIT (безопаснее использовать
M_NOWAIT). Устанавливает rspв NULL если выделение памяти прошло неудачно.
int ng_name_node(node_p node, const char *name); name узлу node.
Имя должно быть уникальным. функция часто вызывается внутри конструктора узла для узлов, которые
соответствуют другой именованной сущности ядра, например устройству или интерфейсу. Назначение имени увеличивает на один счетчик ссылок на узлы.void ng_cutlinks(node_p node); node. Обычно вызывается в ходе выключения узла.void ng_unref(node_p node); shutdown() для освобождения ссылки созданной
ng_make_node_common(). void ng_unname(node_p node); shutdown() перед освобождением узла (через ng_unref()).
Достаточно теории, рассмотрим пример. Это реализация узла типа tee. Как было решено, реализация состоит из открытого заголовочного файла, Си файла и страницы man. Заголовочный файл ng_tee.h и Си файл ng_tee.c.
Нужно сделать несколько замечаний по поводу заголовочного файла:
NG_TEE_NODE_TYPE. NGM_TEE_COOKIE.
NGM_TEE_GET_STATS и
NGM_TEE_CLR_STATS. NGM_TEE_GET_STATS, которая определена в struct
ng_tee_stats. Эта информация общедоступна, поскольку другие типы узлов должны знать это для обмена сообщениями и подключения к узлам tee.
date -u +%s".Несколько замечаний по Си файлу:
ng_tee(8) эта информация хранится в структуре privdata для каждого узла, и
в структуре hookdata для каждого крючка.ng_tee_cmds определяет, как преобразовывать специфичные для данного типа управляющие
сообщения из двоичного вида в ASCII и обратно. Смотрите ниже. ng_tee_typestruct в начале, фактически определяет узел типа tee. Эта структура
содержит версию системы netgraph (для избежания несовместимости), уникальное имя типа
(NG_ECHO_NODE_TYPE), указатели на методы типа узлов, и указатель на массив ng_tee_cmds. Некоторые методы нет необходимости переопределять, поскольку достаточно поведения по умолчанию. NETGRAPH_INIT() нужен для связывания типа. Этот макрос нужен и при загрузке в виде модуля и при непосредственной компиляции в ядре (в данном случае, используя options NETGRAPH_TEE). struct ng_node) содержат счетчик ссылок, чтоб убедиться, что они будут освобождены вовремя. Скрытый эффект в вызове ng_make_node_common() из конструктора в том, что одна ссылка создается. Ссылка освобождается вызовом ng_unref() в методе
ngt_rmnode(). ngt_rmnode() вызывается ng_bypass(). Здесь небольшой клудж, в том, что
два ребра объединяются при отключении узла между ними (в данном случае узла tee).ngt_disconnect() разрушает сам узел, при отключении последнего крючка. Это нужно чтоб узлы не повисали на неопределенное время, после того как им не осталось работы.splnet().
Netgraph простой способ конвертирования управляющих сообщений (по сути, любых структур Си) между двоичным и ASCII видом. Подробное описание выходит за рамки данной статьи, но мы дадим обзор.
Вспомним, что управляющее сообщение имеет фиксированный заголовок (struct ng_mesg) за которым идет полезная нагрузка переменной длины с определенной структурой и содержанием. Вдобавок заголовок управляющего сообщения содержит флаг, показывающий, что сообщение является командой или ответом. Обычно полезная часть сообщения имеет разную структуру в команде и в ответе. Например, для узла "tee" определено управляющее сообщение NGM_TEE_GET_STATS. Когда мы посылаем команду
((msg->header.flags & NGF_RESP) == 0),
полезная нагрузка пустая. Когда посылается ответ на команду
((msg->header.flags& NGF_RESP) != 0), полезная нагрузка содержит структуру ng_tee_stats в которой находится статистика.
Для каждого управляющего сообщения, которое тип узлов понимает, определено как конвертировать полезную нагрузку в (в обоих случаях, команды и ответа) между родной двоичной формой и удобочитаемой ASCII версией. Эти определения называются типы разбора (netgraph parse types).
Поле cmdlist в структуре ng_type, определяющей тип узлов указывает на массив структур ng_cmdlist. Каждый элемент в этом массиве соответствует специфичному для данного типа сообщению, понимаемому этим узлом. В соответствие с typecookie и ID команды (которые однозначно определяют контрольное сообщение), сопоставлено имя ASCII и два типа разбора которые определяют как полезная нагрузка структурирована, по одному для каждого направления (команда и ответ).
Типы разбора строятся на основе типов разбора предопределенных в ng_parse.h. Используя эти типы разбора, вы можете описать структуры Си любой сложности, даже содержащие массивы переменной длины и строки. В узле "tee" есть пример как это сделать для структуры ng_tee_stats возвращаемой управляющим сообщением NGM_TEE_GET_STATS (см. ng_tee.h и ng_tee.c).
Вы можете так же определить собственные типы разбора с нуля, если необходимо. Например, тип узлов
"ksocket" содержит специальный код для преобразования структуры sockaddr
в адреса семейства AF_INET и AF_LOCAL, чтобы сделать их более удобочитаемыми.
Код, имеющий отношение к этому отношение, может быть найден в
ng_ksocket.h и ng_ksocket.c, особенно в секции "STRUCT SOCKADDR PARSE TYPE".
Типы разбора удобный и эффективный способ конвертирования двоичного/ASCII в ядре без большого объема коду по ручному разбору и работы со строками. Когда это действительно сильно влияет на производительность, всегда могут быть использованы двоичные сообщения непосредственно, которые не нужно конвертировать.
Детально информацию о типах разбора можно посмотреть в ng_parse.h
и ng_parse.c.
Несколько вещей, которые нужно иметь виду, если вы собираетесь писать свой собственный тип узлов:
M_PKTHDR
должен быть установлен. m->m_pkthdr.len когда вы изменяете
m->m_len для любого mbuf в цепочке. m->m_len и вызвать m_pullup() перед доступом к данным в mbuf. Не вызывайте m_pullup() если это не нужно. Всегда следует придерживаться следующего шаблона:
struct foobar *f;
if (m->m_len < sizeof(*f) && (m = m_pullup(m, sizeof(*f))) == NULL) {
NG_FREE_META(meta);
return (ENOBUFS);
}
f=mtod(m, struct foobar *);
...
disconnect()
и shutdown() для предотвращения утечек памяти т.п. Я случайно оставил таймер запущенным, и это имело гибельный результат.timeout(9)), проверьте что первым в вашем обработчике стоит вызовsplnet() (и splx() перед выходом, конечно). Вызов timeout() не сохраняет уровень SPL в обработчике событий.Работа над Netgraph все еще продолжается, и помощники приветствуются! Есть несколько идей, по поводу будущей работы.
еще много типов узлов не написано:
ng_ppp(8)
например, сжатие Deflate для PPP, 3DES шифрование PPP и т. д. ipfw(4) как узла netgraph. Во FreeBSD сейчас имеется четыре реализации PPP: sppp(4), pppd(8),
ppp(8), и порт MPD. Это достаточно глупо. Используя netgraph, это может быть объединено в один демон, работающий в пользовательском режиме, который будет выполнять все согласования и настройки, в то время как маршрутизация данных будет полностью происходить в ядре, через узлы ng_ppp(8). Это позволит объединить гибкость и удобство настройки демонов, работающих в пользовательском режиме, со скоростью работы в ядре. Сегодня MPD единственная реализация которая полностью основана на netgraph, но есть планы так же переработать ppp(8).
Не все типы узлов, которые определяют свои собственные управляющие сообщения поддерживают преобразование между двоичным видом и ASCII. Одна из задач - завершить эту работу для узлов, которые в этом еще не сделано.
Одна из проблем, к которой возможно придется обратиться - это управление потом. Сейчас когда вы посылаете пакет данных, если конечный получатель узла не может принять его из-за переполнения очереди передачи или по другой причине, все что может быть сделано это отбросить пакет и вернуть ENOBUFS.
Возможно, мы сможем определить новый код возврата ESLOWDOWN или что-то, что будет означать
"пакет данных не отброшен; очередь полна; уменьшите скорость и попробуйте позже." Другой вариант определить типы метаинформации эквивалентные XOFF (остановить передачу) и XON (возобновить передачу).
Netgraph объектно-ориентированный, но преимущества объектно-ориентированной архитектуры должны использоваться более полно без ущерба производительности. Пока слишком много видимых полей в структурах, которые не должны быть доступны, и т. д., так же как много других разных доработок.
Также, страницы man для всех узлов (например, ng_tee(8)) в действительности должны находиться в разделе 4, а не 8.
Было бы удобно сделать новое общее управляющее сообщение NGM_ELECTROCUTE, которое если послать его узлу выключит узел вместе со всеми узлами связанными с ним непосредственно или через другие узлы. Это позволит выполнить быструю очистку сложного графа в netgraph одним ударом. В дополнение можно сделать новую опцию сокета (см. setsockopt(2)) которую нужно установить для сокета ng_socket(8)
чтоб при его закрытии автоматически посылалось сообщение NGM_ELECTROCUTE.
Вместе две этих вещи позволят более надежно избежать в netgraph "утечку узлов".
В базовую систему netgraph несложно включить "обнаружение бесконечных петель". Каждый узел должен иметь свой закрытый счетчик. Счетчик должен увеличиваться перед каждым обращением к методу rcvdata() данного узла, и уменьшаться потом. Если счетчик достиг нереально большого значения, мы считаем что обнаружена бесконечная петля (и избегаем паники ядра).
Можно создать и улучшить много узлов:
Теоретически, сетевая подсистема BSD может быть полностью заменена на netgraph. Конечно, скорее всего, это никогда не случиться, но это хороший мысленный эксперимент. Каждое сетевое устройство должно быть постоянным узлом netgraph (как устройства Ethernet). Вверху каждого устройства Ethernet должен быть мультиплексор Ethertype. К нему должны быть подключены узлы IP, ARP, IPX, AppleTalk и т. д. Узел IP должен быть просто мультиплексором IP протокола, над которым должны находиться узлы TCP, UDP, и т. д. Узлы TCP и UDP должны, наконец, иметь узлы, похожие на сокеты сверху. И т. д., и т. д.
Другие сумасшедшие идеи (отречение: это сумасшедшие идеи):
ioctl(2)
и управляющими сообщениями. Обращайтесь напрямую к вашему SCSI диску через ngctl(8)! Полная интеграция между netgraph и devfs(8). Конечно есть еще много сумасшедших идей о которых мы еще не подумали.
/*
* netgraph.h
*
* Copyright (c) 1996-1999 Whistle Communications, Inc.
* All rights reserved.
*
* Subject to the following obligations and disclaimer of warranty, use and
* redistribution of this software, in source or object code forms, with or
* without modifications are expressly permitted by Whistle Communications;
* provided, however, that:
* 1. Any and all reproductions of the source or object code must include the
* copyright notice above and the following disclaimer of warranties; and
* 2. No rights are granted, in any manner or form, to use Whistle
* Communications, Inc. trademarks, including the mark "WHISTLE
* COMMUNICATIONS" on advertising, endorsements, or otherwise except as
* such appears in the above copyright notice or in the software.
*
* THIS SOFTWARE IS BEING PROVIDED BY WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS "AS IS", AND
* TO THE MAXIMUM EXTENT PERMITTED BY LAW, WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS MAKES NO
* REPRESENTATIONS OR WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, REGARDING THIS SOFTWARE,
* INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY AND ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
* MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR NON-INFRINGEMENT.
* WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS DOES NOT WARRANT, GUARANTEE, OR MAKE ANY
* REPRESENTATIONS REGARDING THE USE OF, OR THE RESULTS OF THE USE OF THIS
* SOFTWARE IN TERMS OF ITS CORRECTNESS, ACCURACY, RELIABILITY OR OTHERWISE.
* IN NO EVENT SHALL WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DAMAGES
* RESULTING FROM OR ARISING OUT OF ANY USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, INCLUDING
* WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY,
* PUNITIVE, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR
* SERVICES, LOSS OF USE, DATA OR PROFITS, HOWEVER CAUSED AND UNDER ANY
* THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
* (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF
* THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS IS ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY
* OF SUCH DAMAGE.
*
* Author: Julian Elischer <julian@whistle.com>
*
* $FreeBSD: src/sys/netgraph/netgraph.h,v 1.6 1999/12/29 04:46:00 peter Exp $
* $Whistle: netgraph.h,v 1.29 1999/11/01 07:56:13 julian Exp $
*/
#ifndef _NETGRAPH_NETGRAPH_H_
#define _NETGRAPH_NETGRAPH_H_ 1
#include <sys/queue.h>
#include <sys/malloc.h>
#include <sys/module.h>
#ifndef _KERNEL
#error "This file should not be included in user level programs"
#endif
/*
* Structure of a hook
*/
struct ng_hook {
char *name; /* what this node knows this link as */
void *private; /* node dependant ID for this hook */
int flags; /* info about this hook/link */
int refs; /* dont actually free this till 0 */
struct ng_hook *peer; /* the other end of this link */
struct ng_node *node; /* The node this hook is attached to */
LIST_ENTRY(ng_hook) hooks; /* linked list of all hooks on node */
};
typedef struct ng_hook *hook_p;
/* Flags for a hook */
#define HK_INVALID 0x0001 /* don't trust it! */
/*
* Structure of a node
*/
struct ng_node {
char *name; /* optional globally unique name */
struct ng_type *type; /* the installed 'type' */
int flags; /* see below for bit definitions */
int sleepers; /* #procs sleeping on this node */
int refs; /* number of references to this node */
int numhooks; /* number of hooks */
int colour; /* for graph colouring algorithms */
void *private; /* node type dependant node ID */
ng_ID_t ID; /* Unique per node */
LIST_HEAD(hooks, ng_hook) hooks; /* linked list of node hooks */
LIST_ENTRY(ng_node) nodes; /* linked list of all nodes */
LIST_ENTRY(ng_node) idnodes; /* ID hash collision list */
};
typedef struct ng_node *node_p;
/* Flags for a node */
#define NG_INVALID 0x001 /* free when all sleepers and refs go to 0 */
#define NG_BUSY 0x002 /* callers should sleep or wait */
#define NG_TOUCHED 0x004 /* to avoid cycles when 'flooding' */
#define NGF_TYPE1 0x10000000 /* reserved for type specific storage */
#define NGF_TYPE2 0x20000000 /* reserved for type specific storage */
#define NGF_TYPE3 0x40000000 /* reserved for type specific storage */
#define NGF_TYPE4 0x80000000 /* reserved for type specific storage */
/*
* The structure that holds meta_data about a data packet (e.g. priority)
* Nodes might add or subtract options as needed if there is room.
* They might reallocate the struct to make more room if they need to.
* Meta-data is still experimental.
*/
struct meta_field_header {
u_long cookie; /* cookie for the field. Skip fields you don't
* know about (same cookie as in messgaes) */
u_short type; /* field ID */
u_short len; /* total len of this field including extra
* data */
char data[0]; /* data starts here */
};
/* To zero out an option 'in place' set it's cookie to this */
#define NGM_INVALID_COOKIE 865455152
/* This part of the metadata is always present if the pointer is non NULL */
struct ng_meta {
char priority; /* -ve is less priority, 0 is default */
char discardability; /* higher is less valuable.. discard first */
u_short allocated_len; /* amount malloc'd */
u_short used_len; /* sum of all fields, options etc. */
u_short flags; /* see below.. generic flags */
struct meta_field_header options[0]; /* add as (if) needed */
};
typedef struct ng_meta *meta_p;
/* Flags for meta-data */
#define NGMF_TEST 0x01 /* discard at the last moment before sending */
#define NGMF_TRACE 0x02 /* trace when handing this data to a node */
/* node method definitions */
typedef int ng_constructor_t(node_p *node);
typedef int ng_rcvmsg_t(node_p node, struct ng_mesg *msg,
const char *retaddr, struct ng_mesg **resp);
typedef int ng_shutdown_t(node_p node);
typedef int ng_newhook_t(node_p node, hook_p hook, const char *name);
typedef hook_p ng_findhook_t(node_p node, const char *name);
typedef int ng_connect_t(hook_p hook);
typedef int ng_rcvdata_t(hook_p hook, struct mbuf *m, meta_p meta);
typedef int ng_disconnect_t(hook_p hook);
/*
* Command list -- each node type specifies the command that it knows
* how to convert between ASCII and binary using an array of these.
* The last element in the array must be a terminator with cookie=0.
*/
struct ng_cmdlist {
u_int32_t cookie; /* command typecookie */
int cmd; /* command number */
const char *name; /* command name */
const struct ng_parse_type *mesgType; /* args if !NGF_RESP */
const struct ng_parse_type *respType; /* args if NGF_RESP */
};
/*
* Structure of a node type
*/
struct ng_type {
u_int32_t version; /* must equal NG_VERSION */
const char *name; /* Unique type name */
modeventhand_t mod_event; /* Module event handler (optional) */
ng_constructor_t *constructor; /* Node constructor */
ng_rcvmsg_t *rcvmsg; /* control messages come here */
ng_shutdown_t *shutdown; /* reset, and free resources */
ng_newhook_t *newhook; /* first notification of new hook */
ng_findhook_t *findhook; /* only if you have 23000 hooks */
ng_connect_t *connect; /* final notification of new hook */
ng_rcvdata_t *rcvdata; /* date comes here */
ng_rcvdata_t *rcvdataq; /* or here if been queued */
ng_disconnect_t *disconnect; /* notify on disconnect */
const struct ng_cmdlist *cmdlist; /* commands we can convert */
/* R/W data private to the base netgraph code DON'T TOUCH! */
LIST_ENTRY(ng_type) types; /* linked list of all types */
int refs; /* number of instances */
};
/* Send data packet with meta-data */
#define NG_SEND_DATA(error, hook, m, a) \
do { \
(error) = ng_send_data((hook), (m), (a)); \
(m) = NULL; \
(a) = NULL; \
} while (0)
/* Send queued data packet with meta-data */
#define NG_SEND_DATAQ(error, hook, m, a) \
do { \
(error) = ng_send_dataq((hook), (m), (a)); \
(m) = NULL; \
(a) = NULL; \
} while (0)
/* Free metadata */
#define NG_FREE_META(a) \
do { \
if ((a)) { \
FREE((a), M_NETGRAPH); \
a = NULL; \
} \
} while (0)
/* Free any data packet and/or meta-data */
#define NG_FREE_DATA(m, a) \
do { \
if ((m)) { \
m_freem((m)); \
m = NULL; \
} \
NG_FREE_META((a)); \
} while (0)
/*
* Use the NETGRAPH_INIT() macro to link a node type into the
* netgraph system. This works for types compiled into the kernel
* as well as KLD modules. The first argument should be the type
* name (eg, echo) and the second a pointer to the type struct.
*
* If a different link time is desired, e.g., a device driver that
* needs to install its netgraph type before probing, use the
* NETGRAPH_INIT_ORDERED() macro instead. Deivce drivers probably
* want to use SI_SUB_DRIVERS instead of SI_SUB_PSEUDO.
*/
#define NETGRAPH_INIT_ORDERED(typename, typestructp, sub, order) \
static moduledata_t ng_##typename##_mod = { \
"ng_" #typename, \
ng_mod_event, \
(typestructp) \
}; \
DECLARE_MODULE(ng_##typename, ng_##typename##_mod, sub, order)
#define NETGRAPH_INIT(tn, tp) \
NETGRAPH_INIT_ORDERED(tn, tp, SI_SUB_PSEUDO, SI_ORDER_ANY)
/* Special malloc() type for netgraph structs and ctrl messages */
MALLOC_DECLARE(M_NETGRAPH);
int ng_bypass(hook_p hook1, hook_p hook2);
void ng_cutlinks(node_p node);
int ng_con_nodes(node_p node,
const char *name, node_p node2, const char *name2);
void ng_destroy_hook(hook_p hook);
hook_p ng_findhook(node_p node, const char *name);
node_p ng_findname(node_p node, const char *name);
struct ng_type *ng_findtype(const char *type);
int ng_make_node(const char *type, node_p *nodepp);
int ng_make_node_common(struct ng_type *typep, node_p *nodep);
int ng_mkpeer(node_p node, const char *name, const char *name2, char *type);
int ng_mod_event(module_t mod, int what, void *arg);
int ng_name_node(node_p node, const char *name);
int ng_newtype(struct ng_type *tp);
ng_ID_t ng_node2ID(node_p node);
int ng_path2node(node_p here, const char *path, node_p *dest, char **rtnp);
int ng_path_parse(char *addr, char **node, char **path, char **hook);
int ng_queue_data(hook_p hook, struct mbuf *m, meta_p meta);
int ng_queue_msg(node_p here, struct ng_mesg *msg, int len,
const char *address);
void ng_release_node(node_p node);
void ng_rmnode(node_p node);
int ng_send_data(hook_p hook, struct mbuf *m, meta_p meta);
int ng_send_dataq(hook_p hook, struct mbuf *m, meta_p meta);
int ng_send_msg(node_p here, struct ng_mesg *msg,
const char *address, struct ng_mesg **resp);
void ng_unname(node_p node);
void ng_unref(node_p node);
int ng_wait_node(node_p node, char *msg);
#endif /* _NETGRAPH_NETGRAPH_H_ */
/*
* ng_ksocket.c
*
* Copyright (c) 1996-1999 Whistle Communications, Inc.
* All rights reserved.
*
* Subject to the following obligations and disclaimer of warranty, use and
* redistribution of this software, in source or object code forms, with or
* without modifications are expressly permitted by Whistle Communications;
* provided, however, that:
* 1. Any and all reproductions of the source or object code must include the
* copyright notice above and the following disclaimer of warranties; and
* 2. No rights are granted, in any manner or form, to use Whistle
* Communications, Inc. trademarks, including the mark "WHISTLE
* COMMUNICATIONS" on advertising, endorsements, or otherwise except as
* such appears in the above copyright notice or in the software.
*
* THIS SOFTWARE IS BEING PROVIDED BY WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS "AS IS", AND
* TO THE MAXIMUM EXTENT PERMITTED BY LAW, WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS MAKES NO
* REPRESENTATIONS OR WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, REGARDING THIS SOFTWARE,
* INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY AND ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
* MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR NON-INFRINGEMENT.
* WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS DOES NOT WARRANT, GUARANTEE, OR MAKE ANY
* REPRESENTATIONS REGARDING THE USE OF, OR THE RESULTS OF THE USE OF THIS
* SOFTWARE IN TERMS OF ITS CORRECTNESS, ACCURACY, RELIABILITY OR OTHERWISE.
* IN NO EVENT SHALL WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DAMAGES
* RESULTING FROM OR ARISING OUT OF ANY USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, INCLUDING
* WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY,
* PUNITIVE, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR
* SERVICES, LOSS OF USE, DATA OR PROFITS, HOWEVER CAUSED AND UNDER ANY
* THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
* (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF
* THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS IS ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY
* OF SUCH DAMAGE.
*
* Author: Archie Cobbs <archie@whistle.com>
*
* $FreeBSD: src/sys/netgraph/ng_ksocket.c,v 1.5 1999/12/07 05:50:47 julian Exp $
* $Whistle: ng_ksocket.c,v 1.1 1999/11/16 20:04:40 archie Exp $
*/
/*
* Kernel socket node type. This node type is basically a kernel-mode
* version of a socket... kindof like the reverse of the socket node type.
*/
#include <sys/param.h>
#include <sys/systm.h>
#include <sys/kernel.h>
#include <sys/mbuf.h>
#include <sys/proc.h>
#include <sys/malloc.h>
#include <sys/ctype.h>
#include <sys/protosw.h>
#include <sys/errno.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/socketvar.h>
#include <sys/uio.h>
#include <sys/un.h>
#include <netgraph/ng_message.h>
#include <netgraph/netgraph.h>
#include <netgraph/ng_parse.h>
#include <netgraph/ng_ksocket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <netatalk/at.h>
#define OFFSETOF(s, e) ((char *)&((s *)0)->e - (char *)((s *)0))
#define SADATA_OFFSET (OFFSETOF(struct sockaddr, sa_data))
/* Node private data */
struct ng_ksocket_private {
hook_p hook;
struct socket *so;
};
typedef struct ng_ksocket_private *priv_p;
/* Netgraph node methods */
static ng_constructor_t ng_ksocket_constructor;
static ng_rcvmsg_t ng_ksocket_rcvmsg;
static ng_shutdown_t ng_ksocket_rmnode;
static ng_newhook_t ng_ksocket_newhook;
static ng_rcvdata_t ng_ksocket_rcvdata;
static ng_disconnect_t ng_ksocket_disconnect;
/* Alias structure */
struct ng_ksocket_alias {
const char *name;
const int value;
const int family;
};
/* Protocol family aliases */
static const struct ng_ksocket_alias ng_ksocket_families[] = {
{ "local", PF_LOCAL },
{ "inet", PF_INET },
{ "inet6", PF_INET6 },
{ "atalk", PF_APPLETALK },
{ "ipx", PF_IPX },
{ "atm", PF_ATM },
{ NULL, -1 },
};
/* Socket type aliases */
static const struct ng_ksocket_alias ng_ksocket_types[] = {
{ "stream", SOCK_STREAM },
{ "dgram", SOCK_DGRAM },
{ "raw", SOCK_RAW },
{ "rdm", SOCK_RDM },
{ "seqpacket", SOCK_SEQPACKET },
{ NULL, -1 },
};
/* Protocol aliases */
static const struct ng_ksocket_alias ng_ksocket_protos[] = {
{ "ip", IPPROTO_IP, PF_INET },
{ "raw", IPPROTO_IP, PF_INET },
{ "icmp", IPPROTO_ICMP, PF_INET },
{ "igmp", IPPROTO_IGMP, PF_INET },
{ "tcp", IPPROTO_TCP, PF_INET },
{ "udp", IPPROTO_UDP, PF_INET },
{ "gre", IPPROTO_GRE, PF_INET },
{ "esp", IPPROTO_ESP, PF_INET },
{ "ah", IPPROTO_AH, PF_INET },
{ "swipe", IPPROTO_SWIPE, PF_INET },
{ "encap", IPPROTO_ENCAP, PF_INET },
{ "divert", IPPROTO_DIVERT, PF_INET },
{ "ddp", ATPROTO_DDP, PF_APPLETALK },
{ "aarp", ATPROTO_AARP, PF_APPLETALK },
{ NULL, -1 },
};
/* Helper functions */
static void ng_ksocket_incoming(struct socket *so, void *arg, int waitflag);
static int ng_ksocket_parse(const struct ng_ksocket_alias *aliases,
const char *s, int family);
/************************************************************************
STRUCT SOCKADDR PARSE TYPE
************************************************************************/
/* Get the length of the data portion of a generic struct sockaddr */
static int
ng_parse_generic_sockdata_getLength(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *start, const u_char *buf)
{
const struct sockaddr *sa;
sa = (const struct sockaddr *)(buf - SADATA_OFFSET);
return sa->sa_len - SADATA_OFFSET;
}
/* Type for the variable length data portion of a generic struct sockaddr */
static const struct ng_parse_type ng_ksocket_generic_sockdata_type = {
&ng_parse_bytearray_type,
&ng_parse_generic_sockdata_getLength
};
/* Type for a generic struct sockaddr */
static const struct ng_parse_struct_info ng_parse_generic_sockaddr_type_info = {
{
{ "len", &ng_parse_int8_type },
{ "family", &ng_parse_int8_type },
{ "data", &ng_ksocket_generic_sockdata_type },
{ NULL }
}
};
static const struct ng_parse_type ng_ksocket_generic_sockaddr_type = {
&ng_parse_struct_type,
&ng_parse_generic_sockaddr_type_info
};
/* Convert a struct sockaddr from ASCII to binary. If its a protocol
family that we specially handle, do that, otherwise defer to the
generic parse type ng_ksocket_generic_sockaddr_type. */
static int
ng_ksocket_sockaddr_parse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const char *s, int *off, const u_char *const start,
u_char *const buf, int *buflen)
{
struct sockaddr *const sa = (struct sockaddr *)buf;
enum ng_parse_token tok;
char fambuf[32];
int family, len;
char *t;
/* If next token is a left curly brace, use generic parse type */
if ((tok = ng_parse_get_token(s, off, &len)) == T_LBRACE) {
return (*ng_ksocket_generic_sockaddr_type.supertype->parse)
(&ng_ksocket_generic_sockaddr_type,
s, off, start, buf, buflen);
}
/* Get socket address family followed by a slash */
while (isspace(s[*off]))
(*off)++;
if ((t = index(s + *off, '/')) == NULL)
return (EINVAL);
if ((len = t - (s + *off)) > sizeof(fambuf) - 1)
return (EINVAL);
strncpy(fambuf, s + *off, len);
fambuf[len] = '\0';
*off += len + 1;
if ((family = ng_ksocket_parse(ng_ksocket_families, fambuf, 0)) == -1)
return (EINVAL);
/* Set family */
if (*buflen < SADATA_OFFSET)
return (ERANGE);
sa->sa_family = family;
/* Set family-specific data and length */
switch (sa->sa_family) {
case PF_LOCAL: /* Get pathname */
{
const int pathoff = OFFSETOF(struct sockaddr_un, sun_path);
struct sockaddr_un *const sun = (struct sockaddr_un *)sa;
int toklen, pathlen;
char *path;
if ((path = ng_get_string_token(s, off, &toklen)) == NULL)
return (EINVAL);
pathlen = strlen(path);
if (pathlen > SOCK_MAXADDRLEN) {
FREE(path, M_NETGRAPH);
return (E2BIG);
}
if (*buflen < pathoff + pathlen) {
FREE(path, M_NETGRAPH);
return (ERANGE);
}
*off += toklen;
bcopy(path, sun->sun_path, pathlen);
sun->sun_len = pathoff + pathlen;
FREE(path, M_NETGRAPH);
break;
}
case PF_INET: /* Get an IP address with optional port */
{
struct sockaddr_in *const sin = (struct sockaddr_in *)sa;
int i;
/* Parse this: <ipaddress>[:port] */
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
u_long val;
char *eptr;
val = strtoul(s + *off, &eptr, 10);
if (val > 0xff || eptr == s + *off)
return (EINVAL);
*off += (eptr - (s + *off));
((u_char *)&sin->sin_addr)[i] = (u_char)val;
if (i < 3) {
if (s[*off] != '.')
return (EINVAL);
(*off)++;
} else if (s[*off] == ':') {
(*off)++;
val = strtoul(s + *off, &eptr, 10);
if (val > 0xffff || eptr == s + *off)
return (EINVAL);
*off += (eptr - (s + *off));
sin->sin_port = htons(val);
} else
sin->sin_port = 0;
}
bzero(&sin->sin_zero, sizeof(sin->sin_zero));
sin->sin_len = sizeof(*sin);
break;
}
#if 0
case PF_APPLETALK: /* XXX implement these someday */
case PF_INET6:
case PF_IPX:
#endif
default:
return (EINVAL);
}
/* Done */
*buflen = sa->sa_len;
return (0);
}
/* Convert a struct sockaddr from binary to ASCII */
static int
ng_ksocket_sockaddr_unparse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *data, int *off, char *cbuf, int cbuflen)
{
const struct sockaddr *sa = (const struct sockaddr *)(data + *off);
int slen = 0;
/* Output socket address, either in special or generic format */
switch (sa->sa_family) {
case PF_LOCAL:
{
const int pathoff = OFFSETOF(struct sockaddr_un, sun_path);
const struct sockaddr_un *sun = (const struct sockaddr_un *)sa;
const int pathlen = sun->sun_len - pathoff;
char pathbuf[SOCK_MAXADDRLEN + 1];
char *pathtoken;
bcopy(sun->sun_path, pathbuf, pathlen);
pathbuf[pathlen] = '\0';
if ((pathtoken = ng_encode_string(pathbuf)) == NULL)
return (ENOMEM);
slen += snprintf(cbuf, cbuflen, "local/%s", pathtoken);
FREE(pathtoken, M_NETGRAPH);
if (slen >= cbuflen)
return (ERANGE);
*off += sun->sun_len;
return (0);
}
case PF_INET:
{
const struct sockaddr_in *sin = (const struct sockaddr_in *)sa;
slen += snprintf(cbuf, cbuflen, "inet/%d.%d.%d.%d",
((const u_char *)&sin->sin_addr)[0],
((const u_char *)&sin->sin_addr)[1],
((const u_char *)&sin->sin_addr)[2],
((const u_char *)&sin->sin_addr)[3]);
if (sin->sin_port != 0) {
slen += snprintf(cbuf + strlen(cbuf),
cbuflen - strlen(cbuf), ":%d",
(u_int)ntohs(sin->sin_port));
}
if (slen >= cbuflen)
return (ERANGE);
*off += sizeof(*sin);
return(0);
}
#if 0
case PF_APPLETALK: /* XXX implement these someday */
case PF_INET6:
case PF_IPX:
#endif
default:
return (*ng_ksocket_generic_sockaddr_type.supertype->unparse)
(&ng_ksocket_generic_sockaddr_type,
data, off, cbuf, cbuflen);
}
}
/* Parse type for struct sockaddr */
static const struct ng_parse_type ng_ksocket_sockaddr_type = {
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
&ng_ksocket_sockaddr_parse,
&ng_ksocket_sockaddr_unparse,
NULL /* no such thing as a default struct sockaddr */
};
/************************************************************************
STRUCT NG_KSOCKET_SOCKOPT PARSE TYPE
************************************************************************/
/* Get length of the struct ng_ksocket_sockopt value field, which is the
just the excess of the message argument portion over the length of
the struct ng_ksocket_sockopt. */
static int
ng_parse_sockoptval_getLength(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *start, const u_char *buf)
{
static const int offset = OFFSETOF(struct ng_ksocket_sockopt, value);
const struct ng_ksocket_sockopt *sopt;
const struct ng_mesg *msg;
sopt = (const struct ng_ksocket_sockopt *)(buf - offset);
msg = (const struct ng_mesg *)((const u_char *)sopt - sizeof(*msg));
return msg->header.arglen - sizeof(*sopt);
}
/* Parse type for the option value part of a struct ng_ksocket_sockopt
XXX Eventually, we should handle the different socket options specially.
XXX This would avoid byte order problems, eg an integer value of 1 is
XXX going to be "[1]" for little endian or "[3=1]" for big endian. */
static const struct ng_parse_type ng_ksocket_sockoptval_type = {
&ng_parse_bytearray_type,
&ng_parse_sockoptval_getLength
};
/* Parse type for struct ng_ksocket_sockopt */
static const struct ng_parse_struct_info ng_ksocket_sockopt_type_info
= NG_KSOCKET_SOCKOPT_INFO(&ng_ksocket_sockoptval_type);
static const struct ng_parse_type ng_ksocket_sockopt_type = {
&ng_parse_struct_type,
&ng_ksocket_sockopt_type_info,
};
/* List of commands and how to convert arguments to/from ASCII */
static const struct ng_cmdlist ng_ksocket_cmds[] = {
{
NGM_KSOCKET_COOKIE,
NGM_KSOCKET_BIND,
"bind",
&ng_ksocket_sockaddr_type,
NULL
},
{
NGM_KSOCKET_COOKIE,
NGM_KSOCKET_LISTEN,
"listen",
&ng_parse_int32_type,
NULL
},
{
NGM_KSOCKET_COOKIE,
NGM_KSOCKET_ACCEPT,
"accept",
NULL,
&ng_ksocket_sockaddr_type
},
{
NGM_KSOCKET_COOKIE,
NGM_KSOCKET_CONNECT,
"connect",
&ng_ksocket_sockaddr_type,
NULL
},
{
NGM_KSOCKET_COOKIE,
NGM_KSOCKET_GETNAME,
"getname",
NULL,
&ng_ksocket_sockaddr_type
},
{
NGM_KSOCKET_COOKIE,
NGM_KSOCKET_GETPEERNAME,
"getpeername",
NULL,
&ng_ksocket_sockaddr_type
},
{
NGM_KSOCKET_COOKIE,
NGM_KSOCKET_SETOPT,
"setopt",
&ng_ksocket_sockopt_type,
NULL
},
{
NGM_KSOCKET_COOKIE,
NGM_KSOCKET_GETOPT,
"getopt",
&ng_ksocket_sockopt_type,
&ng_ksocket_sockopt_type
},
{ 0 }
};
/* Node type descriptor */
static struct ng_type ng_ksocket_typestruct = {
NG_VERSION,
NG_KSOCKET_NODE_TYPE,
NULL,
ng_ksocket_constructor,
ng_ksocket_rcvmsg,
ng_ksocket_rmnode,
ng_ksocket_newhook,
NULL,
NULL,
ng_ksocket_rcvdata,
ng_ksocket_rcvdata,
ng_ksocket_disconnect,
ng_ksocket_cmds
};
NETGRAPH_INIT(ksocket, &ng_ksocket_typestruct);
#define ERROUT(x) do { error = (x); goto done; } while (0)
/************************************************************************
NETGRAPH NODE STUFF
************************************************************************/
/*
* Node type constructor
*/
static int
ng_ksocket_constructor(node_p *nodep)
{
priv_p priv;
int error;
/* Allocate private structure */
MALLOC(priv, priv_p, sizeof(*priv), M_NETGRAPH, M_WAITOK);
if (priv == NULL)
return (ENOMEM);
bzero(priv, sizeof(*priv));
/* Call generic node constructor */
if ((error = ng_make_node_common(&ng_ksocket_typestruct, nodep))) {
FREE(priv, M_NETGRAPH);
return (error);
}
(*nodep)->private = priv;
/* Done */
return (0);
}
/*
* Give our OK for a hook to be added. The hook name is of the
* form "<family>:<type>:<proto>" where the three components may
* be decimal numbers or else aliases from the above lists.
*
* Connecting a hook amounts to opening the socket. Disconnecting
* the hook closes the socket and destroys the node as well.
*/
static int
ng_ksocket_newhook(node_p node, hook_p hook, const char *name0)
{
struct proc *p = curproc ? curproc : &proc0; /* XXX broken */
const priv_p priv = node->private;
char *s1, *s2, name[NG_HOOKLEN+1];
int family, type, protocol, error;
/* Check if we're already connected */
if (priv->hook != NULL)
return (EISCONN);
/* Extract family, type, and protocol from hook name */
snprintf(name, sizeof(name), "%s", name0);
s1 = name;
if ((s2 = index(s1, '/')) == NULL)
return (EINVAL);
*s2++ = '\0';
if ((family = ng_ksocket_parse(ng_ksocket_families, s1, 0)) == -1)
return (EINVAL);
s1 = s2;
if ((s2 = index(s1, '/')) == NULL)
return (EINVAL);
*s2++ = '\0';
if ((type = ng_ksocket_parse(ng_ksocket_types, s1, 0)) == -1)
return (EINVAL);
s1 = s2;
if ((protocol = ng_ksocket_parse(ng_ksocket_protos, s1, family)) == -1)
return (EINVAL);
/* Create the socket */
if ((error = socreate(family, &priv->so, type, protocol, p)) != 0)
return (error);
/* XXX call soreserve() ? */
/* Add our hook for incoming data */
priv->so->so_upcallarg = (caddr_t)node;
priv->so->so_upcall = ng_ksocket_incoming;
priv->so->so_rcv.sb_flags |= SB_UPCALL;
/* OK */
priv->hook = hook;
return (0);
}
/*
* Receive a control message
*/
static int
ng_ksocket_rcvmsg(node_p node, struct ng_mesg *msg,
const char *raddr, struct ng_mesg **rptr)
{
struct proc *p = curproc ? curproc : &proc0; /* XXX broken */
const priv_p priv = node->private;
struct socket *const so = priv->so;
struct ng_mesg *resp = NULL;
int error = 0;
switch (msg->header.typecookie) {
case NGM_KSOCKET_COOKIE:
switch (msg->header.cmd) {
case NGM_KSOCKET_BIND:
{
struct sockaddr *const sa
= (struct sockaddr *)msg->data;
/* Sanity check */
if (msg->header.arglen < SADATA_OFFSET
|| msg->header.arglen < sa->sa_len)
ERROUT(EINVAL);
if (so == NULL)
ERROUT(ENXIO);
/* Bind */
error = sobind(so, sa, p);
break;
}
case NGM_KSOCKET_LISTEN:
{
/* Sanity check */
if (msg->header.arglen != sizeof(int))
ERROUT(EINVAL);
if (so == NULL)
ERROUT(ENXIO);
/* Listen */
if ((error = solisten(so, *((int *)msg->data), p)) != 0)
break;
/* Notify sender when we get a connection attempt */
/* XXX implement me */
error = ENODEV;
break;
}
case NGM_KSOCKET_ACCEPT:
{
/* Sanity check */
if (msg->header.arglen != 0)
ERROUT(EINVAL);
if (so == NULL)
ERROUT(ENXIO);
/* Accept on the socket in a non-blocking way */
/* Create a new ksocket node for the new connection */
/* Return a response with the peer's sockaddr and
the absolute name of the newly created node */
/* XXX implement me */
error = ENODEV;
break;
}
case NGM_KSOCKET_CONNECT:
{
struct sockaddr *const sa
= (struct sockaddr *)msg->data;
/* Sanity check */
if (msg->header.arglen < SADATA_OFFSET
|| msg->header.arglen < sa->sa_len)
ERROUT(EINVAL);
if (so == NULL)
ERROUT(ENXIO);
/* Do connect */
if ((so->so_state & SS_ISCONNECTING) != 0)
ERROUT(EALREADY);
if ((error = soconnect(so, sa, p)) != 0) {
so->so_state &= ~SS_ISCONNECTING;
ERROUT(error);
}
if ((so->so_state & SS_ISCONNECTING) != 0)
/* Notify sender when we connect */
/* XXX implement me */
ERROUT(EINPROGRESS);
break;
}
case NGM_KSOCKET_GETNAME:
case NGM_KSOCKET_GETPEERNAME:
{
int (*func)(struct socket *so, struct sockaddr **nam);
struct sockaddr *sa = NULL;
int len;
/* Sanity check */
if (msg->header.arglen != 0)
ERROUT(EINVAL);
if (so == NULL)
ERROUT(ENXIO);
/* Get function */
if (msg->header.cmd == NGM_KSOCKET_GETPEERNAME) {
if ((so->so_state
& (SS_ISCONNECTED|SS_ISCONFIRMING)) == 0)
ERROUT(ENOTCONN);
func = so->so_proto->pr_usrreqs->pru_peeraddr;
} else
func = so->so_proto->pr_usrreqs->pru_sockaddr;
/* Get local or peer address */
if ((error = (*func)(so, &sa)) != 0)
goto bail;
len = (sa == NULL) ? 0 : sa->sa_len;
/* Send it back in a response */
NG_MKRESPONSE(resp, msg, len, M_NOWAIT);
if (resp == NULL) {
error = ENOMEM;
goto bail;
}
bcopy(sa, resp->data, len);
bail:
/* Cleanup */
if (sa != NULL)
FREE(sa, M_SONAME);
break;
}
case NGM_KSOCKET_GETOPT:
{
struct ng_ksocket_sockopt *ksopt =
(struct ng_ksocket_sockopt *)msg->data;
struct sockopt sopt;
/* Sanity check */
if (msg->header.arglen != sizeof(*ksopt))
ERROUT(EINVAL);
if (so == NULL)
ERROUT(ENXIO);
/* Get response with room for option value */
NG_MKRESPONSE(resp, msg, sizeof(*ksopt)
+ NG_KSOCKET_MAX_OPTLEN, M_NOWAIT);
if (resp == NULL)
ERROUT(ENOMEM);
/* Get socket option, and put value in the response */
sopt.sopt_dir = SOPT_GET;
sopt.sopt_level = ksopt->level;
sopt.sopt_name = ksopt->name;
sopt.sopt_p = p;
sopt.sopt_valsize = NG_KSOCKET_MAX_OPTLEN;
ksopt = (struct ng_ksocket_sockopt *)resp->data;
sopt.sopt_val = ksopt->value;
if ((error = sogetopt(so, &sopt)) != 0) {
FREE(resp, M_NETGRAPH);
break;
}
/* Set actual value length */
resp->header.arglen = sizeof(*ksopt)
+ sopt.sopt_valsize;
break;
}
case NGM_KSOCKET_SETOPT:
{
struct ng_ksocket_sockopt *const ksopt =
(struct ng_ksocket_sockopt *)msg->data;
const int valsize = msg->header.arglen - sizeof(*ksopt);
struct sockopt sopt;
/* Sanity check */
if (valsize < 0)
ERROUT(EINVAL);
if (so == NULL)
ERROUT(ENXIO);
/* Set socket option */
sopt.sopt_dir = SOPT_SET;
sopt.sopt_level = ksopt->level;
sopt.sopt_name = ksopt->name;
sopt.sopt_val = ksopt->value;
sopt.sopt_valsize = valsize;
sopt.sopt_p = p;
error = sosetopt(so, &sopt);
break;
}
default:
error = EINVAL;
break;
}
break;
default:
error = EINVAL;
break;
}
if (rptr)
*rptr = resp;
else if (resp)
FREE(resp, M_NETGRAPH);
done:
FREE(msg, M_NETGRAPH);
return (error);
}
/*
* Receive incoming data on our hook. Send it out the socket.
*/
static int
ng_ksocket_rcvdata(hook_p hook, struct mbuf *m, meta_p meta)
{
struct proc *p = curproc ? curproc : &proc0; /* XXX broken */
const node_p node = hook->node;
const priv_p priv = node->private;
struct socket *const so = priv->so;
int error;
NG_FREE_META(meta);
error = (*so->so_proto->pr_usrreqs->pru_sosend)(so, 0, 0, m, 0, 0, p);
return (error);
}
/*
* Destroy node
*/
static int
ng_ksocket_rmnode(node_p node)
{
const priv_p priv = node->private;
/* Close our socket (if any) */
if (priv->so != NULL) {
priv->so->so_upcall = NULL;
priv->so->so_rcv.sb_flags &= ~SB_UPCALL;
soclose(priv->so);
priv->so = NULL;
}
/* Take down netgraph node */
node->flags |= NG_INVALID;
ng_cutlinks(node);
ng_unname(node);
bzero(priv, sizeof(*priv));
FREE(priv, M_NETGRAPH);
node->private = NULL;
ng_unref(node); /* let the node escape */
return (0);
}
/*
* Hook disconnection
*/
static int
ng_ksocket_disconnect(hook_p hook)
{
KASSERT(hook->node->numhooks == 0,
("%s: numhooks=%d?", __FUNCTION__, hook->node->numhooks));
ng_rmnode(hook->node);
return (0);
}
/************************************************************************
HELPER STUFF
************************************************************************/
/*
* When incoming data is appended to the socket, we get notified here.
*/
static void
ng_ksocket_incoming(struct socket *so, void *arg, int waitflag)
{
const node_p node = arg;
const priv_p priv = node->private;
meta_p meta = NULL;
struct sockaddr *nam;
struct mbuf *m;
struct uio auio;
int s, flags, error;
s = splnet();
/* Sanity check */
if ((node->flags & NG_INVALID) != 0) {
splx(s);
return;
}
KASSERT(so == priv->so, ("%s: wrong socket", __FUNCTION__));
KASSERT(priv->hook != NULL, ("%s: no hook", __FUNCTION__));
/* Read and forward available mbuf's */
auio.uio_procp = NULL;
auio.uio_resid = 1000000000;
flags = MSG_DONTWAIT;
do {
if ((error = (*so->so_proto->pr_usrreqs->pru_soreceive)
(so, &nam, &auio, &m, (struct mbuf **)0, &flags)) == 0
&& m != NULL) {
struct mbuf *n;
/* Don't trust the various socket layers to get the
packet header and length correct (eg. kern/15175) */
for (n = m, m->m_pkthdr.len = 0; n; n = n->m_next)
m->m_pkthdr.len += n->m_len;
NG_SEND_DATA(error, priv->hook, m, meta);
}
} while (error == 0 && m != NULL);
splx(s);
}
/*
* Parse out either an integer value or an alias.
*/
static int
ng_ksocket_parse(const struct ng_ksocket_alias *aliases,
const char *s, int family)
{
int k, val;
char *eptr;
/* Try aliases */
for (k = 0; aliases[k].name != NULL; k++) {
if (strcmp(s, aliases[k].name) == 0
&& aliases[k].family == family)
return aliases[k].value;
}
/* Try parsing as a number */
val = (int)strtoul(s, &eptr, 10);
if (val < 0 || *eptr != '\0')
return (-1);
return (val);
}
/*
* ng_ksocket.h
*
* Copyright (c) 1996-1999 Whistle Communications, Inc.
* All rights reserved.
*
* Subject to the following obligations and disclaimer of warranty, use and
* redistribution of this software, in source or object code forms, with or
* without modifications are expressly permitted by Whistle Communications;
* provided, however, that:
* 1. Any and all reproductions of the source or object code must include the
* copyright notice above and the following disclaimer of warranties; and
* 2. No rights are granted, in any manner or form, to use Whistle
* Communications, Inc. trademarks, including the mark "WHISTLE
* COMMUNICATIONS" on advertising, endorsements, or otherwise except as
* such appears in the above copyright notice or in the software.
*
* THIS SOFTWARE IS BEING PROVIDED BY WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS "AS IS", AND
* TO THE MAXIMUM EXTENT PERMITTED BY LAW, WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS MAKES NO
* REPRESENTATIONS OR WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, REGARDING THIS SOFTWARE,
* INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY AND ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
* MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR NON-INFRINGEMENT.
* WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS DOES NOT WARRANT, GUARANTEE, OR MAKE ANY
* REPRESENTATIONS REGARDING THE USE OF, OR THE RESULTS OF THE USE OF THIS
* SOFTWARE IN TERMS OF ITS CORRECTNESS, ACCURACY, RELIABILITY OR OTHERWISE.
* IN NO EVENT SHALL WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DAMAGES
* RESULTING FROM OR ARISING OUT OF ANY USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, INCLUDING
* WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY,
* PUNITIVE, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR
* SERVICES, LOSS OF USE, DATA OR PROFITS, HOWEVER CAUSED AND UNDER ANY
* THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
* (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF
* THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS IS ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY
* OF SUCH DAMAGE.
*
* Author: Archie Cobbs <archie@whistle.com>
*
* $FreeBSD: src/sys/netgraph/ng_ksocket.h,v 1.2 1999/11/30 02:45:21 archie Exp $
* $Whistle: ng_ksocket.h,v 1.1 1999/11/16 20:04:40 archie Exp $
*/
#ifndef _NETGRAPH_KSOCKET_H_
#define _NETGRAPH_KSOCKET_H_
/* Node type name and magic cookie */
#define NG_KSOCKET_NODE_TYPE "ksocket"
#define NGM_KSOCKET_COOKIE 942710669
/* For NGM_KSOCKET_SETOPT and NGM_KSOCKET_GETOPT control messages */
struct ng_ksocket_sockopt {
u_int32_t level; /* second arg of [gs]etsockopt() */
u_int32_t name; /* third arg of [gs]etsockopt() */
u_char value[0]; /* fourth arg of [gs]etsockopt() */
};
/* Max length socket option we can return via NGM_KSOCKET_GETOPT
XXX This should not be necessary, we should dynamically size
XXX the response. Until then.. */
#define NG_KSOCKET_MAX_OPTLEN 1024
/* Keep this in sync with the above structure definition */
#define NG_KSOCKET_SOCKOPT_INFO(svtype) { \
{ \
{ "level", &ng_parse_int32_type }, \
{ "name", &ng_parse_int32_type }, \
{ "value", (svtype) }, \
{ NULL }, \
} \
}
/* Netgraph commands */
enum {
NGM_KSOCKET_BIND = 1,
NGM_KSOCKET_LISTEN,
NGM_KSOCKET_ACCEPT,
NGM_KSOCKET_CONNECT,
NGM_KSOCKET_GETNAME,
NGM_KSOCKET_GETPEERNAME,
NGM_KSOCKET_SETOPT,
NGM_KSOCKET_GETOPT,
};
#endif /* _NETGRAPH_KSOCKET_H_ */
/*
* ng_message.h
*
* Copyright (c) 1996-1999 Whistle Communications, Inc.
* All rights reserved.
*
* Subject to the following obligations and disclaimer of warranty, use and
* redistribution of this software, in source or object code forms, with or
* without modifications are expressly permitted by Whistle Communications;
* provided, however, that:
* 1. Any and all reproductions of the source or object code must include the
* copyright notice above and the following disclaimer of warranties; and
* 2. No rights are granted, in any manner or form, to use Whistle
* Communications, Inc. trademarks, including the mark "WHISTLE
* COMMUNICATIONS" on advertising, endorsements, or otherwise except as
* such appears in the above copyright notice or in the software.
*
* THIS SOFTWARE IS BEING PROVIDED BY WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS "AS IS", AND
* TO THE MAXIMUM EXTENT PERMITTED BY LAW, WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS MAKES NO
* REPRESENTATIONS OR WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, REGARDING THIS SOFTWARE,
* INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY AND ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
* MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR NON-INFRINGEMENT.
* WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS DOES NOT WARRANT, GUARANTEE, OR MAKE ANY
* REPRESENTATIONS REGARDING THE USE OF, OR THE RESULTS OF THE USE OF THIS
* SOFTWARE IN TERMS OF ITS CORRECTNESS, ACCURACY, RELIABILITY OR OTHERWISE.
* IN NO EVENT SHALL WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DAMAGES
* RESULTING FROM OR ARISING OUT OF ANY USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, INCLUDING
* WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY,
* PUNITIVE, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR
* SERVICES, LOSS OF USE, DATA OR PROFITS, HOWEVER CAUSED AND UNDER ANY
* THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
* (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF
* THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS IS ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY
* OF SUCH DAMAGE.
*
* Author: Julian Elischer <julian@whistle.com>
*
* $FreeBSD: src/sys/netgraph/ng_message.h,v 1.4 1999/12/29 04:46:00 peter Exp $
* $Whistle: ng_message.h,v 1.12 1999/01/25 01:17:44 archie Exp $
*/
#ifndef _NETGRAPH_NG_MESSAGE_H_
#define _NETGRAPH_NG_MESSAGE_H_ 1
/* ASCII string size limits */
#define NG_TYPELEN 15 /* max type name len (16 with null) */
#define NG_HOOKLEN 15 /* max hook name len (16 with null) */
#define NG_NODELEN 15 /* max node name len (16 with null) */
#define NG_PATHLEN 511 /* max path len (512 with null) */
#define NG_CMDSTRLEN 15 /* max command string (16 with null) */
#define NG_TEXTRESPONSE 1024 /* allow this length for a text response */
/* A netgraph message */
struct ng_mesg {
struct ng_msghdr {
u_char version; /* must == NG_VERSION */
u_char spare; /* pad to 2 bytes */
u_int16_t arglen; /* length of data */
u_int32_t flags; /* message status */
u_int32_t token; /* match with reply */
u_int32_t typecookie; /* node's type cookie */
u_int32_t cmd; /* command identifier */
u_char cmdstr[NG_CMDSTRLEN+1]; /* cmd string + \0 */
} header;
char data[0]; /* placeholder for actual data */
};
/* Keep this in sync with the above structure definition */
#define NG_GENERIC_NG_MESG_INFO(dtype) { \
{ \
{ "version", &ng_parse_int8_type }, \
{ "spare", &ng_parse_int8_type }, \
{ "arglen", &ng_parse_int16_type }, \
{ "flags", &ng_parse_int32_type }, \
{ "token", &ng_parse_int32_type }, \
{ "typecookie", &ng_parse_int32_type }, \
{ "cmd", &ng_parse_int32_type }, \
{ "cmdstr", &ng_parse_cmdbuf_type }, \
{ "data", (dtype) }, \
{ NULL }, \
} \
}
/* Negraph type binary compatibility field */
#define NG_VERSION 2
/* Flags field flags */
#define NGF_ORIG 0x0000 /* the msg is the original request */
#define NGF_RESP 0x0001 /* the message is a response */
/* Type of a unique node ID */
#define ng_ID_t unsigned int
/*
* Here we describe the "generic" messages that all nodes inherently
* understand. With the exception of NGM_TEXT_STATUS, these are handled
* automatically by the base netgraph code.
*/
/* Generic message type cookie */
#define NGM_GENERIC_COOKIE 851672668
/* Generic messages defined for this type cookie */
#define NGM_SHUTDOWN 1 /* shut down node */
#define NGM_MKPEER 2 /* create and attach a peer node */
#define NGM_CONNECT 3 /* connect two nodes */
#define NGM_NAME 4 /* give a node a name */
#define NGM_RMHOOK 5 /* break a connection btw. two nodes */
#define NGM_NODEINFO 6 /* get nodeinfo for the target */
#define NGM_LISTHOOKS 7 /* get list of hooks on node */
#define NGM_LISTNAMES 8 /* list all globally named nodes */
#define NGM_LISTNODES 9 /* list all nodes, named and unnamed */
#define NGM_LISTTYPES 10 /* list all installed node types */
#define NGM_TEXT_STATUS 11 /* (optional) get text status report */
#define NGM_BINARY2ASCII 12 /* convert struct ng_mesg to ascii */
#define NGM_ASCII2BINARY 13 /* convert ascii to struct ng_mesg */
/* Structure used for NGM_MKPEER */
struct ngm_mkpeer {
char type[NG_TYPELEN + 1]; /* peer type */
char ourhook[NG_HOOKLEN + 1]; /* hook name */
char peerhook[NG_HOOKLEN + 1]; /* peer hook name */
};
/* Keep this in sync with the above structure definition */
#define NG_GENERIC_MKPEER_INFO() { \
{ \
{ "type", &ng_parse_typebuf_type }, \
{ "ourhook", &ng_parse_hookbuf_type }, \
{ "peerhook", &ng_parse_hookbuf_type }, \
{ NULL }, \
} \
}
/* Structure used for NGM_CONNECT */
struct ngm_connect {
char path[NG_PATHLEN + 1]; /* peer path */
char ourhook[NG_HOOKLEN + 1]; /* hook name */
char peerhook[NG_HOOKLEN + 1]; /* peer hook name */
};
/* Keep this in sync with the above structure definition */
#define NG_GENERIC_CONNECT_INFO() { \
{ \
{ "path", &ng_parse_pathbuf_type }, \
{ "ourhook", &ng_parse_hookbuf_type }, \
{ "peerhook", &ng_parse_hookbuf_type }, \
{ NULL }, \
} \
}
/* Structure used for NGM_NAME */
struct ngm_name {
char name[NG_NODELEN + 1]; /* node name */
};
/* Keep this in sync with the above structure definition */
#define NG_GENERIC_NAME_INFO() { \
{ \
{ "name", &ng_parse_nodebuf_type }, \
{ NULL }, \
} \
}
/* Structure used for NGM_RMHOOK */
struct ngm_rmhook {
char ourhook[NG_HOOKLEN + 1]; /* hook name */
};
/* Keep this in sync with the above structure definition */
#define NG_GENERIC_RMHOOK_INFO() { \
{ \
{ "hook", &ng_parse_hookbuf_type }, \
{ NULL }, \
} \
}
/* Structure used for NGM_NODEINFO */
struct nodeinfo {
char name[NG_NODELEN + 1]; /* node name (if any) */
char type[NG_TYPELEN + 1]; /* peer type */
ng_ID_t id; /* unique identifier */
u_int32_t hooks; /* number of active hooks */
};
/* Keep this in sync with the above structure definition */
#define NG_GENERIC_NODEINFO_INFO() { \
{ \
{ "name", &ng_parse_nodebuf_type }, \
{ "type", &ng_parse_typebuf_type }, \
{ "id", &ng_parse_int32_type }, \
{ "hooks", &ng_parse_int32_type }, \
{ NULL }, \
} \
}
/* Structure used for NGM_LISTHOOKS */
struct linkinfo {
char ourhook[NG_HOOKLEN + 1]; /* hook name */
char peerhook[NG_HOOKLEN + 1]; /* peer hook */
struct nodeinfo nodeinfo;
};
/* Keep this in sync with the above structure definition */
#define NG_GENERIC_LINKINFO_INFO(nitype) { \
{ \
{ "ourhook", &ng_parse_hookbuf_type }, \
{ "peerhook", &ng_parse_hookbuf_type }, \
{ "nodeinfo", (nitype) }, \
{ NULL }, \
} \
}
struct hooklist {
struct nodeinfo nodeinfo; /* node information */
struct linkinfo link[0]; /* info about each hook */
};
/* Keep this in sync with the above structure definition */
#define NG_GENERIC_HOOKLIST_INFO(nitype,litype) { \
{ \
{ "nodeinfo", (nitype) }, \
{ "linkinfo", (litype) }, \
{ NULL }, \
} \
}
/* Structure used for NGM_LISTNAMES/NGM_LISTNODES */
struct namelist {
u_int32_t numnames;
struct nodeinfo nodeinfo[0];
};
/* Keep this in sync with the above structure definition */
#define NG_GENERIC_LISTNODES_INFO(niarraytype) { \
{ \
{ "numnames", &ng_parse_int32_type }, \
{ "nodeinfo", (niarraytype) }, \
{ NULL }, \
} \
}
/* Structure used for NGM_LISTTYPES */
struct typeinfo {
char typename[NG_TYPELEN + 1]; /* name of type */
u_int32_t numnodes; /* number alive */
};
/* Keep this in sync with the above structure definition */
#define NG_GENERIC_TYPEINFO_INFO() { \
{ \
{ "typename", &ng_parse_typebuf_type }, \
{ "typeinfo", &ng_parse_int32_type }, \
{ NULL }, \
} \
}
struct typelist {
u_int32_t numtypes;
struct typeinfo typeinfo[0];
};
/* Keep this in sync with the above structure definition */
#define NG_GENERIC_TYPELIST_INFO(tiarraytype) { \
{ \
{ "numtypes", &ng_parse_int32_type }, \
{ "typeinfo", (tiarraytype) }, \
{ NULL }, \
} \
}
/*
* For netgraph nodes that are somehow associated with file descriptors
* (e.g., a device that has a /dev entry and is also a netgraph node),
* we define a generic ioctl for requesting the corresponding nodeinfo
* structure and for assigning a name (if there isn't one already).
*
* For these to you need to also #include <sys/ioccom.h>.
*/
#define NGIOCGINFO _IOR('N', 40, struct nodeinfo) /* get node info */
#define NGIOCSETNAME _IOW('N', 41, struct ngm_name) /* set node name */
#ifdef _KERNEL
/*
* Allocate and initialize a netgraph message "msg" with "len"
* extra bytes of argument. Sets "msg" to NULL if fails.
* Does not initialize token.
*/
#define NG_MKMESSAGE(msg, cookie, cmdid, len, how) \
do { \
MALLOC((msg), struct ng_mesg *, sizeof(struct ng_mesg) \
+ (len), M_NETGRAPH, (how)); \
if ((msg) == NULL) \
break; \
bzero((msg), sizeof(struct ng_mesg) + (len)); \
(msg)->header.version = NG_VERSION; \
(msg)->header.typecookie = (cookie); \
(msg)->header.cmd = (cmdid); \
(msg)->header.arglen = (len); \
strncpy((msg)->header.cmdstr, #cmdid, \
sizeof((msg)->header.cmdstr) - 1); \
} while (0)
/*
* Allocate and initialize a response "rsp" to a message "msg"
* with "len" extra bytes of argument. Sets "rsp" to NULL if fails.
*/
#define NG_MKRESPONSE(rsp, msg, len, how) \
do { \
MALLOC((rsp), struct ng_mesg *, sizeof(struct ng_mesg) \
+ (len), M_NETGRAPH, (how)); \
if ((rsp) == NULL) \
break; \
bzero((rsp), sizeof(struct ng_mesg) + (len)); \
(rsp)->header.version = NG_VERSION; \
(rsp)->header.arglen = (len); \
(rsp)->header.token = (msg)->header.token; \
(rsp)->header.typecookie = (msg)->header.typecookie; \
(rsp)->header.cmd = (msg)->header.cmd; \
bcopy((msg)->header.cmdstr, (rsp)->header.cmdstr, \
sizeof((rsp)->header.cmdstr)); \
(rsp)->header.flags |= NGF_RESP; \
} while (0)
#endif /* _KERNEL */
#endif /* _NETGRAPH_NG_MESSAGE_H_ */
/*
* ng_parse.c
*
* Copyright (c) 1999 Whistle Communications, Inc.
* All rights reserved.
*
* Subject to the following obligations and disclaimer of warranty, use and
* redistribution of this software, in source or object code forms, with or
* without modifications are expressly permitted by Whistle Communications;
* provided, however, that:
* 1. Any and all reproductions of the source or object code must include the
* copyright notice above and the following disclaimer of warranties; and
* 2. No rights are granted, in any manner or form, to use Whistle
* Communications, Inc. trademarks, including the mark "WHISTLE
* COMMUNICATIONS" on advertising, endorsements, or otherwise except as
* such appears in the above copyright notice or in the software.
*
* THIS SOFTWARE IS BEING PROVIDED BY WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS "AS IS", AND
* TO THE MAXIMUM EXTENT PERMITTED BY LAW, WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS MAKES NO
* REPRESENTATIONS OR WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, REGARDING THIS SOFTWARE,
* INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY AND ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
* MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR NON-INFRINGEMENT.
* WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS DOES NOT WARRANT, GUARANTEE, OR MAKE ANY
* REPRESENTATIONS REGARDING THE USE OF, OR THE RESULTS OF THE USE OF THIS
* SOFTWARE IN TERMS OF ITS CORRECTNESS, ACCURACY, RELIABILITY OR OTHERWISE.
* IN NO EVENT SHALL WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DAMAGES
* RESULTING FROM OR ARISING OUT OF ANY USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, INCLUDING
* WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY,
* PUNITIVE, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR
* SERVICES, LOSS OF USE, DATA OR PROFITS, HOWEVER CAUSED AND UNDER ANY
* THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
* (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF
* THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS IS ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY
* OF SUCH DAMAGE.
*
* Author: Archie Cobbs <archie@whistle.com>
*
* $Whistle: ng_parse.c,v 1.3 1999/11/29 01:43:48 archie Exp $
* $FreeBSD: src/sys/netgraph/ng_parse.c,v 1.3 1999/12/07 05:50:47 julian Exp $
*/
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/param.h>
#include <sys/systm.h>
#include <sys/errno.h>
#include <sys/malloc.h>
#include <sys/ctype.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <netgraph/ng_message.h>
#include <netgraph/netgraph.h>
#include <netgraph/ng_parse.h>
/* Compute alignment for primitive integral types */
struct int16_temp {
char x;
int16_t y;
};
struct int32_temp {
char x;
int32_t y;
};
struct int64_temp {
char x;
int64_t y;
};
#define INT8_ALIGNMENT 1
#define INT16_ALIGNMENT ((int)&((struct int16_temp *)0)->y)
#define INT32_ALIGNMENT ((int)&((struct int32_temp *)0)->y)
#define INT64_ALIGNMENT ((int)&((struct int64_temp *)0)->y)
/* Type of composite object: struct, array, or fixedarray */
enum comptype {
CT_STRUCT,
CT_ARRAY,
CT_FIXEDARRAY,
};
/* Composite types helper functions */
static int ng_parse_composite(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const char *s, int *off, const u_char *start,
u_char *const buf, int *buflen, enum comptype ctype);
static int ng_unparse_composite(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *data, int *off, char *cbuf, int cbuflen,
enum comptype ctype);
static int ng_get_composite_elem_default(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
int index, const u_char *start, u_char *buf,
int *buflen, enum comptype ctype);
static int ng_get_composite_len(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *start, const u_char *buf,
enum comptype ctype);
static const struct ng_parse_type *ng_get_composite_etype(const struct
ng_parse_type *type, int index, enum comptype ctype);
static int ng_parse_get_elem_pad(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
int index, enum comptype ctype, int posn);
/* Parsing helper functions */
static int ng_parse_skip_value(const char *s, int off, int *lenp);
/* Poor man's virtual method calls */
#define METHOD(t,m) (ng_get_ ## m ## _method(t))
#define INVOKE(t,m) (*METHOD(t,m))
static ng_parse_t *ng_get_parse_method(const struct ng_parse_type *t);
static ng_unparse_t *ng_get_unparse_method(const struct ng_parse_type *t);
static ng_getDefault_t *ng_get_getDefault_method(const
struct ng_parse_type *t);
static ng_getAlign_t *ng_get_getAlign_method(const struct ng_parse_type *t);
#define ALIGNMENT(t) (METHOD(t, getAlign) == NULL ? \
0 : INVOKE(t, getAlign)(t))
/* For converting binary to string */
#define NG_PARSE_APPEND(fmt, args...) \
do { \
int len; \
\
len = snprintf((cbuf), (cbuflen), \
fmt , ## args); \
if (len >= (cbuflen)) \
return (ERANGE); \
(cbuf) += len; \
(cbuflen) -= len; \
} while (0)
/************************************************************************
PUBLIC FUNCTIONS
************************************************************************/
/*
* Convert an ASCII string to binary according to the supplied type descriptor
*/
int
ng_parse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const char *string, int *off, u_char *buf, int *buflen)
{
return INVOKE(type, parse)(type, string, off, buf, buf, buflen);
}
/*
* Convert binary to an ASCII string according to the supplied type descriptor
*/
int
ng_unparse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *data, char *cbuf, int cbuflen)
{
int off = 0;
return INVOKE(type, unparse)(type, data, &off, cbuf, cbuflen);
}
/*
* Fill in the default value according to the supplied type descriptor
*/
int
ng_parse_getDefault(const struct ng_parse_type *type, u_char *buf, int *buflen)
{
ng_getDefault_t *const func = METHOD(type, getDefault);
if (func == NULL)
return (EOPNOTSUPP);
return (*func)(type, buf, buf, buflen);
}
/************************************************************************
STRUCTURE TYPE
************************************************************************/
static int
ng_struct_parse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const char *s, int *off, const u_char *const start,
u_char *const buf, int *buflen)
{
return ng_parse_composite(type, s, off, start, buf, buflen, CT_STRUCT);
}
static int
ng_struct_unparse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *data, int *off, char *cbuf, int cbuflen)
{
return ng_unparse_composite(type, data, off, cbuf, cbuflen, CT_STRUCT);
}
static int
ng_struct_getDefault(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *const start, u_char *buf, int *buflen)
{
int off = 0;
return ng_parse_composite(type,
"{}", &off, start, buf, buflen, CT_STRUCT);
}
static int
ng_struct_getAlign(const struct ng_parse_type *type)
{
const struct ng_parse_struct_info *si = type->info;
const struct ng_parse_struct_field *field;
int align = 0;
for (field = si->fields; field->name != NULL; field++) {
int falign = ALIGNMENT(field->type);
if (falign > align)
align = falign;
}
return align;
}
const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_struct_type = {
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
ng_struct_parse,
ng_struct_unparse,
ng_struct_getDefault,
ng_struct_getAlign
};
/************************************************************************
FIXED LENGTH ARRAY TYPE
************************************************************************/
static int
ng_fixedarray_parse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const char *s, int *off, const u_char *const start,
u_char *const buf, int *buflen)
{
return ng_parse_composite(type,
s, off, start, buf, buflen, CT_FIXEDARRAY);
}
static int
ng_fixedarray_unparse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *data, int *off, char *cbuf, int cbuflen)
{
return ng_unparse_composite(type,
data, off, cbuf, cbuflen, CT_FIXEDARRAY);
}
static int
ng_fixedarray_getDefault(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *const start, u_char *buf, int *buflen)
{
int off = 0;
return ng_parse_composite(type,
"[]", &off, start, buf, buflen, CT_FIXEDARRAY);
}
static int
ng_fixedarray_getAlign(const struct ng_parse_type *type)
{
const struct ng_parse_fixedarray_info *fi = type->info;
return ALIGNMENT(fi->elementType);
}
const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_fixedarray_type = {
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
ng_fixedarray_parse,
ng_fixedarray_unparse,
ng_fixedarray_getDefault,
ng_fixedarray_getAlign
};
/************************************************************************
VARIABLE LENGTH ARRAY TYPE
************************************************************************/
static int
ng_array_parse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const char *s, int *off, const u_char *const start,
u_char *const buf, int *buflen)
{
return ng_parse_composite(type, s, off, start, buf, buflen, CT_ARRAY);
}
static int
ng_array_unparse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *data, int *off, char *cbuf, int cbuflen)
{
return ng_unparse_composite(type, data, off, cbuf, cbuflen, CT_ARRAY);
}
static int
ng_array_getDefault(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *const start, u_char *buf, int *buflen)
{
int off = 0;
return ng_parse_composite(type,
"[]", &off, start, buf, buflen, CT_ARRAY);
}
static int
ng_array_getAlign(const struct ng_parse_type *type)
{
const struct ng_parse_array_info *ai = type->info;
return ALIGNMENT(ai->elementType);
}
const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_array_type = {
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
ng_array_parse,
ng_array_unparse,
ng_array_getDefault,
ng_array_getAlign
};
/************************************************************************
INT8 TYPE
************************************************************************/
static int
ng_int8_parse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const char *s, int *off, const u_char *const start,
u_char *const buf, int *buflen)
{
long val;
int8_t val8;
char *eptr;
val = strtol(s + *off, &eptr, 0);
if (val < -0x80 || val > 0xff || eptr == s + *off)
return (EINVAL);
*off = eptr - s;
val8 = (int8_t)val;
bcopy(&val8, buf, sizeof(int8_t));
*buflen = sizeof(int8_t);
return (0);
}
static int
ng_int8_unparse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *data, int *off, char *cbuf, int cbuflen)
{
int8_t val;
bcopy(data + *off, &val, sizeof(int8_t));
NG_PARSE_APPEND("%d", (int)val);
*off += sizeof(int8_t);
return (0);
}
static int
ng_int8_getDefault(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *const start, u_char *buf, int *buflen)
{
int8_t val;
if (*buflen < sizeof(int8_t))
return (ERANGE);
val = 0;
bcopy(&val, buf, sizeof(int8_t));
*buflen = sizeof(int8_t);
return (0);
}
static int
ng_int8_getAlign(const struct ng_parse_type *type)
{
return INT8_ALIGNMENT;
}
const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_int8_type = {
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
ng_int8_parse,
ng_int8_unparse,
ng_int8_getDefault,
ng_int8_getAlign
};
/************************************************************************
INT16 TYPE
************************************************************************/
static int
ng_int16_parse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const char *s, int *off, const u_char *const start,
u_char *const buf, int *buflen)
{
long val;
int16_t val16;
char *eptr;
val = strtol(s + *off, &eptr, 0);
if (val < -0x8000 || val > 0xffff || eptr == s + *off)
return (EINVAL);
*off = eptr - s;
val16 = (int16_t)val;
bcopy(&val16, buf, sizeof(int16_t));
*buflen = sizeof(int16_t);
return (0);
}
static int
ng_int16_unparse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *data, int *off, char *cbuf, int cbuflen)
{
int16_t val;
bcopy(data + *off, &val, sizeof(int16_t));
NG_PARSE_APPEND("%d", (int)val);
*off += sizeof(int16_t);
return (0);
}
static int
ng_int16_getDefault(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *const start, u_char *buf, int *buflen)
{
int16_t val;
if (*buflen < sizeof(int16_t))
return (ERANGE);
val = 0;
bcopy(&val, buf, sizeof(int16_t));
*buflen = sizeof(int16_t);
return (0);
}
static int
ng_int16_getAlign(const struct ng_parse_type *type)
{
return INT16_ALIGNMENT;
}
const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_int16_type = {
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
ng_int16_parse,
ng_int16_unparse,
ng_int16_getDefault,
ng_int16_getAlign
};
/************************************************************************
INT32 TYPE
************************************************************************/
static int
ng_int32_parse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const char *s, int *off, const u_char *const start,
u_char *const buf, int *buflen)
{
long val; /* assumes long is at least 32 bits */
int32_t val32;
char *eptr;
val = strtol(s + *off, &eptr, 0);
if (val < (long)-0x80000000
|| val > (u_long)0xffffffff || eptr == s + *off)
return (EINVAL);
*off = eptr - s;
val32 = (int32_t)val;
bcopy(&val32, buf, sizeof(int32_t));
*buflen = sizeof(int32_t);
return (0);
}
static int
ng_int32_unparse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *data, int *off, char *cbuf, int cbuflen)
{
int32_t val;
bcopy(data + *off, &val, sizeof(int32_t));
NG_PARSE_APPEND("%ld", (long)val);
*off += sizeof(int32_t);
return (0);
}
static int
ng_int32_getDefault(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *const start, u_char *buf, int *buflen)
{
int32_t val;
if (*buflen < sizeof(int32_t))
return (ERANGE);
val = 0;
bcopy(&val, buf, sizeof(int32_t));
*buflen = sizeof(int32_t);
return (0);
}
static int
ng_int32_getAlign(const struct ng_parse_type *type)
{
return INT32_ALIGNMENT;
}
const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_int32_type = {
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
ng_int32_parse,
ng_int32_unparse,
ng_int32_getDefault,
ng_int32_getAlign
};
/************************************************************************
INT64 TYPE
************************************************************************/
static int
ng_int64_parse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const char *s, int *off, const u_char *const start,
u_char *const buf, int *buflen)
{
quad_t val;
int64_t val64;
char *eptr;
val = strtoq(s + *off, &eptr, 0);
if (eptr == s + *off)
return (EINVAL);
*off = eptr - s;
val64 = (int64_t)val;
bcopy(&val64, buf, sizeof(int64_t));
*buflen = sizeof(int64_t);
return (0);
}
static int
ng_int64_unparse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *data, int *off, char *cbuf, int cbuflen)
{
int64_t val;
bcopy(data + *off, &val, sizeof(int64_t));
NG_PARSE_APPEND("%lld", (long long)val);
*off += sizeof(int64_t);
return (0);
}
static int
ng_int64_getDefault(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *const start, u_char *buf, int *buflen)
{
int64_t val;
if (*buflen < sizeof(int64_t))
return (ERANGE);
val = 0;
bcopy(&val, buf, sizeof(int64_t));
*buflen = sizeof(int64_t);
return (0);
}
static int
ng_int64_getAlign(const struct ng_parse_type *type)
{
return INT64_ALIGNMENT;
}
const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_int64_type = {
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
ng_int64_parse,
ng_int64_unparse,
ng_int64_getDefault,
ng_int64_getAlign
};
/************************************************************************
STRING TYPE
************************************************************************/
static int
ng_string_parse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const char *s, int *off, const u_char *const start,
u_char *const buf, int *buflen)
{
char *sval;
int len;
if ((sval = ng_get_string_token(s, off, &len)) == NULL)
return (EINVAL);
*off += len;
len = strlen(sval) + 1;
bcopy(sval, buf, len);
FREE(sval, M_NETGRAPH);
*buflen = len;
return (0);
}
static int
ng_string_unparse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *data, int *off, char *cbuf, int cbuflen)
{
const char *const raw = (const char *)data + *off;
char *const s = ng_encode_string(raw);
if (s == NULL)
return (ENOMEM);
NG_PARSE_APPEND("%s", s);
*off += strlen(raw) + 1;
FREE(s, M_NETGRAPH);
return (0);
}
static int
ng_string_getDefault(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *const start, u_char *buf, int *buflen)
{
if (*buflen < 1)
return (ERANGE);
buf[0] = (u_char)'\0';
*buflen = 1;
return (0);
}
const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_string_type = {
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
ng_string_parse,
ng_string_unparse,
ng_string_getDefault,
NULL
};
/************************************************************************
FIXED BUFFER STRING TYPE
************************************************************************/
static int
ng_fixedstring_parse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const char *s, int *off, const u_char *const start,
u_char *const buf, int *buflen)
{
const struct ng_parse_fixedsstring_info *const fi = type->info;
char *sval;
int len;
if ((sval = ng_get_string_token(s, off, &len)) == NULL)
return (EINVAL);
if (strlen(sval) + 1 > fi->bufSize)
return (E2BIG);
*off += len;
len = strlen(sval) + 1;
bcopy(sval, buf, len);
FREE(sval, M_NETGRAPH);
bzero(buf + len, fi->bufSize - len);
*buflen = fi->bufSize;
return (0);
}
static int
ng_fixedstring_unparse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *data, int *off, char *cbuf, int cbuflen)
{
const struct ng_parse_fixedsstring_info *const fi = type->info;
int error, temp = *off;
if ((error = ng_string_unparse(type, data, &temp, cbuf, cbuflen)) != 0)
return (error);
*off += fi->bufSize;
return (0);
}
static int
ng_fixedstring_getDefault(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *const start, u_char *buf, int *buflen)
{
const struct ng_parse_fixedsstring_info *const fi = type->info;
if (*buflen < fi->bufSize)
return (ERANGE);
bzero(buf, fi->bufSize);
*buflen = fi->bufSize;
return (0);
}
const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_fixedstring_type = {
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
ng_fixedstring_parse,
ng_fixedstring_unparse,
ng_fixedstring_getDefault,
NULL
};
const struct ng_parse_fixedsstring_info ng_parse_nodebuf_info = {
NG_NODELEN + 1
};
const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_nodebuf_type = {
&ng_parse_fixedstring_type,
&ng_parse_nodebuf_info
};
const struct ng_parse_fixedsstring_info ng_parse_hookbuf_info = {
NG_HOOKLEN + 1
};
const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_hookbuf_type = {
&ng_parse_fixedstring_type,
&ng_parse_hookbuf_info
};
const struct ng_parse_fixedsstring_info ng_parse_pathbuf_info = {
NG_PATHLEN + 1
};
const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_pathbuf_type = {
&ng_parse_fixedstring_type,
&ng_parse_pathbuf_info
};
const struct ng_parse_fixedsstring_info ng_parse_typebuf_info = {
NG_TYPELEN + 1
};
const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_typebuf_type = {
&ng_parse_fixedstring_type,
&ng_parse_typebuf_info
};
const struct ng_parse_fixedsstring_info ng_parse_cmdbuf_info = {
NG_CMDSTRLEN + 1
};
const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_cmdbuf_type = {
&ng_parse_fixedstring_type,
&ng_parse_cmdbuf_info
};
/************************************************************************
IP ADDRESS TYPE
************************************************************************/
static int
ng_ipaddr_parse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const char *s, int *off, const u_char *const start,
u_char *const buf, int *buflen)
{
int i, error;
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
if ((error = ng_int8_parse(&ng_parse_int8_type,
s, off, start, buf + i, buflen)) != 0)
return (error);
if (i < 3 && s[*off] != '.')
return (EINVAL);
(*off)++;
}
*buflen = 4;
return (0);
}
static int
ng_ipaddr_unparse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *data, int *off, char *cbuf, int cbuflen)
{
struct in_addr ip;
bcopy(data + *off, &ip, sizeof(ip));
NG_PARSE_APPEND("%d.%d.%d.%d", ((u_char *)&ip)[0],
((u_char *)&ip)[1], ((u_char *)&ip)[2], ((u_char *)&ip)[3]);
*off += sizeof(ip);
return (0);
}
static int
ng_ipaddr_getDefault(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *const start, u_char *buf, int *buflen)
{
struct in_addr ip = { 0 };
if (*buflen < sizeof(ip))
return (ERANGE);
bcopy(&ip, buf, sizeof(ip));
*buflen = sizeof(ip);
return (0);
}
const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_ipaddr_type = {
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
ng_ipaddr_parse,
ng_ipaddr_unparse,
ng_ipaddr_getDefault,
ng_int32_getAlign
};
/************************************************************************
BYTE ARRAY TYPE
************************************************************************/
/* Get the length of a byte array */
static int
ng_parse_bytearray_subtype_getLength(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *start, const u_char *buf)
{
ng_parse_array_getLength_t *const getLength = type->private;
return (*getLength)(type, start, buf);
}
static int
ng_bytearray_elem_unparse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *data, int *off, char *cbuf, int cbuflen)
{
int8_t val;
bcopy(data + *off, &val, sizeof(int8_t));
NG_PARSE_APPEND("0x%02x", (int)val & 0xff); /* always hex format */
*off += sizeof(int8_t);
return (0);
}
/* Byte array element type is int8, but always output in hex format */
const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_bytearray_elem_type = {
&ng_parse_int8_type,
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
ng_bytearray_elem_unparse,
NULL,
NULL
};
static const struct ng_parse_array_info ng_parse_bytearray_subtype_info = {
&ng_parse_bytearray_elem_type,
&ng_parse_bytearray_subtype_getLength,
NULL
};
static const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_bytearray_subtype = {
&ng_parse_array_type,
&ng_parse_bytearray_subtype_info
};
static int
ng_bytearray_parse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const char *s, int *off, const u_char *const start,
u_char *const buf, int *buflen)
{
char *str;
int toklen;
/* We accept either an array of bytes or a string constant */
if ((str = ng_get_string_token(s, off, &toklen)) != NULL) {
ng_parse_array_getLength_t *const getLength = type->info;
int arraylen, slen;
arraylen = (*getLength)(type, start, buf);
if (arraylen > *buflen) {
FREE(str, M_NETGRAPH);
return (ERANGE);
}
slen = strlen(str) + 1;
if (slen > arraylen) {
FREE(str, M_NETGRAPH);
return (E2BIG);
}
bcopy(str, buf, slen);
bzero(buf + slen, arraylen - slen);
FREE(str, M_NETGRAPH);
*off += toklen;
*buflen = arraylen;
return (0);
} else {
struct ng_parse_type subtype;
subtype = ng_parse_bytearray_subtype;
(const void *)subtype.private = type->info;
return ng_array_parse(&subtype, s, off, start, buf, buflen);
}
}
static int
ng_bytearray_unparse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *data, int *off, char *cbuf, int cbuflen)
{
struct ng_parse_type subtype;
subtype = ng_parse_bytearray_subtype;
(const void *)subtype.private = type->info;
return ng_array_unparse(&subtype, data, off, cbuf, cbuflen);
}
static int
ng_bytearray_getDefault(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *const start, u_char *buf, int *buflen)
{
struct ng_parse_type subtype;
subtype = ng_parse_bytearray_subtype;
(const void *)subtype.private = type->info;
return ng_array_getDefault(&subtype, start, buf, buflen);
}
const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_bytearray_type = {
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
ng_bytearray_parse,
ng_bytearray_unparse,
ng_bytearray_getDefault,
NULL
};
/************************************************************************
STRUCT NG_MESG TYPE
************************************************************************/
/* Get msg->header.arglen when "buf" is pointing to msg->data */
static int
ng_parse_ng_mesg_getLength(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *start, const u_char *buf)
{
const struct ng_mesg *msg;
msg = (const struct ng_mesg *)(buf - sizeof(*msg));
return msg->header.arglen;
}
/* Type for the variable length data portion of a struct ng_mesg */
static const struct ng_parse_type ng_msg_data_type = {
&ng_parse_bytearray_type,
&ng_parse_ng_mesg_getLength
};
/* Type for the entire struct ng_mesg header with data section */
static const struct ng_parse_struct_info
ng_parse_ng_mesg_type_info = NG_GENERIC_NG_MESG_INFO(&ng_msg_data_type);
const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_ng_mesg_type = {
&ng_parse_struct_type,
&ng_parse_ng_mesg_type_info,
};
/************************************************************************
COMPOSITE HELPER ROUTINES
************************************************************************/
/*
* Convert a structure or array from ASCII to binary
*/
static int
ng_parse_composite(const struct ng_parse_type *type, const char *s,
int *off, const u_char *const start, u_char *const buf, int *buflen,
const enum comptype ctype)
{
const int num = ng_get_composite_len(type, start, buf, ctype);
int nextIndex = 0; /* next implicit array index */
u_int index; /* field or element index */
int *foff; /* field value offsets in string */
int align, len, blen, error = 0;
/* Initialize */
MALLOC(foff, int *, num * sizeof(*foff), M_NETGRAPH, M_NOWAIT);
if (foff == NULL) {
error = ENOMEM;
goto done;
}
bzero(foff, num * sizeof(*foff));
/* Get opening brace/bracket */
if (ng_parse_get_token(s, off, &len)
!= (ctype == CT_STRUCT ? T_LBRACE : T_LBRACKET)) {
error = EINVAL;
goto done;
}
*off += len;
/* Get individual element value positions in the string */
for (;;) {
enum ng_parse_token tok;
/* Check for closing brace/bracket */
tok = ng_parse_get_token(s, off, &len);
if (tok == (ctype == CT_STRUCT ? T_RBRACE : T_RBRACKET)) {
*off += len;
break;
}
/* For arrays, the 'name' (ie, index) is optional, so
distinguish name from values by seeing if the next
token is an equals sign */
if (ctype != CT_STRUCT) {
int len2, off2;
char *eptr;
/* If an opening brace/bracket, index is implied */
if (tok == T_LBRACE || tok == T_LBRACKET) {
index = nextIndex++;
goto gotIndex;
}
/* Might be an index, might be a value, either way... */
if (tok != T_WORD) {
error = EINVAL;
goto done;
}
/* If no equals sign follows, index is implied */
off2 = *off + len;
if (ng_parse_get_token(s, &off2, &len2) != T_EQUALS) {
index = nextIndex++;
goto gotIndex;
}
/* Index was specified explicitly; parse it */
index = (u_int)strtoul(s + *off, &eptr, 0);
if (index < 0 || eptr - (s + *off) != len) {
error = EINVAL;
goto done;
}
nextIndex = index + 1;
*off += len + len2;
gotIndex:
} else { /* a structure field */
const struct ng_parse_struct_field *field = NULL;
const struct ng_parse_struct_info *si = type->info;
/* Find the field by name (required) in field list */
if (tok != T_WORD) {
error = EINVAL;
goto done;
}
for (index = 0; index < num; index++) {
field = &si->fields[index];
if (strncmp(&s[*off], field->name, len) == 0
&& field->name[len] == '\0')
break;
}
if (index == num) {
error = ENOENT;
goto done;
}
*off += len;
/* Get equals sign */
if (ng_parse_get_token(s, off, &len) != T_EQUALS) {
error = EINVAL;
goto done;
}
*off += len;
}
/* Check array index */
if (index >= num) {
error = E2BIG;
goto done;
}
/* Save value's position and skip over it for now */
if (foff[index] != 0) {
error = EALREADY; /* duplicate */
goto done;
}
while (isspace(s[*off]))
(*off)++;
foff[index] = *off;
if ((error = ng_parse_skip_value(s, *off, &len)) != 0)
goto done;
*off += len;
}
/* Now build binary structure from supplied values and defaults */
for (blen = index = 0; index < num; index++) {
const struct ng_parse_type *const
etype = ng_get_composite_etype(type, index, ctype);
int k, pad, vlen;
/* Zero-pad any alignment bytes */
pad = ng_parse_get_elem_pad(type, index, ctype, blen);
for (k = 0; k < pad; k++) {
if (blen >= *buflen) {
error = ERANGE;
goto done;
}
buf[blen++] = 0;
}
/* Get value */
vlen = *buflen - blen;
if (foff[index] == 0) { /* use default value */
error = ng_get_composite_elem_default(type, index,
start, buf + blen, &vlen, ctype);
} else { /* parse given value */
*off = foff[index];
error = INVOKE(etype, parse)(etype,
s, off, start, buf + blen, &vlen);
}
if (error != 0)
goto done;
blen += vlen;
}
/* Make total composite structure size a multiple of its alignment */
if ((align = ALIGNMENT(type)) != 0) {
while (blen % align != 0) {
if (blen >= *buflen) {
error = ERANGE;
goto done;
}
buf[blen++] = 0;
}
}
/* Done */
*buflen = blen;
done:
FREE(foff, M_NETGRAPH);
return (error);
}
/*
* Convert an array or structure from binary to ASCII
*/
static int
ng_unparse_composite(const struct ng_parse_type *type, const u_char *data,
int *off, char *cbuf, int cbuflen, const enum comptype ctype)
{
const int num = ng_get_composite_len(type, data, data + *off, ctype);
int nextIndex = 0, didOne = 0;
int error, index;
/* Opening brace/bracket */
NG_PARSE_APPEND("%c", (ctype == CT_STRUCT) ? '{' : '[');
/* Do each item */
for (index = 0; index < num; index++) {
const struct ng_parse_type *const
etype = ng_get_composite_etype(type, index, ctype);
u_char temp[1024];
/* Skip any alignment pad bytes */
*off += ng_parse_get_elem_pad(type, index, ctype, *off);
/* See if element is equal to its default value; skip if so */
if (*off < sizeof(temp)) {
int tempsize = sizeof(temp) - *off;
bcopy(data, temp, *off);
if (ng_get_composite_elem_default(type, index, temp,
temp + *off, &tempsize, ctype) == 0
&& bcmp(temp + *off, data + *off, tempsize) == 0) {
*off += tempsize;
continue;
}
}
/* Print name= */
NG_PARSE_APPEND(" ");
if (ctype != CT_STRUCT) {
if (index != nextIndex) {
nextIndex = index;
NG_PARSE_APPEND("%d=", index);
}
nextIndex++;
} else {
const struct ng_parse_struct_info *si = type->info;
NG_PARSE_APPEND("%s=", si->fields[index].name);
}
/* Print value */
if ((error = INVOKE(etype, unparse)
(etype, data, off, cbuf, cbuflen)) != 0)
return (error);
cbuflen -= strlen(cbuf);
cbuf += strlen(cbuf);
didOne = 1;
}
/* Closing brace/bracket */
NG_PARSE_APPEND("%s%c",
didOne ? " " : "", (ctype == CT_STRUCT) ? '}' : ']');
return (0);
}
/*
* Generate the default value for an element of an array or structure
* Returns EOPNOTSUPP if default value is unspecified.
*/
static int
ng_get_composite_elem_default(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
int index, const u_char *const start, u_char *buf, int *buflen,
const enum comptype ctype)
{
const struct ng_parse_type *etype;
ng_getDefault_t *func;
switch (ctype) {
case CT_STRUCT:
break;
case CT_ARRAY:
{
const struct ng_parse_array_info *const ai = type->info;
if (ai->getDefault != NULL) {
return (*ai->getDefault)(type,
index, start, buf, buflen);
}
break;
}
case CT_FIXEDARRAY:
{
const struct ng_parse_fixedarray_info *const fi = type->info;
if (*fi->getDefault != NULL) {
return (*fi->getDefault)(type,
index, start, buf, buflen);
}
break;
}
default:
panic("%s", __FUNCTION__);
}
/* Default to element type default */
etype = ng_get_composite_etype(type, index, ctype);
func = METHOD(etype, getDefault);
if (func == NULL)
return (EOPNOTSUPP);
return (*func)(etype, start, buf, buflen);
}
/*
* Get the number of elements in a struct, variable or fixed array.
*/
static int
ng_get_composite_len(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *const start, const u_char *buf,
const enum comptype ctype)
{
switch (ctype) {
case CT_STRUCT:
{
const struct ng_parse_struct_info *const si = type->info;
int numFields = 0;
for (numFields = 0; ; numFields++) {
const struct ng_parse_struct_field *const
fi = &si->fields[numFields];
if (fi->name == NULL)
break;
}
return (numFields);
}
case CT_ARRAY:
{
const struct ng_parse_array_info *const ai = type->info;
return (*ai->getLength)(type, start, buf);
}
case CT_FIXEDARRAY:
{
const struct ng_parse_fixedarray_info *const fi = type->info;
return fi->length;
}
default:
panic("%s", __FUNCTION__);
}
return (0);
}
/*
* Return the type of the index'th element of a composite structure
*/
static const struct ng_parse_type *
ng_get_composite_etype(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
int index, const enum comptype ctype)
{
const struct ng_parse_type *etype = NULL;
switch (ctype) {
case CT_STRUCT:
{
const struct ng_parse_struct_info *const si = type->info;
etype = si->fields[index].type;
break;
}
case CT_ARRAY:
{
const struct ng_parse_array_info *const ai = type->info;
etype = ai->elementType;
break;
}
case CT_FIXEDARRAY:
{
const struct ng_parse_fixedarray_info *const fi = type->info;
etype = fi->elementType;
break;
}
default:
panic("%s", __FUNCTION__);
}
return (etype);
}
/*
* Get the number of bytes to skip to align for the next
* element in a composite structure.
*/
static int
ng_parse_get_elem_pad(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
int index, enum comptype ctype, int posn)
{
const struct ng_parse_type *const
etype = ng_get_composite_etype(type, index, ctype);
int align;
/* Get element's alignment, and possibly override */
align = ALIGNMENT(etype);
if (ctype == CT_STRUCT) {
const struct ng_parse_struct_info *si = type->info;
if (si->fields[index].alignment != 0)
align = si->fields[index].alignment;
}
/* Return number of bytes to skip to align */
return (align ? (align - (posn % align)) % align : 0);
}
/************************************************************************
PARSING HELPER ROUTINES
************************************************************************/
/*
* Skip over a value
*/
static int
ng_parse_skip_value(const char *s, int off0, int *lenp)
{
int len, nbracket, nbrace;
int off = off0;
len = nbracket = nbrace = 0;
do {
switch (ng_parse_get_token(s, &off, &len)) {
case T_LBRACKET:
nbracket++;
break;
case T_LBRACE:
nbrace++;
break;
case T_RBRACKET:
if (nbracket-- == 0)
return (EINVAL);
break;
case T_RBRACE:
if (nbrace-- == 0)
return (EINVAL);
break;
case T_EOF:
return (EINVAL);
default:
break;
}
off += len;
} while (nbracket > 0 || nbrace > 0);
*lenp = off - off0;
return (0);
}
/*
* Find the next token in the string, starting at offset *startp.
* Returns the token type, with *startp pointing to the first char
* and *lenp the length.
*/
enum ng_parse_token
ng_parse_get_token(const char *s, int *startp, int *lenp)
{
char *t;
int i;
while (isspace(s[*startp]))
(*startp)++;
switch (s[*startp]) {
case '\0':
*lenp = 0;
return T_EOF;
case '{':
*lenp = 1;
return T_LBRACE;
case '}':
*lenp = 1;
return T_RBRACE;
case '[':
*lenp = 1;
return T_LBRACKET;
case ']':
*lenp = 1;
return T_RBRACKET;
case '=':
*lenp = 1;
return T_EQUALS;
case '"':
if ((t = ng_get_string_token(s, startp, lenp)) == NULL)
return T_ERROR;
FREE(t, M_NETGRAPH);
return T_STRING;
default:
for (i = *startp + 1; s[i] != '\0' && !isspace(s[i])
&& s[i] != '{' && s[i] != '}' && s[i] != '['
&& s[i] != ']' && s[i] != '=' && s[i] != '"'; i++)
;
*lenp = i - *startp;
return T_WORD;
}
}
/*
* Get a string token, which must be enclosed in double quotes.
* The normal C backslash escapes are recognized.
*/
char *
ng_get_string_token(const char *s, int *startp, int *lenp)
{
char *cbuf, *p;
int start, off;
while (isspace(s[*startp]))
(*startp)++;
start = *startp;
if (s[*startp] != '"')
return (NULL);
MALLOC(cbuf, char *, strlen(s + start), M_NETGRAPH, M_NOWAIT);
if (cbuf == NULL)
return (NULL);
strcpy(cbuf, s + start + 1);
for (off = 1, p = cbuf; *p != '\0'; off++, p++) {
if (*p == '"') {
*p = '\0';
*lenp = off + 1;
return (cbuf);
} else if (p[0] == '\\' && p[1] != '\0') {
int x, k;
char *v;
strcpy(p, p + 1);
v = p;
switch (*p) {
case 't':
*v = '\t';
off++;
continue;
case 'n':
*v = '\n';
off++;
continue;
case 'r':
*v = '\r';
off++;
continue;
case 'v':
*v = '\v';
off++;
continue;
case 'f':
*v = '\f';
off++;
continue;
case '"':
*v = '"';
off++;
continue;
case '0': case '1': case '2': case '3':
case '4': case '5': case '6': case '7':
for (x = k = 0;
k < 3 && *v >= '0' && *v <= '7'; v++) {
x = (x << 3) + (*v - '0');
off++;
}
*--v = (char)x;
break;
case 'x':
for (v++, x = k = 0;
k < 2 && isxdigit(*v); v++) {
x = (x << 4) + (isdigit(*v) ?
(*v - '0') :
(tolower(*v) - 'a' + 10));
off++;
}
*--v = (char)x;
break;
default:
continue;
}
strcpy(p, v);
}
}
return (NULL); /* no closing quote */
}
/*
* Encode a string so it can be safely put in double quotes.
* Caller must free the result.
*/
char *
ng_encode_string(const char *raw)
{
char *cbuf;
int off = 0;
MALLOC(cbuf, char *, strlen(raw) * 4 + 3, M_NETGRAPH, M_NOWAIT);
if (cbuf == NULL)
return (NULL);
cbuf[off++] = '"';
for ( ; *raw != '\0'; raw++) {
switch (*raw) {
case '\t':
cbuf[off++] = '\\';
cbuf[off++] = 't';
break;
case '\f':
cbuf[off++] = '\\';
cbuf[off++] = 'f';
break;
case '\n':
cbuf[off++] = '\\';
cbuf[off++] = 'n';
break;
case '\r':
cbuf[off++] = '\\';
cbuf[off++] = 'r';
break;
case '\v':
cbuf[off++] = '\\';
cbuf[off++] = 'v';
break;
case '"':
case '\\':
cbuf[off++] = '\\';
cbuf[off++] = *raw;
break;
default:
if (*raw < 0x20 || *raw > 0x7e) {
off += sprintf(cbuf + off,
"\\x%02x", (u_char)*raw);
break;
}
cbuf[off++] = *raw;
break;
}
}
cbuf[off++] = '"';
cbuf[off] = '\0';
return (cbuf);
}
/************************************************************************
VIRTUAL METHOD LOOKUP
************************************************************************/
static ng_parse_t *
ng_get_parse_method(const struct ng_parse_type *t)
{
while (t != NULL && t->parse == NULL)
t = t->supertype;
return (t ? t->parse : NULL);
}
static ng_unparse_t *
ng_get_unparse_method(const struct ng_parse_type *t)
{
while (t != NULL && t->unparse == NULL)
t = t->supertype;
return (t ? t->unparse : NULL);
}
static ng_getDefault_t *
ng_get_getDefault_method(const struct ng_parse_type *t)
{
while (t != NULL && t->getDefault == NULL)
t = t->supertype;
return (t ? t->getDefault : NULL);
}
static ng_getAlign_t *
ng_get_getAlign_method(const struct ng_parse_type *t)
{
while (t != NULL && t->getAlign == NULL)
t = t->supertype;
return (t ? t->getAlign : NULL);
}
/*
* ng_parse.h
*
* Copyright (c) 1999 Whistle Communications, Inc.
* All rights reserved.
*
* Subject to the following obligations and disclaimer of warranty, use and
* redistribution of this software, in source or object code forms, with or
* without modifications are expressly permitted by Whistle Communications;
* provided, however, that:
* 1. Any and all reproductions of the source or object code must include the
* copyright notice above and the following disclaimer of warranties; and
* 2. No rights are granted, in any manner or form, to use Whistle
* Communications, Inc. trademarks, including the mark "WHISTLE
* COMMUNICATIONS" on advertising, endorsements, or otherwise except as
* such appears in the above copyright notice or in the software.
*
* THIS SOFTWARE IS BEING PROVIDED BY WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS "AS IS", AND
* TO THE MAXIMUM EXTENT PERMITTED BY LAW, WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS MAKES NO
* REPRESENTATIONS OR WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, REGARDING THIS SOFTWARE,
* INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY AND ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
* MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR NON-INFRINGEMENT.
* WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS DOES NOT WARRANT, GUARANTEE, OR MAKE ANY
* REPRESENTATIONS REGARDING THE USE OF, OR THE RESULTS OF THE USE OF THIS
* SOFTWARE IN TERMS OF ITS CORRECTNESS, ACCURACY, RELIABILITY OR OTHERWISE.
* IN NO EVENT SHALL WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DAMAGES
* RESULTING FROM OR ARISING OUT OF ANY USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, INCLUDING
* WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY,
* PUNITIVE, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR
* SERVICES, LOSS OF USE, DATA OR PROFITS, HOWEVER CAUSED AND UNDER ANY
* THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
* (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF
* THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS IS ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY
* OF SUCH DAMAGE.
*
* Author: Archie Cobbs <archie@whistle.com>
*
* $Whistle: ng_parse.h,v 1.2 1999/11/29 01:43:48 archie Exp $
* $FreeBSD: src/sys/netgraph/ng_parse.h,v 1.2 1999/12/01 19:41:15 archie Exp $
*/
#ifndef _NETGRAPH_PARSE_H_
#define _NETGRAPH_PARSE_H_
/*
This defines a library of routines for converting between various C
language types in binary form and ASCII strings. Types are user
definable. Several pre-defined types are supplied, for some common
C types: structures, variable and fixed length arrays, integer types,
variable and fixed length strings, IP addresses, etc.
A netgraph node type may provide a list of types that correspond to
the structures it expects to send and receive in the arguments field
of a control message. This allows these messages to be converted
between their native binary form and the corresponding ASCII form.
A future use of the ASCII form may be for inter-machine communication
of control messages, because the ASCII form is machine independent
whereas the native binary form is not.
Syntax
------
Structures:
'{' [ <name>=<value> ... ] '}'
Omitted fields have their default values by implication.
The order in which the fields are specified does not matter.
Arrays:
'[' [ [index=]<value> ... ] ']'
Element value may be specified with or without the "<index>=" prefix;
If omitted, the index after the previous element is used.
Omitted fields have their default values by implication.
Strings:
"foo bar blah\r\n"
That is, strings are specified just like C strings. The usual
backslash escapes are accepted.
Other simple types (integers, IP addresses) have their obvious forms.
Example
-------
Suppose we have a netgraph command that takes as an argument
a 'struct foo' shown below. Here is an example of a possible
value for the structure, and the corresponding ASCII encoding
of that value:
Structure Binary value
--------- ------------
struct foo {
struct in_addr ip; 01 02 03 04
int bar; 00 00 00 00
char label[8]; 61 62 63 0a 00 00 00 00
u_char alen; 03 00
short ary[0]; 05 00 00 00 0a 00
};
ASCII value
-----------
{ ip=1.2.3.4 label="abc\n" alen=3 ary=[ 5 2=10 ] }
Note that omitted fields and array elements get their default
values ("bar" and ary[2]), and that the alignment is handled
automatically (the extra 00 byte after "num"). Also, since byte
order and alignment are inherently machine dependent, so is this
conversion process. The above example shows an x86 (little
endian) encoding. Also the above example is tricky because the
structure is variable length, depending on 'alen', the number of
elements in the array 'ary'.
Here is how one would define a parse type for the above structure,
subclassing the pre-defined types below. We construct the type in
a 'bottom up' fashion, defining each field's type first, then the
type for the whole structure ('//' comments used to avoid breakage).
// Super-type info for 'label' field
struct ng_parse_fixedsstring_info foo_label_info = { 8 };
// Parse type for 'label' field
struct ng_parse_type foo_label_type = {
&ng_parse_fixedstring_type // super-type
&foo_label_info // super-type info
};
#define OFFSETOF(s, e) ((char *)&((s *)0)->e - (char *)((s *)0))
// Function to compute the length of the array 'ary', which
// is variable length, depending on the previous field 'alen'.
// Upon entry 'buf' will be pointing at &ary[0].
int
foo_ary_getLength(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *start, const u_char *buf)
{
const struct foo *f;
f = (const struct foo *)(buf - OFFSETOF(struct foo, ary));
return f->alen;
}
// Super-type info for 'ary' field
struct ng_parse_array_info foo_ary_info = {
&ng_parse_int16_type, // element type
&foo_ary_getLength // func to get array length
}
// Parse type for 'ary' field
struct ng_parse_type foo_ary_type = {
&ng_parse_array_type, // super-type
&foo_ary_info // super-type info
};
// Super-type info for struct foo
struct ng_parse_struct_info foo_fields = {
{ "ip", &ng_parse_ipaddr_type },
{ "bar", &ng_parse_int32_type },
{ "label", &foo_label_type },
{ "alen", &ng_parse_int8_type },
{ "ary", &foo_ary_type },
{ NULL }
};
// Parse type for struct foo
struct ng_parse_type foo_type = {
&ng_parse_struct_type, // super-type
&foo_fields // super-type info
};
To define a type, you can define it as a sub-type of a predefined
type as shown above, possibly overriding some of the predefined
type's methods, or define an entirely new syntax, with the restriction
that the ASCII representation of your type's value must not contain
any whitespace or any of these characters: { } [ ] = "
See ng_ksocket.c for an example of how to do this for 'struct sockaddr'.
See ng_parse.c to see implementations of the pre-defined types below.
*/
/************************************************************************
METHODS REQUIRED BY A TYPE
************************************************************************/
/*
* Three methods are required for a type. These may be given explicitly
* or, if NULL, inherited from the super-type. The 'getDefault' method
* is always optional; the others are required if there is no super-type.
*/
struct ng_parse_type;
/*
* Convert ASCII to binary according to the supplied type.
*
* The ASCII characters begin at offset *off in 'string'. The binary
* representation is put into 'buf', which has at least *buflen bytes.
* 'start' points to the first byte output by ng_parse() (ie, start <= buf).
*
* Upon return, *buflen contains the length of the new binary data, and
* *off is updated to point just past the end of the parsed range of
* characters, or, in the case of an error, to the offending character(s).
*
* Return values:
* 0 Success; *buflen holds the length of the data
* and *off points just past the last char parsed.
* EALREADY Field specified twice
* ENOENT Unknown field
* E2BIG Array or character string overflow
* ERANGE Output was longer than *buflen bytes
* EINVAL Parse failure or other invalid content
* ENOMEM Out of memory
* EOPNOTSUPP Mandatory array/structure element missing
*/
typedef int ng_parse_t(const struct ng_parse_type *type, const char *string,
int *off, const u_char *start,
u_char *buf, int *buflen);
/*
* Convert binary to ASCII according to the supplied type.
*
* The results are put into 'buf', which is at least buflen bytes long.
* *off points to the current byte in 'data' and should be updated
* before return to point just past the last byte unparsed.
*
* Returns:
* 0 Success
* ERANGE Output was longer than buflen bytes
*/
typedef int ng_unparse_t(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *data, int *off, char *buf, int buflen);
/*
* Compute the default value according to the supplied type.
*
* Store the result in 'buf', which is at least *buflen bytes long.
* Upon return *buflen contains the length of the output.
*
* Returns:
* 0 Success
* ERANGE Output was longer than *buflen bytes
* EOPNOTSUPP Default value is not specified for this type
*/
typedef int ng_getDefault_t(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *start, u_char *buf, int *buflen);
/*
* Return the alignment requirement of this type. Zero is same as one.
*/
typedef int ng_getAlign_t(const struct ng_parse_type *type);
/************************************************************************
TYPE DEFINITION
************************************************************************/
/*
* This structure describes a type, which may be a sub-type of another
* type by pointing to it with 'supertype' and possibly omitting methods.
* Typically the super-type requires some type-specific info, which is
* supplied by the 'info' field.
*
* The 'private' field is ignored by all of the pre-defined types.
* Sub-types may use it as they see fit.
*
* The 'getDefault' method may always be omitted (even if there is no
* super-type), which means the value for any item of this type must
* always be explicitly given.
*/
struct ng_parse_type {
const struct ng_parse_type *supertype; /* super-type, if any */
const void *info; /* type-specific info */
void *private; /* client private info */
ng_parse_t *parse; /* parse method */
ng_unparse_t *unparse; /* unparse method */
ng_getDefault_t *getDefault; /* get default value method */
ng_getAlign_t *getAlign; /* get alignment */
};
/************************************************************************
PRE-DEFINED TYPES
************************************************************************/
/*
* STRUCTURE TYPE
*
* This type supports arbitrary C structures. The normal field alignment
* rules for the local machine are applied. Fields are always parsed in
* field order, no matter what order they are listed in the ASCII string.
*
* Default value: Determined on a per-field basis
* Additional info: struct ng_parse_struct_info *
*/
extern const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_struct_type;
/* Each field has a name, type, and optional alignment override. If the
override is non-zero, the alignment is determined from the field type.
Note: add an extra struct ng_parse_struct_field with name == NULL
to indicate the end of the list. */
struct ng_parse_struct_info {
struct ng_parse_struct_field {
const char *name; /* field name */
const struct ng_parse_type
*type; /* field type */
int alignment; /* override alignment */
} fields[0];
};
/*
* FIXED LENGTH ARRAY TYPE
*
* This type supports fixed length arrays, having any element type.
*
* Default value: As returned by getDefault for each index
* Additional info: struct ng_parse_fixedarray_info *
*/
extern const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_fixedarray_type;
/*
* Get the default value for the element at index 'index'. This method
* may be NULL, in which case the default value is computed from the
* element type. Otherwise, it should fill in the default value at *buf
* (having size *buflen) and update *buflen to the length of the filled-in
* value before return. If there is not enough routine return ERANGE.
*/
typedef int ng_parse_array_getDefault_t(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
int index, const u_char *start,
u_char *buf, int *buflen);
struct ng_parse_fixedarray_info {
const struct ng_parse_type *elementType;
int length;
ng_parse_array_getDefault_t *getDefault;
};
/*
* VARIABLE LENGTH ARRAY TYPE
*
* Same as fixed length arrays, except that the length is determined
* by a function instead of a constant value.
*
* Default value: Same as with fixed length arrays
* Additional info: struct ng_parse_array_info *
*/
extern const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_array_type;
/*
* Return the length of the array. If the array is a field in a structure,
* all prior fields are guaranteed to be filled in already. Upon entry,
* 'start' is equal to the first byte parsed in this run, while 'buf' points
* to the first element of the array to be filled in.
*/
typedef int ng_parse_array_getLength_t(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *start, const u_char *buf);
struct ng_parse_array_info {
const struct ng_parse_type *elementType;
ng_parse_array_getLength_t *getLength;
ng_parse_array_getDefault_t *getDefault;
};
/*
* ARBITRARY LENGTH STRING TYPE
*
* For arbirary length, NUL-terminated strings.
*
* Default value: Empty string
* Additional info: None required
*/
extern const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_string_type;
/*
* BOUNDED LENGTH STRING TYPE
*
* These are strings that have a fixed-size buffer, and always include
* a terminating NUL character.
*
* Default value: Empty string
* Additional info: struct ng_parse_fixedsstring_info *
*/
extern const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_fixedstring_type;
struct ng_parse_fixedsstring_info {
int bufSize; /* size of buffer (including NUL) */
};
/*
* COMMONLY USED BOUNDED LENGTH STRING TYPES
*/
extern const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_nodebuf_type; /* NG_NODELEN + 1 */
extern const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_hookbuf_type; /* NG_HOOKLEN + 1 */
extern const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_pathbuf_type; /* NG_PATHLEN + 1 */
extern const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_typebuf_type; /* NG_TYPELEN + 1 */
extern const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_cmdbuf_type; /* NG_CMDSTRLEN + 1 */
/*
* INTEGER TYPES
*
* Default value: 0
* Additional info: None required
*/
extern const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_int8_type;
extern const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_int16_type;
extern const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_int32_type;
extern const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_int64_type;
/*
* IP ADDRESS TYPE
*
* Default value: 0.0.0.0
* Additional info: None required
*/
extern const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_ipaddr_type;
/*
* VARIABLE LENGTH BYTE ARRAY TYPE
*
* The bytes are displayed in hex. The ASCII form may be either an
* array of bytes or a string constant, in which case the array is
* zero-filled after the string bytes.
*
* Default value: All bytes are zero
* Additional info: ng_parse_array_getLength_t *
*/
extern const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_bytearray_type;
/*
* NETGRAPH CONTROL MESSAGE TYPE
*
* This is the parse type for a struct ng_mesg.
*
* Default value: All fields zero
* Additional info: None required
*/
extern const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_ng_mesg_type;
/************************************************************************
CONVERSTION AND PARSING ROUTINES
************************************************************************/
/* Tokens for parsing structs and arrays */
enum ng_parse_token {
T_LBRACE, /* '{' */
T_RBRACE, /* '}' */
T_LBRACKET, /* '[' */
T_RBRACKET, /* ']' */
T_EQUALS, /* '=' */
T_STRING, /* string in double quotes */
T_ERROR, /* error parsing string in double quotes */
T_WORD, /* anything else containing no whitespace */
T_EOF, /* end of string reached */
};
/*
* See typedef ng_parse_t for definition
*/
extern int ng_parse(const struct ng_parse_type *type, const char *string,
int *off, u_char *buf, int *buflen);
/*
* See typedef ng_unparse_t for definition (*off assumed to be zero).
*/
extern int ng_unparse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *data, char *buf, int buflen);
/*
* See typedef ng_getDefault_t for definition
*/
extern int ng_parse_getDefault(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
u_char *buf, int *buflen);
/*
* Parse a token: '*startp' is the offset to start looking. Upon
* successful return, '*startp' equals the beginning of the token
* and '*lenp' the length. If error, '*startp' points at the
* offending character(s).
*/
extern enum ng_parse_token ng_parse_get_token(const char *s,
int *startp, int *lenp);
/*
* Like above, but specifically for getting a string token and returning
* the string value. The string token must be enclosed in double quotes
* and the normal C backslash escapes are recognized. The caller must
* eventually free() the returned result. Returns NULL if token is
* not a string token, or parse or other error.
*/
extern char *ng_get_string_token(const char *s, int *startp, int *lenp);
/*
* Convert a raw string into a doubly-quoted string including any
* necessary backslash escapes. Caller must free the result.
* Returns NULL if ENOMEM.
*/
extern char *ng_encode_string(const char *s);
#endif /* _NETGRAPH_PARSE_H_ */
/*
* ng_tee.c
*
* Copyright (c) 1996-1999 Whistle Communications, Inc.
* All rights reserved.
*
* Subject to the following obligations and disclaimer of warranty, use and
* redistribution of this software, in source or object code forms, with or
* without modifications are expressly permitted by Whistle Communications;
* provided, however, that:
* 1. Any and all reproductions of the source or object code must include the
* copyright notice above and the following disclaimer of warranties; and
* 2. No rights are granted, in any manner or form, to use Whistle
* Communications, Inc. trademarks, including the mark "WHISTLE
* COMMUNICATIONS" on advertising, endorsements, or otherwise except as
* such appears in the above copyright notice or in the software.
*
* THIS SOFTWARE IS BEING PROVIDED BY WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS "AS IS", AND
* TO THE MAXIMUM EXTENT PERMITTED BY LAW, WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS MAKES NO
* REPRESENTATIONS OR WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, REGARDING THIS SOFTWARE,
* INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY AND ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
* MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR NON-INFRINGEMENT.
* WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS DOES NOT WARRANT, GUARANTEE, OR MAKE ANY
* REPRESENTATIONS REGARDING THE USE OF, OR THE RESULTS OF THE USE OF THIS
* SOFTWARE IN TERMS OF ITS CORRECTNESS, ACCURACY, RELIABILITY OR OTHERWISE.
* IN NO EVENT SHALL WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DAMAGES
* RESULTING FROM OR ARISING OUT OF ANY USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, INCLUDING
* WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY,
* PUNITIVE, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR
* SERVICES, LOSS OF USE, DATA OR PROFITS, HOWEVER CAUSED AND UNDER ANY
* THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
* (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF
* THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS IS ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY
* OF SUCH DAMAGE.
*
* Author: Julian Elischer <julian@whistle.com>
*
* $FreeBSD: src/sys/netgraph/ng_tee.c,v 1.7 2000/01/27 01:32:53 archie Exp $
* $Whistle: ng_tee.c,v 1.18 1999/11/01 09:24:52 julian Exp $
*/
/*
* This node is like the tee(1) command and is useful for ``snooping.''
* It has 4 hooks: left, right, left2right, and right2left. Data
* entering from the right is passed to the left and duplicated on
* right2left, and data entering from the left is passed to the right
* and duplicated on left2right. Data entering from left2right is
* sent to right, and data from right2left to left.
*/
#include <sys/param.h>
#include <sys/systm.h>
#include <sys/errno.h>
#include <sys/kernel.h>
#include <sys/malloc.h>
#include <sys/mbuf.h>
#include <netgraph/ng_message.h>
#include <netgraph/netgraph.h>
#include <netgraph/ng_parse.h>
#include <netgraph/ng_tee.h>
/* Per hook info */
struct hookinfo {
hook_p hook;
struct ng_tee_hookstat stats;
};
/* Per node info */
struct privdata {
node_p node;
struct hookinfo left;
struct hookinfo right;
struct hookinfo left2right;
struct hookinfo right2left;
};
typedef struct privdata *sc_p;
/* Netgraph methods */
static ng_constructor_t ngt_constructor;
static ng_rcvmsg_t ngt_rcvmsg;
static ng_shutdown_t ngt_rmnode;
static ng_newhook_t ngt_newhook;
static ng_rcvdata_t ngt_rcvdata;
static ng_disconnect_t ngt_disconnect;
/* Parse type for struct ng_tee_hookstat */
static const struct ng_parse_struct_info
ng_tee_hookstat_type_info = NG_TEE_HOOKSTAT_INFO;
static const struct ng_parse_type ng_tee_hookstat_type = {
&ng_parse_struct_type,
&ng_tee_hookstat_type_info,
};
/* Parse type for struct ng_tee_stats */
static const struct ng_parse_struct_info
ng_tee_stats_type_info = NG_TEE_STATS_INFO(&ng_tee_hookstat_type);
static const struct ng_parse_type ng_tee_stats_type = {
&ng_parse_struct_type,
&ng_tee_stats_type_info,
};
/* List of commands and how to convert arguments to/from ASCII */
static const struct ng_cmdlist ng_tee_cmds[] = {
{
NGM_TEE_COOKIE,
NGM_TEE_GET_STATS,
"getstats",
NULL,
&ng_tee_stats_type
},
{
NGM_TEE_COOKIE,
NGM_TEE_CLR_STATS,
"clrstats",
NULL,
NULL
},
{ 0 }
};
/* Netgraph type descriptor */
static struct ng_type ng_tee_typestruct = {
NG_VERSION,
NG_TEE_NODE_TYPE,
NULL,
ngt_constructor,
ngt_rcvmsg,
ngt_rmnode,
ngt_newhook,
NULL,
NULL,
ngt_rcvdata,
ngt_rcvdata,
ngt_disconnect,
ng_tee_cmds
};
NETGRAPH_INIT(tee, &ng_tee_typestruct);
/*
* Node constructor
*/
static int
ngt_constructor(node_p *nodep)
{
sc_p privdata;
int error = 0;
MALLOC(privdata, sc_p, sizeof(*privdata), M_NETGRAPH, M_WAITOK);
if (privdata == NULL)
return (ENOMEM);
bzero(privdata, sizeof(*privdata));
if ((error = ng_make_node_common(&ng_tee_typestruct, nodep))) {
FREE(privdata, M_NETGRAPH);
return (error);
}
(*nodep)->private = privdata;
privdata->node = *nodep;
return (0);
}
/*
* Add a hook
*/
static int
ngt_newhook(node_p node, hook_p hook, const char *name)
{
const sc_p sc = node->private;
if (strcmp(name, NG_TEE_HOOK_RIGHT) == 0) {
sc->right.hook = hook;
bzero(&sc->right.stats, sizeof(sc->right.stats));
hook->private = &sc->right;
} else if (strcmp(name, NG_TEE_HOOK_LEFT) == 0) {
sc->left.hook = hook;
bzero(&sc->left.stats, sizeof(sc->left.stats));
hook->private = &sc->left;
} else if (strcmp(name, NG_TEE_HOOK_RIGHT2LEFT) == 0) {
sc->right2left.hook = hook;
bzero(&sc->right2left.stats, sizeof(sc->right2left.stats));
hook->private = &sc->right2left;
} else if (strcmp(name, NG_TEE_HOOK_LEFT2RIGHT) == 0) {
sc->left2right.hook = hook;
bzero(&sc->left2right.stats, sizeof(sc->left2right.stats));
hook->private = &sc->left2right;
} else
return (EINVAL);
return (0);
}
/*
* Receive a control message
*/
static int
ngt_rcvmsg(node_p node, struct ng_mesg *msg, const char *retaddr,
struct ng_mesg **rptr)
{
const sc_p sc = node->private;
struct ng_mesg *resp = NULL;
int error = 0;
switch (msg->header.typecookie) {
case NGM_TEE_COOKIE:
switch (msg->header.cmd) {
case NGM_TEE_GET_STATS:
{
struct ng_tee_stats *stats;
NG_MKRESPONSE(resp, msg,
sizeof(struct ng_tee_stats), M_NOWAIT);
if (resp == NULL) {
error = ENOMEM;
goto done;
}
stats = (struct ng_tee_stats *) resp->data;
bcopy(&sc->right.stats,
&stats->right, sizeof(stats->right));
bcopy(&sc->left.stats,
&stats->left, sizeof(stats->left));
bcopy(&sc->right2left.stats,
&stats->right2left, sizeof(stats->right2left));
bcopy(&sc->left2right.stats,
&stats->left2right, sizeof(stats->left2right));
break;
}
case NGM_TEE_CLR_STATS:
bzero(&sc->right.stats, sizeof(sc->right.stats));
bzero(&sc->left.stats, sizeof(sc->left.stats));
bzero(&sc->right2left.stats,
sizeof(sc->right2left.stats));
bzero(&sc->left2right.stats,
sizeof(sc->left2right.stats));
break;
default:
error = EINVAL;
break;
}
break;
default:
error = EINVAL;
break;
}
if (rptr)
*rptr = resp;
else if (resp)
FREE(resp, M_NETGRAPH);
done:
FREE(msg, M_NETGRAPH);
return (error);
}
/*
* Receive data on a hook
*
* If data comes in the right link send a copy out right2left, and then
* send the original onwards out through the left link.
* Do the opposite for data coming in from the left link.
* Data coming in right2left or left2right is forwarded
* on through the appropriate destination hook as if it had come
* from the other side.
*/
static int
ngt_rcvdata(hook_p hook, struct mbuf *m, meta_p meta)
{
const sc_p sc = hook->node->private;
struct hookinfo *const hinfo = (struct hookinfo *) hook->private;
struct hookinfo *dest;
struct hookinfo *dup;
int error = 0;
/* Which hook? */
if (hinfo == &sc->left) {
dup = &sc->left2right;
dest = &sc->right;
} else if (hinfo == &sc->right) {
dup = &sc->right2left;
dest = &sc->left;
} else if (hinfo == &sc->right2left) {
dup = NULL;
dest = &sc->left;
} else if (hinfo == &sc->left2right) {
dup = NULL;
dest = &sc->right;
} else
panic("%s: no hook!", __FUNCTION__);
/* Update stats on incoming hook */
hinfo->stats.inOctets += m->m_pkthdr.len;
hinfo->stats.inFrames++;
/* Duplicate packet and meta info if requried */
if (dup != NULL) {
struct mbuf *m2;
meta_p meta2;
/* Copy packet */
m2 = m_dup(m, M_NOWAIT);
if (m2 == NULL) {
NG_FREE_DATA(m, meta);
return (ENOBUFS);
}
/* Copy meta info */
if (meta != NULL) {
MALLOC(meta2, meta_p,
meta->used_len, M_NETGRAPH, M_NOWAIT);
if (meta2 == NULL) {
m_freem(m2);
NG_FREE_DATA(m, meta);
return (ENOMEM);
}
bcopy(meta, meta2, meta->used_len);
meta2->allocated_len = meta->used_len;
} else
meta2 = NULL;
/* Deliver duplicate */
dup->stats.outOctets += m->m_pkthdr.len;
dup->stats.outFrames++;
NG_SEND_DATA(error, dup->hook, m2, meta2);
}
/* Deliver frame out destination hook */
dest->stats.outOctets += m->m_pkthdr.len;
dest->stats.outFrames++;
NG_SEND_DATA(error, dest->hook, m, meta);
return (0);
}
/*
* Shutdown processing
*
* This is tricky. If we have both a left and right hook, then we
* probably want to extricate ourselves and leave the two peers
* still linked to each other. Otherwise we should just shut down as
* a normal node would.
*
* To keep the scope of info correct the routine to "extract" a node
* from two links is in ng_base.c.
*/
static int
ngt_rmnode(node_p node)
{
const sc_p privdata = node->private;
node->flags |= NG_INVALID;
if (privdata->left.hook && privdata->right.hook)
ng_bypass(privdata->left.hook, privdata->right.hook);
ng_cutlinks(node);
ng_unname(node);
node->private = NULL;
ng_unref(privdata->node);
FREE(privdata, M_NETGRAPH);
return (0);
}
/*
* Hook disconnection
*/
static int
ngt_disconnect(hook_p hook)
{
struct hookinfo *const hinfo = (struct hookinfo *) hook->private;
KASSERT(hinfo != NULL, ("%s: null info", __FUNCTION__));
hinfo->hook = NULL;
if (hook->node->numhooks == 0)
ng_rmnode(hook->node);
return (0);
}
/*
* ng_tee.h
*
* Copyright (c) 1996-1999 Whistle Communications, Inc.
* All rights reserved.
*
* Subject to the following obligations and disclaimer of warranty, use and
* redistribution of this software, in source or object code forms, with or
* without modifications are expressly permitted by Whistle Communications;
* provided, however, that:
* 1. Any and all reproductions of the source or object code must include the
* copyright notice above and the following disclaimer of warranties; and
* 2. No rights are granted, in any manner or form, to use Whistle
* Communications, Inc. trademarks, including the mark "WHISTLE
* COMMUNICATIONS" on advertising, endorsements, or otherwise except as
* such appears in the above copyright notice or in the software.
*
* THIS SOFTWARE IS BEING PROVIDED BY WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS "AS IS", AND
* TO THE MAXIMUM EXTENT PERMITTED BY LAW, WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS MAKES NO
* REPRESENTATIONS OR WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, REGARDING THIS SOFTWARE,
* INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY AND ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
* MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR NON-INFRINGEMENT.
* WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS DOES NOT WARRANT, GUARANTEE, OR MAKE ANY
* REPRESENTATIONS REGARDING THE USE OF, OR THE RESULTS OF THE USE OF THIS
* SOFTWARE IN TERMS OF ITS CORRECTNESS, ACCURACY, RELIABILITY OR OTHERWISE.
* IN NO EVENT SHALL WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DAMAGES
* RESULTING FROM OR ARISING OUT OF ANY USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, INCLUDING
* WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY,
* PUNITIVE, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR
* SERVICES, LOSS OF USE, DATA OR PROFITS, HOWEVER CAUSED AND UNDER ANY
* THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
* (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF
* THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS IS ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY
* OF SUCH DAMAGE.
*
* Author: Archie Cobbs <archie@whistle.com>
*
* $FreeBSD: src/sys/netgraph/ng_tee.h,v 1.3 2000/01/27 01:32:53 archie Exp $
* $Whistle: ng_tee.h,v 1.2 1999/01/20 00:22:14 archie Exp $
*/
#ifndef _NETGRAPH_TEE_H_
#define _NETGRAPH_TEE_H_
/* Node type name and magic cookie */
#define NG_TEE_NODE_TYPE "tee"
#define NGM_TEE_COOKIE 916107047
/* Hook names */
#define NG_TEE_HOOK_RIGHT "right"
#define NG_TEE_HOOK_LEFT "left"
#define NG_TEE_HOOK_RIGHT2LEFT "right2left"
#define NG_TEE_HOOK_LEFT2RIGHT "left2right"
/* Statistics structure for one hook */
struct ng_tee_hookstat {
u_int64_t inOctets;
u_int64_t inFrames;
u_int64_t outOctets;
u_int64_t outFrames;
};
/* Keep this in sync with the above structure definition */
#define NG_TEE_HOOKSTAT_INFO { \
{ \
{ "inOctets", &ng_parse_int64_type }, \
{ "inFrames", &ng_parse_int64_type }, \
{ "outOctets", &ng_parse_int64_type }, \
{ "outFrames", &ng_parse_int64_type }, \
{ NULL }, \
} \
}
/* Statistics structure returned by NGM_TEE_GET_STATS */
struct ng_tee_stats {
struct ng_tee_hookstat right;
struct ng_tee_hookstat left;
struct ng_tee_hookstat right2left;
struct ng_tee_hookstat left2right;
};
/* Keep this in sync with the above structure definition */
#define NG_TEE_STATS_INFO(hstype) { \
{ \
{ "right", (hstype) }, \
{ "left", (hstype) }, \
{ "right2left", (hstype) }, \
{ "left2right", (hstype) }, \
{ NULL }, \
} \
}
/* Netgraph commands */
enum {
NGM_TEE_GET_STATS = 1, /* get stats */
NGM_TEE_CLR_STATS, /* clear stats */
};
#endif /* _NETGRAPH_TEE_H_ */
Представьте следующую ситуацию: вы разрабатываете маршрутизатор TCP/IP основанный на FreeBSD. Продукт должен поддерживать синхронные последовательные WAN-линии, то есть выделенные цифровые каналы, работающие на скоростях до T1, где используется инкапсуляция HDLC. Вы должны поддерживать следующие протоколы для передачи IP пакетов через кабель:
На Рисунке 1 показаны все возможные комбинации:

Рисунок 1: Способы передачи IP поверх последовательных синхронных и ISDN WAN соединений
Эта ситуация была показана Джулианом Элисчером (Julian Elischer) <julian@freebsd.org> и мной в 1996 когда мы работали в компании Whistle InterJet. В то время во FreeBSD имелась очень ограниченная поддержка последовательного синхронного оборудования и протоколов. Мы думали использовать OEMing от Emerging Technologies, но вместо этого решили реализовать это сами.
Ответом был netgraph. Netgraph это сетевая подсистема в ядре, следующая принципу UNIX достижения мощности посредством комбинации простых инструментов, каждый их которых предназначен для выполнения одной, вполне определенной задачи. Основная идея проста: есть узлы (nodes) (инструменты) и ребра (edges) которые соединяют пару узлов (отсюда и "граф" в "netgraph"). Пакеты данных идут в двух направлениях вдоль ребер от узла к узлу. Когда узел получает пакет данных, он обрабатывает его, и затем (обычно) отправляет его другому узлу. Обработка может быть простейшим добавлением/удалением заголовков или может быть более сложной или включает другие компоненты системы. Netgraph напоминает потоки (Streams) в System V, но он разработан более гибким и производительным.
Netgraph оказался очень полезным для работы в сети, и сейчас он используется в Whistle InterJet для всех указанных выше комбинаций протоколов (за исключением frame relay поверх ISDN), плюс обычный PPP поверх асинхронных последовательных (таких как модемы и терминальные адаптеры) и PPTP, которые включают шифрование. Во всех этих протоколах данные полностью обрабатываются в ядре. В случае PPP, пакеты согласования (negotiation) обрабатываются отдельно в пользовательском режиме (смотрите порт FreeBSD для mpd).
Глядя на рисунок выше, очевидно, что должны быть узлы и ребра. Менее очевиден факт, что узел может иметь определенное число подключений к другим узлам. Например, вполне возможно иметь одновременно IP, IPX, и PPP в инкапсуляции RFC 1490; конечно, мультиплексирование это та задача, для которой и нужен RFC 1490. В этом случае нужно три ребра подключить к узлу RFC 1490, одно для каждого стека протоколов. Нет требований, чтобы данные следовали строго в определенном направлении, и нет ограничений на действия, которые узел выполняет с пакетом. Узел может быть источником/потребителем данным, например, если он связан с аппаратной частью, или он может просто добавлять/удалять заголовки, мультиплексировать и т. п.
Узлы netgraph существуют в ядре и полупостоянно. Обычно узел существует пока он подключен, к какому либо другому узлу, однако некоторые узлы постоянные, например, узлы, связанные с аппаратной частью; когда число ребер уменьшается до нуля, аппаратное устройство выключается. Поскольку узлы существуют в ядре, они не связаны с каким либо определенным процессом.
Эта картина все еще слишком упрощенная. В реальной жизни узел нужно конфигурировать, запрашивать его состояние и т. д. Например, PPP сложный протокол, с большим количеством опций. Для этого в netgraph определены управляющие сообщения (control messages). Управляющее сообщение это "внешние управление". Вместо следования от узла к узлу как пакеты данных, управляющие сообщения посылаются асинхронно и непосредственно от одного узла к другому. Два узла могут быть не связаны (даже через другие узлы). Для обеспечения этого в netgraph существует простая схема адресации по которой узел можно идентифицировать, используя простую ASCII-строчку.
Управляющие сообщения это просто структуры Си с фиксированным заголовком (структура ng_mesg)
и переменной областью данных. Есть несколько управляющих сообщений, которые все узлы должны понимать;
они называются общие управляющие сообщения (generic control messages) и реализованы в базовой системе.
Например, узлу можно указать разрушить себя или создать/разрушить ребро. Узлы могут также иметь свои собственные управляющие сообщения, зависящие от типа. Каждый тип узла, определяющий свои собственные управляющие сообщения должен иметь уникальное значение typecookie. Комбинация полей typecookie и command в заголовке управляющего сообщения определяет, как его интерпретировать.
На управляющие сообщения часто идут ответы в виде ответного контрольного сообщения (reply control message). Например, чтоб узнать состояние узла или статистику вы можете послать управляющее сообщение "get status"; он затем пошлет вам ответ (который идентифицируется значением token, скопированным из исходного запроса) содержащий запрошенную информацию в поле данных. Заголовок ответного управляющего сообщения обычно такой же, как исходный заголовок, но выставлен флаг reply flag
Netgraph предоставляет способ преобразования этих структур в строки ASCII и обратно для упрощения взаимодействия с человеком.
В netgraph, ребра на самом деле не существуют сами по себе. Вместо этого ребро это просто комбинация двух крючков (hooks), по одному от каждого узла. Крючок узла определяет как узел может быть подключен. Каждый крючок имеет уникальное, статически определенное имя, которое часто отражает его цель. Имя имеет значение только в контексте данного узла; два узла могут иметь крючки с одинаковым названием.
Например, рассмотрим узел Cisco. Cisco HDLC это очень простая схема мультиплексирования протоколов посредством дополнения каждого кадра спереди полем Ethertype перед передачей на физический уровень. Cisco HDLC поддерживает одновременную передачу IP, IPX, AppleTalk, и т. д.
Таким образом, узел netgraph для Cisco HDLC (см ng_cisco(8)) определяет крючки, называемые inet, atalk, and ipx.
Эти крючки предназначены для подключения к соответствующим вышележащим стекам протоколов.
Он так же определяет крючок, называемый downstream который подключается к нижележащему уровню, например узлу, связанному с синхронной последовательной платой. К пакетам, получаемым через крючки inet, atalk, и ipx добавляется два байта заголовка, и затем они отправляются через крючок downstream. Наоборот, из пакетов полученных через downstream удаляется заголовок, и они отправляются вверх через крючок, соответствующий протоколу. Узел так же обрабатывает периодические пакеты "tickle" и запросы, определенные протоколом Cisco HDLC.
Крючки всегда либо подключены, либо не подключены; операция подключения или отключения пары крючков атомарная. Когда пакет посылается через крючок, которые не подключен, он отбрасывается.
Некоторые типы узлов достаточно очевидны, такие как Cisco HDLC. Другие менее очевидны, но предоставляют некоторые интересные функции, например, возможность обращаться непосредственно к устройству или открытому сокету внутри ядра.
Несколько примеров типов узлов, реализованных на настоящий момент во FreeBSD. Все эти типы узлов описаны в соответствующих страницах справочного руководства man.
ng_echo(8)ng_disc(8)ng_tee(8)tee(1). Он копирует данные проходящие через него в любом направлении ("right" или "left"), и полезен для отладки. Пакеты, получаемые через "right" посылаются через "left" и копия шлется через "right2left"; аналогично для пакетов идущих от "left" к "right".
Пакеты, получаемые через "right2left" посылаются через "left" и пакеты получаемы через "left2right", отправляются через "right".

Рисунок 2: Тип узла tee
ng_iface(8)ifconfig -a. Вы можете прописать на этом интерфейсе адрес, как на другом PPP интерфейсе, пинговать удаленную сторону, и т. д. Конечно, узел должен быть подключен к чему либо, иначе пакеты ping будут выходить через крючок inet и исчезать.
К сожалению, FreeBSD в настоящий момент не поддерживает удаление интерфейсов, т. о. однажды создав узел ng_iface(8) он будет существовать до следующей перезагрузки (однако это будет скоро исправлено).

Рисунок 3: Тип узла interface
ng_tty(8)tty(4)). Вы создаете узел установкой дисциплины линии NETGRAPHDISC на последовательной линии. Узел имеет одни крючок называемый "hook". Пакеты, получаемые через "hook" передаются (как последовательные байты) через соответствующее последовательное устройство; данные, получаемые от устройства, формируются в пакеты и посылаются через "hook". Нормальное чтение и запись в последовательную линию блокируются. 
Рисунок 4: Тип узла TTY
ng_socket(8)PF_NETGRAPH. Узел создается, когда программа пользовательского режима создает соответствующий сокет через системный вызов socket(2). Один сокет используется для передачи и получения пакетов данных, а второй для контрольных сообщений. Этот узел поддерживает крючки с произвольными именами, например "hook1", "hook2" и т. д. 
Рисунок 5: Тип узла socket
ng_bpf(8)bpf(4).ng_ksocket(8)ng_socket(8). Каждый узел одновременно является сокетом, полностью расположенном в ядре. Данные, получаемые узлом, записываются в сокет и наоборот. Нормальные bind(2), connect(2), и т. д. операции осуществимы вместо контрольных сообщений. Этот тип узла полезен для туннелирования пакетов через сокет (например, туннелирование IP поверх UDP).ng_ether(8)options NETGRAPH, то каждый интерфейс Ethernet так же является узлом netgraph с таким же именем как интерфейс. Каждый узел имеет два крючка "orphans" и "divert"; только один крючок может быть подключен одновременно. Если "orphans" подключен, то устройство продолжает работать нормально, за исключением того, что все пакеты Ethernet с неизвестным или неподдерживаемым типом, доставляются через этот крючок (в нормальном режиме эти пакеты просто отбрасываются). Когда крючок "divert" подключен то все входящие пакеты доставляются через этот крючок. Пакет полученный через любой из этих крючков передается в кабель. Все пакеты "сырые" кадры Ethernet со стандартным 14-байтным заголовком (но без контрольной суммы). Этот тип узла полезен, например для PPP поверх Ethernet (PPPoE).ar(4) and sr(4)options NETGRAPH, то драйвера ar(4) и sr(4) перестанут работать в нормальном режиме и вместо этого будут работать как постоянные узлы netgraph (с таким же именем как название устройства). Сырые кадры HDLC могут быть прочитаны и записаны через крючок "rawdata".
В некоторых случаях пакеты данных могут иметь связанную метаинформацию которую нужно передать вместе с пакетом. Хотя это редко используется, netgraph предоставляет механизм, чтоб сделать это. Пример метаинформации - приоритеты: некоторые пакеты могут иметь более высокий приоритет чем другие. Типы узлов могут определять свою собственную, специфичную метаинформацию, и netgraph для этой цели определяет структуру ng_meta. Мета информация не воспринимается базовой системой netgraph
Каждый узел netgraph адресуем через строку ASCII, называемую адрес узла (node address) или путь (path). Адрес узла используется только для отправки контрольных сообщений.
Многие узлы имеют имена. Например, узел, ассоциированный с устройством будет обычно иметь такое же имя как устройство. Когда узел имеет имя, он всегда может быть адресован, используя абсолютный адрес, состоящий из имени устройства и двоеточия. Например, если вы создали интерфейсный узел, названный "ng0" его адрес будет "ng0:".
Если узел не имеет имени, вы можете составить его из уникального номера ID узла заключив его в квадратные скобки (каждый узел имеет уникальный номер ID). Таким образом, если узел ng0: умеет номер ID 1234, тогда "[1234]:" так же является адресом этого узла.
Наконец, адрес ".:" или "." всегда указывает на локальный узел (источник).
Относительная адресация так же возможно когда два узла соединены опосредовано. Относительный адрес использует имена последовательных крючков в пути от одного узла к другому. Рассмотрим рисунок:

Рисунок 6: Простая конфигурация узлов
Если узел node1 хочет послать контрольное сообщение узлу node2, он может использовать адрес
".:hook1a" или просто "hook1a". Для обращения к узлу node3, он может использовать адрес ".:hook1a.hook2b" или просто "hook1a.hook2b".
Аналогично, узел node3 может обратиться к узлу node1, используя адрес ".:hook3a.hook2a" или просто "hook3a.hook2a".
Относительные и абсолютные адреса можно сочетать, например, "node1:hook1a.hook2b" будет указывать на узел node3.
Netgraph поставляется с утилитами командной строки и пользовательской библиотекой, которые позволяют взаимодействовать с системой ядра netgraph. Необходимы привилегии root для работы с netgraph из пользовательской режима.
Есть две утилиты командой строки для взаимодействия с netgraph, nghook(8)
и ngctl(8). nghook(8) очень проста: она подключается к любому неподключенному крючку любого узла и позволяет вам передавать и получать пакеты данных через стандартный ввод и стандартный вывод. Вывод может быть дополнительно декодирован в читаемый человеком формат hex/ASCII. В командной строке вы указываете абсолютный адрес узла и имя крючка.
Например, если ваше ядро собрано с options NETGRAPH и вы имеете сетевой интерфейс fxp0, следующая команда перенаправит все сетевые пакеты получаемые картой и выведет их через стандартный вывод в формате hex/ASCII:
nghook -a fxp0: divert
ngctl(8) более функциональная программа, которая позволяет вам делать практически все с netgraph из командной строки. Она работает в пакетном или интерактивном режиме, и поддерживает несколько команд, которые выполняют интересующую работу, в том числе:
connect Соединить пару крючков для объединения двух узлов list Вывести список всех узлов в системе mkpeer Создать узел и подключить его к существующему узлу msg Послать форматированное ASCII сообщение узлу name Назначит узлу имя rmhook Отключить два подключенных крючка show Показать информацию об узле shutdown Удалить/сбросить узел, разрушив все подключения status Получить статус узла в удобочитаемом виде types Показать типы установленных узлов quit Выйти из программы
Эти команды могут быть объединены в скрипт, который делает что-то полезное. Например, предположим, что у вас есть две частные сети, которые разделены, но обе подключены к интернету через машины с FreeBSD. Сеть A имеет внутренние адреса из диапазона 192.168.1.0/24 и внешний IP адрес 1.1.1.1, в то время как сеть B имеет адреса 192.168.2.0/24 и внешний адрес 2.2.2.2. Используя Netgraph, вы можете легко сделать UDP для IP трафика между двумя частными сетями. Пример скрипта, который это может сделать (его можно так же найти в /usr/share/examples/netgraph):
#!/bin/sh
# Этот скрипт устанавливает виртуальный канал точка-точка между двумя
# подсетями, используя UDP пакеты в качестве "глобального канала".
# Эти две подсети могут иметь адреса немаршрутизируемые между двумя
# файрволами.
# Определение локальной и удаленной внутренней сетей, также как и
# локального и удаленного внешних IP адресов и номера UDP порта,
# которые будут использованы для туннеля
#
LOC_INTERIOR_IP=192.168.1.1
LOC_EXTERIOR_IP=1.1.1.1
REM_INTERIOR_IP=192.168.2.1
REM_EXTERIOR_IP=2.2.2.2
REM_INSIDE_NET=192.168.2.0
UDP_TUNNEL_PORT=4028
# Создать интерфейсный узел "ng0", если его еще нету,
# если есть, просто убедиться, что он ни к чему не подключен
#
if ifconfig ng0 >/dev/null 2>&1; then
ifconfig ng0 inet down delete >/dev/null 2>&1
ngctl shutdown ng0:
else
ngctl mkpeer iface dummy inet
fi
# Присоединить UDP сокет к крюку "inet" интерфейсного узла использую
# узел типа ng_ksocket(8).
#
ngctl mkpeer ng0: ksocket inet inet/dgram/udp
# Присоединить UDP сокет к локальному внешнему IP и порту
#
ngctl msg ng0:inet bind inet/${LOC_EXTERIOR_IP}:${UDP_TUNNEL_PORT}
# Установить соединение с внешним IP и портом на удаленном сервере
#
ngctl msg ng0:inet connect inet/${REM_EXTERIOR_IP}:${UDP_TUNNEL_PORT}
# Настроить интерфейс точка-точка
#
ifconfig ng0 ${LOC_INTERIOR_IP} ${REM_INTERIOR_IP}
# Добавить маршрут к удаленной частной сети через туннель
#
route add ${REM_INSIDE_NET} ${REM_INTERIOR_IP}
Далее рассмотрим как можно работать с ngctl(8) в интерактивном режиме.
Пользовательский ввод выделен синим.
Запустим ngctl в интерактивном режиме. Будет показан список доступных команд...
$ ngctl Available commands: connect Connects hook <peerhook> of the node at <relpath> to <hook> debug Get/set debugging verbosity level help Show command summary or get more help on a specific command list Show information about all nodes mkpeer Create and connect a new node to the node at "path" msg Send a netgraph control message to the node at "path" name Assign name <name> to the node at <path> read Read and execute commands from a file rmhook Disconnect hook "hook" of the node at "path" show Show information about the node at <path> shutdown Shutdown the node at <path> status Get human readable status information from the node at <path> types Show information about all installed node types quit Exit program
ngctl создает при запуске узел типа ng_socket(8). Это наш локальный узел netgraph, который используется для взаимодействия с другими узлами в системе. Посмотрим на него. Мы видим, что ngctl назначил ему имя "ngctl652" и его тип "socket", номер ID 45 и он имеет ноль подключенных крючков, т. е. он не подключен к другим узлам.
+ show . Name: ngctl652 Type: socket ID: 00000045 Num hooks: 0
Теперь мы создадим узел "tee" и подключим его к локальному узлу. Мы подключим крючок "right" узла "tee" к крючку "myhook" на локальном узле. Мы можем использовать любое имя для нашего крючка, так как узел типа ng_socket(8) поддерживает крючки с произвольными именами. После этого снова посмотрим на наш локальный узел, чтобы убедиться, что он имеет безымянного соседа типа "tee".
+ help mkpeer Usage: mkpeer [path] <type> <hook> <peerhook> Summary: Create and connect a new node to the node at "path" Description: The mkpeer command atomically creates a new node of type "type" and connects it to the node at "path". The hooks used for the connection are "hook" on the original node and "peerhook" on the new node. If "path" is omitted then "." is assumed. + mkpeer . tee myhook right + show . Name: ngctl652 Type: socket ID: 00000045 Num hooks: 1 Local hook Peer name Peer type Peer ID Peer hook ---------- --------- --------- ------- --------- myhook <unnamed> tee 00000046 right
Аналогично, если мы посмотрим на вывод узла tee, мы увидим, что он подключен к нашему локальному узлу через крючок "right". Узел "tee" все еще безымянны, но мы можем его указать используя абсолютный адрес "[46]:" или относительный адрес ".:myhook" или "myhook"...
+ show .:myhook Name: <unnamed> Type: tee ID: 00000046 Num hooks: 1 Local hook Peer name Peer type Peer ID Peer hook ---------- --------- --------- ------- --------- right ngctl652 socket 00000045 myhook
Теперь назначим ему имя и убедимся, что можем по нему обратиться к этому узлу...
+ name .:myhook mytee + show mytee: Name: mytee Type: tee ID: 00000046 Num hooks: 1 Local hook Peer name Peer type Peer ID Peer hook ---------- --------- --------- ------- --------- right ngctl652 socket 00000045 myhook
Теперь подключим узел Cisco HDLC к другой стороне узла "tee" и снова проверим узел "tee". Мы подключимся к крючку "downstream" узла Cisco HDLC, как будто бы узел tee соответствует подключению к WAN. Cisco HDLC слева (крючек "left") от узла tee наш локальный узел справа (крючок "right") от узла tee...
+ mkpeer mytee: cisco left downstream + show mytee: Name: mytee Type: tee ID: 00000046 Num hooks: 2 Local hook Peer name Peer type Peer ID Peer hook ---------- --------- --------- ------- --------- left <unnamed> cisco 00000047 downstream right ngctl652 socket 00000045 myhook + Rec'd data packet on hook "myhook": 0000: 8f 00 80 35 00 00 00 02 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ...5............ 0010: ff ff 00 20 8c 08 40 00 ... ..@. + Rec'd data packet on hook "myhook": 0000: 8f 00 80 35 00 00 00 02 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ...5............ 0010: ff ff 00 20 b3 18 00 17 ... ....
Эй, что это такое?! Выглядит так, будто мы получаем какие то пакеты данных через наш крючок "myhook". Узел Cisco каждые 10 секунд посылает периодические пакеты keep-alive. Эти пакеты проходят через узел tee (слева направо от крючка "left" к крючку "right") и принимаются крючком "myhook", где ngctl показывает их в консоли.
Теперь посмотрим список всех узлов, существующих в системе. Заметим, что два наших интерфейса Ethernet так же показаны, поскольку это постоянные узлы и мы собирали ядро с options NETGRAPH...
+ list There are 5 total nodes: Name: <unnamed> Type: cisco ID: 00000047 Num hooks: 1 Name: mytee Type: tee ID: 00000046 Num hooks: 2 Name: ngctl652 Type: socket ID: 00000045 Num hooks: 1 Name: fxp1 Type: ether ID: 00000002 Num hooks: 0 Name: fxp0 Type: ether ID: 00000001 Num hooks: 0 + Rec'd data packet on hook "myhook": 0000: 8f 00 80 35 00 00 00 02 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ...5............ 0010: ff ff 00 22 4d 40 40 00 ..."M@@.
OK, давайте выключим (то есть удалим) узел Cisco HDLC, таким образом мы остановим получение данных...
+ shutdown mytee:left + show mytee: Name: mytee Type: tee ID: 00000046 Num hooks: 1 Local hook Peer name Peer type Peer ID Peer hook ---------- --------- --------- ------- --------- right ngctl652 socket 00000045 myhook
Теперь, давайте посмотрим статистику узла tee. Мы пошлем управляющее сообщение и немедленно получим ответ. Команда и ответ конвертируются в/из ASCII автоматически с помощью ngctl, так как управляющие сообщение это двоичная структура...
+ help msg
Usage: msg path command [args ... ]
Aliases: cmd
Summary: Send a netgraph control message to the node at "path"
Description:
The msg command constructs a netgraph control message from the
command name and ASCII arguments (if any) and sends that
message to the node. It does this by first asking the node to
convert the ASCII message into binary format, and re-sending the
result. The typecookie used for the message is assumed to be
the typecookie corresponding to the target node's type.
+ msg mytee: getstats
Rec'd response "getstats" (1) from "mytee:":
Args: { right={ outOctets=72 outFrames=3 } left={ inOctets=72 inFrames=3 }
left2right={ outOctets=72 outFrames=3 } }
Ответ это просто строковая версия структуры ng_tee_stats возвращаемой в ответном управляющем сообщении (Эта структура определена в ng_tee.h).
Мы видим, что три кадра (и 72 байта) прошли через узел слева направо. Каждый кадр был скопирован и отправлен через крючок "left2right" (но поскольку этот крючок не подключен эти кадры были отброшены).
OK, теперь проиграемся с узлом ng_ksocket(8)...
+ mkpeer ksocket myhook2 inet/stream/tcp + msg .:myhook2 connect inet/127.0.0.1:13 ngctl: send msg: Operation now in progress Rec'd data packet on hook "myhook": 0000: 54 75 65 20 46 65 62 20 20 31 20 31 31 3a 30 32 Tue Feb 1 11:02 0010: 3a 32 38 20 32 30 30 30 0d 0a :28 2000..
Мы создали в ядре TCP сокет, используя узел ng_ksocket(8), и подключили его к сервису "daytime" на локальной машине, который возвращает текущее время. Как мы узнали, что нужно использовать "inet/127.0.0.1:13" в качестве аргумента команды "connect"? Это описано в странице справочного руководства man ng_ksocket(8)
OK, поигрались и хватит...
+ quit
Существует так же пользовательская библиотека libnetgraph(3) для использования в программах netgraph. Она предоставляет много полезных вызовов, которые описаны в справочном руководстве man.
Пример использования их можно посмотреть в исходном коде /usr/src/usr.sbin/ngctl.
Как netgraph реализован? Одна из главных целей netgraph это скорость, поэтому он полностью работает в ядре. Другое конструктивное решение в том, что netgraph полностью функциональный. То есть пакеты не ставятся нигде в очередь при перемещении от узла к узлу. Вместо этого используется прямой вызов функций.
Пакеты данных это packet header mbuf'ы, в то время как мета-данные и управляющие сообщения Си-структуры расположенные в куче (используя malloc типа M_NETGRAPH).
Netgraph отчасти имеет объектно-ориентированную архитектуру. Каждый тип узла определен как массив указателей на методы, или функции Си, которые определяют специфическое поведение узлов данного типа. Каждый метод может быть оставлен NULL для того, чтобы оставить поведение по умолчанию.
Аналогично, есть несколько управляющих сообщений, которые понимают узлы всех типов и которые обрабатываются базовой системой (они называются общими управляющими сообщениями, generic control messages). Каждый тип узлов может дополнительно определять свои собственные управляющие сообщения. Управляющие сообщения всегда содержат typecookie и команду, которые вместе определяют, как интерпретировать это сообщение. Каждый тип узлов должен определить свое уникальное значение typecookie если предполагается, что он будет получать свои управляющие сообщения. Общие управляющие сообщения имеют предопределенные значения typecookie.
Netgraph использует подсчет ссылок для структур узлов и крючков. Каждый указатель на узел или крючок считается как одна ссылка. Если узел имеет имя, оно тоже считается ссылкой. Вся связанная с netgraph область памяти выделяется и освобождается используя malloc типа M_NETGRAPH.
Выполнение кода в ядре требует внимательной синхронизации. Узлы netgraph обычно выполняются через splnet() (см. spl(9)). Для большинства типов узлов не требуется дополнительного внимания. Некоторые узлы, однако, взаимодействуют с другими частями ядра, которые выполняются с другим приоритетом. Например, последовательный порт работает через spltty() и поэтому ng_tty(8) должен это учитывать. На этот случай в netgraph есть альтернативные вызовы передачи данных, которые обрабатывают все необходимые очереди авто-магически. (см. ng_queue_data() ниже).
Для реализации нового типа узлов, нужно сделать только две вещи:
ng_type. NETGRAPH_INIT(). Второй шаг простой, поэтому мы обратим внимание на первый шаг. Структура ng_type, из netgraph.h:
/*
* Structure of a node type
*/
struct ng_type {
u_int32_t version; /* должна совпадать с NG_VERSION */
const char *name; /* Уникальное имя типа */
modeventhand_t mod_event; /* Модуль обработки событий (не обязательно) */
ng_constructor_t *constructor; /* Конструктор узла */
ng_rcvmsg_t *rcvmsg; /* сюда поступают управляющие сообщения */
ng_shutdown_t *shutdown; /* сброс и освобождение ресурсов */
ng_newhook_t *newhook; /* первое сообщение о новом крючке */
ng_findhook_t *findhook; /* только если вы имеете несколько крючков */
ng_connect_t *connect; /* заключительное сообщение о новом крючке */
ng_rcvdata_t *rcvdata; /* сюда поступают данные */
ng_rcvdata_t *rcvdataq; /* или сюда, если через очередь */
ng_disconnect_t *disconnect; /* предупреждение об отключении */
const struct ng_cmdlist *cmdlist; /* команды, которые мы можем конвертировать */
/* R/W данные базового кода netgraph, НЕ ТРОГАТЬ! */
LIST_ENTRY(ng_type) types; /* связанный список всех типов */
int refs; /* число экземпляров */
};
Поле version должно совпадать с NG_VERSION. Это для избежания связывания несовместимых типов. Поле name уникальное имя типа узлов, например "tee". mod_event необязательный модуль обработки событий (когда узел загружается и выгружается) - похоже на статические инциализаторы в C++ или Java.
Далее идут методы типа узлов, описано подробнее ниже. cmdlist
предоставляет (дополнительно) информацию по конвертированию управляющих сообщений в/из ASCII (см. ниже), и оставшаяся часть используется только в базовом коде netgraph.
Каждый тип узлов должен реализовать методы, определенные в структуре ng_type. Каждый метод имеет реализацию по умолчанию, которая используется, если тип узлов не определяет данные метод.
int constructor(node_p *node);ng_make_node_common() и установив node->private если необходимо. Инициализация узла и выделение памяти для данного экземпляра
узла должно производиться здесь.
Сначала нужно вызвать ng_make_node_common(); он создаст узел и установит число указателей в 1.
Действие по умолчанию: Просто вызывает ng_make_node_common().
Когда переопределять: Если требуется специфичная для данного узла инициализация или выделение ресурсов.
int rcvmsg(node_p node, struct ng_mesg *msg,
const char *retaddr, struct ng_mesg **resp);retaddr.
Функция rcvmsg() ответственна за освобождение msg. Ответ, если есть,
может возвращен синхронно, если resp != NULL установкой *resp так,
чтоб он указывал на ответ. Общие управляющие сообщения (за исключением NGM_TEXT_STATUS)
обрабатываются базовой системой, и нет необходимости обрабатывать их здесь.
Действие по умолчанию: Обрабатывает все общие контрольные сообщения; иначе возвращает EINVAL.
Когда переопределять: Если вы определяете управляющие сообщения специфичные для данного типа, или если вы хотите реализовать управляющие сообщения определенные некоторыми другими типами узлов.
int shutdown(node_p node);ng_cutlinks(),
освободить всю частную память данного экземпляра узла, освободить присвоенное имя (если было) через ng_unname(), и освободить сам узел вызвав ng_unref() (этот вызов освобождает
ссылку добавленную в ng_make_node_common()). В случае постоянного узла, все крючки
должны быть отключены и связанное устройство (или что там) сбрасывается, но узел не должен удаляться
(т. е., используется только вызов ng_cutlinks()).
Действие по умолчанию: Вызвать ng_cutlinks(), ng_unname(), и ng_unref().
Когда переопределять: Когда вы должны отменить то, что вы сделали в конструкторе.
int newhook(node_p node, hook_p hook, const char *name);Если узлу нужна информация по данному крючку, этот метод должен инициализировать соответственно hook->private.
Действие по умолчанию: Ничего; подключение крючка всегда разрешено.
Когда переопределять: Всегда, если вы не планируете разрешать крючки с произвольными именами без инициализации и выделения ресурсов, и рассматривать все крючки одинаково при подключении.
hook_p findhook(node_p node, const char *name);Действие по умолчанию: Выполняет линейный поиск по списку крючков, подключенных к данному узлу.
Когда переопределять: Когда ваш узел поддерживает большое число одновременно подключенных крючков (скажем, больше чем 50).
int connect(hook_p hook);Действие по умолчанию: Ничего; подключение крючка принимается.
Когда переопределять: У меня никогда не было причин переопределять этот метод.
int rcvdata(hook_p hook, struct mbuf *m, meta_p meta);m == NULL (например, если посылается только meta),
таким образом, узлы должны учитывать эту возможность.
Действие по умолчанию: Отбросить пакет и метаинформацию.
Когда переопределять: Всегда, если вы не хотите игнорировать полученные пакеты.
int rcvdataq(hook_p hook, struct mbuf *m, meta_p meta);Замысел в том, что некоторые узлы могут захотеть посылать данные используя механизм очереди, вместо
функционального механизма. Это требует взаимодействия с типом узлов получателя, который должен
реализовать этот метод надлежащим образом для того, чтобы делать что-то отличное от rcvdata().
Действие по умолчанию: Вызвать метод rcvdata().
Когда переопределять: Никогда, если у вас нет причин рассматривать очередь входящих данных отдельно от данных без очереди.
int disconnect(hook_p hook);connect().
Хотя функция возвращает int, она должна в действительности возвращать void
поскольку возвращаемое значение игнорируется; отключение крючка не может быть блокировано узлом.
Функция должна проверять есть ли еще крючки (hook->node->numhooks == 0) и если был отключен последний крючок, вызывать ng_rmnode() для самоликвидации, если так надо. Это позволяет
избежать полностью неподключенных узлов, которые задерживаются в системе после завершения своей работы.
Действие по умолчанию: Ничего не делает.
Когда переопределять: Почти всегда.
int mod_event(module_t mod, int what, void *arg); what который может быть
либо MOD_LOAD либо MOD_UNLOAD. Параметр arg указатель на структуру
ng_type, определяющую тип узлов. Этот метод никогда не вызывается для
MOD_UNLOAD пока существуют узлы данного типа.
В настоящий момент только вызывается только со значение MOD_UNLOAD когда
вызывается kldunload(2). Однако в будущем выгрузка типа узлов может быть реализована как мера по "уборке мусора".
Действие по умолчанию: Ничего не делает. Если не переопределен, MOD_LOAD и MOD_UNLOAD нормально завершаются.
Когда переопределять: Если ваш тип нуждается в специфической инициализации или выделении
ресурсов при загрузке, или откате этого при выгрузке. Также, если ваш тип не поддерживает выгрузку (может быть из-за неразрушимых связей с другими частями ядра) возвращение ошибки в MOD_UNLOAD
предотвратит выгрузку типа.
Каждый тип узлов включает два заголовочных файла.
Заголовочный файл netgraph.h определяет базовые структуры netgraph (хороший объектно-ориентированный дизайн диктует, что определения структур ng_node и
ng_hook здесь фактически нет; вместо этого они должны быть скрыты внутри базового кода netgraph).
Структуры узлов освобождаются когда счетчик указателей уменьшается до нуля после вызова
ng_unref(). Если узел имеет имя, оно считается ссылкой; для удаления имени (и ссылка), вызывается
ng_unname(). Особенный интерес представляет структура ng_type, поскольку она должна быть предоставлена для каждого типа узлов.
Заголовочный файлng_message.h определяет структуры и макросы, имеющие отношение к обработке управляющие сообщений. В нем определена структура ng_mesg, с
которой начинается любое управляющее сообщение. Он также является "публичным заголовочным файлом" для всех
общих управляющих сообщений, которые имеют значение typecookie NGM_GENERIC_COOKIE.
Общие управляющие сообщения:
NGM_SHUTDOWNОтключает от целевого узла все крючки и удаляет узел (или сбрасывает его, если он постоянный) NGM_MKPEERСоздает новый узел и подключается к нему NGM_CONNECTПодключить крючок целевого узла к другому узлу NGM_NAMEНазначить имя целевому узлу NGM_RMHOOKОтключить целевой узел от другого узла NGM_NODEINFOПолучить информацию по целевому узлу NGM_LISTHOOKSПолучить список крючков, подключенных к данному узлу NGM_LISTNAMESПолучить список всех именованных узлов* NGM_LISTNODESПолучить список всех узлов, с именем и без имени* NGM_LISTTYPESПолучить список всех установленных типов узлов* NGM_TEXT_STATUSПолучить в удобочитаемом виде информацию о состоянии узла (может быть не реализовано) NGM_BINARY2ASCIIПреобразовать управляющее сообщение из двоичного вида в ASCII NGM_ASCII2BINARYпреобразовать управляющее сообщение из ASCII в двоичный вид * Не связано в каким либо конкретным узлом
Для большинства перечисленных команд в ng_message.h определены соответствующие структуры Си.
Заголовочные файлы netgraph.h и ng_message.h некоторые широко используемые функции и макросы:
int ng_send_data(hook_p hook, struct mbuf *m, meta_p meta); m и связанные метаданные meta
наружу через крючок hook и возвращает в error код ошибки.
Оба или один из параметров m и meta могут бытьNULL. В любом
случае, необходимо освободить m и meta при вызове этой функции, поэтому
переменные должны быть сброшены в NULL после вызова (это производится автоматически, если вместо функции вы используете макрос NG_SEND_DATA()). int ng_send_dataq(hook_p hook, struct mbuf *m, meta_p meta); ng_send_data(), за исключением того, что узел-получатель
получает данные через его метод rcvdataq() вместо rcvdata(). Если тип узлов
не переопределяет rcvdataq(), его вызов эквивалентен ng_send_data().int ng_queue_data(hook_p hook, struct mbuf *m, meta_p meta); ng_send_data(), за исключением того, что его безопасно
вызывать вне контекста splnet(). mbuf и метаинформация будут поставлены в очередь и доставлены позже, в splnet(). int ng_send_msg(node_p here, struct ng_mesg *msg, const char *address, struct ng_mesg **resp); msg от локального узла
here узлу с адресом address, который может быть абсолютным или относительным
адресом. Если resp не NULL, и получатель желает послать ответ синхронно, он
устанавливает указатель *resp на него. В этом случае вызывающий узел должен обработать и
освободить*resp.
int ng_queue_msg(node_p here, struct ng_mesg *msg, const char *address); ng_send_msg(), за исключением того, что его можно
вызывать вне контекста splnet(). Сообщение будет поставлено в очередь и доставлено
позже splnet(). Синхронный ответ невозможен.NG_SEND_DATA(error, hook, m, meta) ng_send_data(). Он просто вызывает
ng_send_data() и потом устанавливает m и meta в NULL.
Один или оба параметра m и meta могут быть NULL, но они должны
быть переменными (они не могут быть константой NULL из-за природы работы макроса). NG_SEND_DATAQ(error, hook, m, meta) ng_send_dataq(). Он просто вызывает
ng_send_dataq() и потом устанавливает m и meta в NULL.
Один или оба параметра m и meta могут быть NULL, но они должны
быть переменными (они не могут быть константой NULL из-за природы работы макроса).NG_FREE_DATA(m, meta) m и meta и устанавливают в NULL.
Один или оба параметра m и meta могут быть NULL, но они должны
быть переменными (они не могут быть константой NULL из-за природы работы макроса).NG_FREE_META(meta) meta и устанавливает в NULL. Параметр
meta может иметь значение NULL, он должен быть переменной (он не может
быть константой NULL из-за природы работы макроса). NG_MKRESPONSE(rsp, msg, len, how) msg. Этот ответ имеет len байт места для аргументов (len
должна быть нулевой, если аргументов нет).msg должен быть указателем на существующую
структуру ng_mesg в то время как rspдолжен иметь тип ng_mesg *. how это M_WAITили M_NOWAIT (безопаснее использовать
M_NOWAIT). Устанавливает rspв NULL если выделение памяти прошло неудачно.
int ng_name_node(node_p node, const char *name); name узлу node.
Имя должно быть уникальным. функция часто вызывается внутри конструктора узла для узлов, которые
соответствуют другой именованной сущности ядра, например устройству или интерфейсу. Назначение имени увеличивает на один счетчик ссылок на узлы.void ng_cutlinks(node_p node); node. Обычно вызывается в ходе выключения узла.void ng_unref(node_p node); shutdown() для освобождения ссылки созданной
ng_make_node_common(). void ng_unname(node_p node); shutdown() перед освобождением узла (через ng_unref()).
Достаточно теории, рассмотрим пример. Это реализация узла типа tee. Как было решено, реализация состоит из открытого заголовочного файла, Си файла и страницы man. Заголовочный файл ng_tee.h и Си файл ng_tee.c.
Нужно сделать несколько замечаний по поводу заголовочного файла:
NG_TEE_NODE_TYPE. NGM_TEE_COOKIE.
NGM_TEE_GET_STATS и
NGM_TEE_CLR_STATS. NGM_TEE_GET_STATS, которая определена в struct
ng_tee_stats. Эта информация общедоступна, поскольку другие типы узлов должны знать это для обмена сообщениями и подключения к узлам tee.
date -u +%s".Несколько замечаний по Си файлу:
ng_tee(8) эта информация хранится в структуре privdata для каждого узла, и
в структуре hookdata для каждого крючка.ng_tee_cmds определяет, как преобразовывать специфичные для данного типа управляющие
сообщения из двоичного вида в ASCII и обратно. Смотрите ниже. ng_tee_typestruct в начале, фактически определяет узел типа tee. Эта структура
содержит версию системы netgraph (для избежания несовместимости), уникальное имя типа
(NG_ECHO_NODE_TYPE), указатели на методы типа узлов, и указатель на массив ng_tee_cmds. Некоторые методы нет необходимости переопределять, поскольку достаточно поведения по умолчанию. NETGRAPH_INIT() нужен для связывания типа. Этот макрос нужен и при загрузке в виде модуля и при непосредственной компиляции в ядре (в данном случае, используя options NETGRAPH_TEE). struct ng_node) содержат счетчик ссылок, чтоб убедиться, что они будут освобождены вовремя. Скрытый эффект в вызове ng_make_node_common() из конструктора в том, что одна ссылка создается. Ссылка освобождается вызовом ng_unref() в методе
ngt_rmnode(). ngt_rmnode() вызывается ng_bypass(). Здесь небольшой клудж, в том, что
два ребра объединяются при отключении узла между ними (в данном случае узла tee).ngt_disconnect() разрушает сам узел, при отключении последнего крючка. Это нужно чтоб узлы не повисали на неопределенное время, после того как им не осталось работы.splnet().
Netgraph простой способ конвертирования управляющих сообщений (по сути, любых структур Си) между двоичным и ASCII видом. Подробное описание выходит за рамки данной статьи, но мы дадим обзор.
Вспомним, что управляющее сообщение имеет фиксированный заголовок (struct ng_mesg) за которым идет полезная нагрузка переменной длины с определенной структурой и содержанием. Вдобавок заголовок управляющего сообщения содержит флаг, показывающий, что сообщение является командой или ответом. Обычно полезная часть сообщения имеет разную структуру в команде и в ответе. Например, для узла "tee" определено управляющее сообщение NGM_TEE_GET_STATS. Когда мы посылаем команду
((msg->header.flags & NGF_RESP) == 0),
полезная нагрузка пустая. Когда посылается ответ на команду
((msg->header.flags& NGF_RESP) != 0), полезная нагрузка содержит структуру ng_tee_stats в которой находится статистика.
Для каждого управляющего сообщения, которое тип узлов понимает, определено как конвертировать полезную нагрузку в (в обоих случаях, команды и ответа) между родной двоичной формой и удобочитаемой ASCII версией. Эти определения называются типы разбора (netgraph parse types).
Поле cmdlist в структуре ng_type, определяющей тип узлов указывает на массив структур ng_cmdlist. Каждый элемент в этом массиве соответствует специфичному для данного типа сообщению, понимаемому этим узлом. В соответствие с typecookie и ID команды (которые однозначно определяют контрольное сообщение), сопоставлено имя ASCII и два типа разбора которые определяют как полезная нагрузка структурирована, по одному для каждого направления (команда и ответ).
Типы разбора строятся на основе типов разбора предопределенных в ng_parse.h. Используя эти типы разбора, вы можете описать структуры Си любой сложности, даже содержащие массивы переменной длины и строки. В узле "tee" есть пример как это сделать для структуры ng_tee_stats возвращаемой управляющим сообщением NGM_TEE_GET_STATS (см. ng_tee.h и ng_tee.c).
Вы можете так же определить собственные типы разбора с нуля, если необходимо. Например, тип узлов
"ksocket" содержит специальный код для преобразования структуры sockaddr
в адреса семейства AF_INET и AF_LOCAL, чтобы сделать их более удобочитаемыми.
Код, имеющий отношение к этому отношение, может быть найден в
ng_ksocket.h и ng_ksocket.c, особенно в секции "STRUCT SOCKADDR PARSE TYPE".
Типы разбора удобный и эффективный способ конвертирования двоичного/ASCII в ядре без большого объема коду по ручному разбору и работы со строками. Когда это действительно сильно влияет на производительность, всегда могут быть использованы двоичные сообщения непосредственно, которые не нужно конвертировать.
Детально информацию о типах разбора можно посмотреть в ng_parse.h
и ng_parse.c.
Несколько вещей, которые нужно иметь виду, если вы собираетесь писать свой собственный тип узлов:
M_PKTHDR
должен быть установлен. m->m_pkthdr.len когда вы изменяете
m->m_len для любого mbuf в цепочке. m->m_len и вызвать m_pullup() перед доступом к данным в mbuf. Не вызывайте m_pullup() если это не нужно. Всегда следует придерживаться следующего шаблона:
struct foobar *f;
if (m->m_len < sizeof(*f) && (m = m_pullup(m, sizeof(*f))) == NULL) {
NG_FREE_META(meta);
return (ENOBUFS);
}
f=mtod(m, struct foobar *);
...
disconnect()
и shutdown() для предотвращения утечек памяти т.п. Я случайно оставил таймер запущенным, и это имело гибельный результат.timeout(9)), проверьте что первым в вашем обработчике стоит вызовsplnet() (и splx() перед выходом, конечно). Вызов timeout() не сохраняет уровень SPL в обработчике событий.Работа над Netgraph все еще продолжается, и помощники приветствуются! Есть несколько идей, по поводу будущей работы.
еще много типов узлов не написано:
ng_ppp(8)
например, сжатие Deflate для PPP, 3DES шифрование PPP и т. д. ipfw(4) как узла netgraph. Во FreeBSD сейчас имеется четыре реализации PPP: sppp(4), pppd(8),
ppp(8), и порт MPD. Это достаточно глупо. Используя netgraph, это может быть объединено в один демон, работающий в пользовательском режиме, который будет выполнять все согласования и настройки, в то время как маршрутизация данных будет полностью происходить в ядре, через узлы ng_ppp(8). Это позволит объединить гибкость и удобство настройки демонов, работающих в пользовательском режиме, со скоростью работы в ядре. Сегодня MPD единственная реализация которая полностью основана на netgraph, но есть планы так же переработать ppp(8).
Не все типы узлов, которые определяют свои собственные управляющие сообщения поддерживают преобразование между двоичным видом и ASCII. Одна из задач - завершить эту работу для узлов, которые в этом еще не сделано.
Одна из проблем, к которой возможно придется обратиться - это управление потом. Сейчас когда вы посылаете пакет данных, если конечный получатель узла не может принять его из-за переполнения очереди передачи или по другой причине, все что может быть сделано это отбросить пакет и вернуть ENOBUFS.
Возможно, мы сможем определить новый код возврата ESLOWDOWN или что-то, что будет означать
"пакет данных не отброшен; очередь полна; уменьшите скорость и попробуйте позже." Другой вариант определить типы метаинформации эквивалентные XOFF (остановить передачу) и XON (возобновить передачу).
Netgraph объектно-ориентированный, но преимущества объектно-ориентированной архитектуры должны использоваться более полно без ущерба производительности. Пока слишком много видимых полей в структурах, которые не должны быть доступны, и т. д., так же как много других разных доработок.
Также, страницы man для всех узлов (например, ng_tee(8)) в действительности должны находиться в разделе 4, а не 8.
Было бы удобно сделать новое общее управляющее сообщение NGM_ELECTROCUTE, которое если послать его узлу выключит узел вместе со всеми узлами связанными с ним непосредственно или через другие узлы. Это позволит выполнить быструю очистку сложного графа в netgraph одним ударом. В дополнение можно сделать новую опцию сокета (см. setsockopt(2)) которую нужно установить для сокета ng_socket(8)
чтоб при его закрытии автоматически посылалось сообщение NGM_ELECTROCUTE.
Вместе две этих вещи позволят более надежно избежать в netgraph "утечку узлов".
В базовую систему netgraph несложно включить "обнаружение бесконечных петель". Каждый узел должен иметь свой закрытый счетчик. Счетчик должен увеличиваться перед каждым обращением к методу rcvdata() данного узла, и уменьшаться потом. Если счетчик достиг нереально большого значения, мы считаем что обнаружена бесконечная петля (и избегаем паники ядра).
Можно создать и улучшить много узлов:
Теоретически, сетевая подсистема BSD может быть полностью заменена на netgraph. Конечно, скорее всего, это никогда не случиться, но это хороший мысленный эксперимент. Каждое сетевое устройство должно быть постоянным узлом netgraph (как устройства Ethernet). Вверху каждого устройства Ethernet должен быть мультиплексор Ethertype. К нему должны быть подключены узлы IP, ARP, IPX, AppleTalk и т. д. Узел IP должен быть просто мультиплексором IP протокола, над которым должны находиться узлы TCP, UDP, и т. д. Узлы TCP и UDP должны, наконец, иметь узлы, похожие на сокеты сверху. И т. д., и т. д.
Другие сумасшедшие идеи (отречение: это сумасшедшие идеи):
ioctl(2)
и управляющими сообщениями. Обращайтесь напрямую к вашему SCSI диску через ngctl(8)! Полная интеграция между netgraph и devfs(8). Конечно есть еще много сумасшедших идей о которых мы еще не подумали.
/*
* netgraph.h
*
* Copyright (c) 1996-1999 Whistle Communications, Inc.
* All rights reserved.
*
* Subject to the following obligations and disclaimer of warranty, use and
* redistribution of this software, in source or object code forms, with or
* without modifications are expressly permitted by Whistle Communications;
* provided, however, that:
* 1. Any and all reproductions of the source or object code must include the
* copyright notice above and the following disclaimer of warranties; and
* 2. No rights are granted, in any manner or form, to use Whistle
* Communications, Inc. trademarks, including the mark "WHISTLE
* COMMUNICATIONS" on advertising, endorsements, or otherwise except as
* such appears in the above copyright notice or in the software.
*
* THIS SOFTWARE IS BEING PROVIDED BY WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS "AS IS", AND
* TO THE MAXIMUM EXTENT PERMITTED BY LAW, WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS MAKES NO
* REPRESENTATIONS OR WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, REGARDING THIS SOFTWARE,
* INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY AND ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
* MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR NON-INFRINGEMENT.
* WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS DOES NOT WARRANT, GUARANTEE, OR MAKE ANY
* REPRESENTATIONS REGARDING THE USE OF, OR THE RESULTS OF THE USE OF THIS
* SOFTWARE IN TERMS OF ITS CORRECTNESS, ACCURACY, RELIABILITY OR OTHERWISE.
* IN NO EVENT SHALL WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DAMAGES
* RESULTING FROM OR ARISING OUT OF ANY USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, INCLUDING
* WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY,
* PUNITIVE, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR
* SERVICES, LOSS OF USE, DATA OR PROFITS, HOWEVER CAUSED AND UNDER ANY
* THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
* (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF
* THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS IS ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY
* OF SUCH DAMAGE.
*
* Author: Julian Elischer <julian@whistle.com>
*
* $FreeBSD: src/sys/netgraph/netgraph.h,v 1.6 1999/12/29 04:46:00 peter Exp $
* $Whistle: netgraph.h,v 1.29 1999/11/01 07:56:13 julian Exp $
*/
#ifndef _NETGRAPH_NETGRAPH_H_
#define _NETGRAPH_NETGRAPH_H_ 1
#include <sys/queue.h>
#include <sys/malloc.h>
#include <sys/module.h>
#ifndef _KERNEL
#error "This file should not be included in user level programs"
#endif
/*
* Structure of a hook
*/
struct ng_hook {
char *name; /* what this node knows this link as */
void *private; /* node dependant ID for this hook */
int flags; /* info about this hook/link */
int refs; /* dont actually free this till 0 */
struct ng_hook *peer; /* the other end of this link */
struct ng_node *node; /* The node this hook is attached to */
LIST_ENTRY(ng_hook) hooks; /* linked list of all hooks on node */
};
typedef struct ng_hook *hook_p;
/* Flags for a hook */
#define HK_INVALID 0x0001 /* don't trust it! */
/*
* Structure of a node
*/
struct ng_node {
char *name; /* optional globally unique name */
struct ng_type *type; /* the installed 'type' */
int flags; /* see below for bit definitions */
int sleepers; /* #procs sleeping on this node */
int refs; /* number of references to this node */
int numhooks; /* number of hooks */
int colour; /* for graph colouring algorithms */
void *private; /* node type dependant node ID */
ng_ID_t ID; /* Unique per node */
LIST_HEAD(hooks, ng_hook) hooks; /* linked list of node hooks */
LIST_ENTRY(ng_node) nodes; /* linked list of all nodes */
LIST_ENTRY(ng_node) idnodes; /* ID hash collision list */
};
typedef struct ng_node *node_p;
/* Flags for a node */
#define NG_INVALID 0x001 /* free when all sleepers and refs go to 0 */
#define NG_BUSY 0x002 /* callers should sleep or wait */
#define NG_TOUCHED 0x004 /* to avoid cycles when 'flooding' */
#define NGF_TYPE1 0x10000000 /* reserved for type specific storage */
#define NGF_TYPE2 0x20000000 /* reserved for type specific storage */
#define NGF_TYPE3 0x40000000 /* reserved for type specific storage */
#define NGF_TYPE4 0x80000000 /* reserved for type specific storage */
/*
* The structure that holds meta_data about a data packet (e.g. priority)
* Nodes might add or subtract options as needed if there is room.
* They might reallocate the struct to make more room if they need to.
* Meta-data is still experimental.
*/
struct meta_field_header {
u_long cookie; /* cookie for the field. Skip fields you don't
* know about (same cookie as in messgaes) */
u_short type; /* field ID */
u_short len; /* total len of this field including extra
* data */
char data[0]; /* data starts here */
};
/* To zero out an option 'in place' set it's cookie to this */
#define NGM_INVALID_COOKIE 865455152
/* This part of the metadata is always present if the pointer is non NULL */
struct ng_meta {
char priority; /* -ve is less priority, 0 is default */
char discardability; /* higher is less valuable.. discard first */
u_short allocated_len; /* amount malloc'd */
u_short used_len; /* sum of all fields, options etc. */
u_short flags; /* see below.. generic flags */
struct meta_field_header options[0]; /* add as (if) needed */
};
typedef struct ng_meta *meta_p;
/* Flags for meta-data */
#define NGMF_TEST 0x01 /* discard at the last moment before sending */
#define NGMF_TRACE 0x02 /* trace when handing this data to a node */
/* node method definitions */
typedef int ng_constructor_t(node_p *node);
typedef int ng_rcvmsg_t(node_p node, struct ng_mesg *msg,
const char *retaddr, struct ng_mesg **resp);
typedef int ng_shutdown_t(node_p node);
typedef int ng_newhook_t(node_p node, hook_p hook, const char *name);
typedef hook_p ng_findhook_t(node_p node, const char *name);
typedef int ng_connect_t(hook_p hook);
typedef int ng_rcvdata_t(hook_p hook, struct mbuf *m, meta_p meta);
typedef int ng_disconnect_t(hook_p hook);
/*
* Command list -- each node type specifies the command that it knows
* how to convert between ASCII and binary using an array of these.
* The last element in the array must be a terminator with cookie=0.
*/
struct ng_cmdlist {
u_int32_t cookie; /* command typecookie */
int cmd; /* command number */
const char *name; /* command name */
const struct ng_parse_type *mesgType; /* args if !NGF_RESP */
const struct ng_parse_type *respType; /* args if NGF_RESP */
};
/*
* Structure of a node type
*/
struct ng_type {
u_int32_t version; /* must equal NG_VERSION */
const char *name; /* Unique type name */
modeventhand_t mod_event; /* Module event handler (optional) */
ng_constructor_t *constructor; /* Node constructor */
ng_rcvmsg_t *rcvmsg; /* control messages come here */
ng_shutdown_t *shutdown; /* reset, and free resources */
ng_newhook_t *newhook; /* first notification of new hook */
ng_findhook_t *findhook; /* only if you have 23000 hooks */
ng_connect_t *connect; /* final notification of new hook */
ng_rcvdata_t *rcvdata; /* date comes here */
ng_rcvdata_t *rcvdataq; /* or here if been queued */
ng_disconnect_t *disconnect; /* notify on disconnect */
const struct ng_cmdlist *cmdlist; /* commands we can convert */
/* R/W data private to the base netgraph code DON'T TOUCH! */
LIST_ENTRY(ng_type) types; /* linked list of all types */
int refs; /* number of instances */
};
/* Send data packet with meta-data */
#define NG_SEND_DATA(error, hook, m, a) \
do { \
(error) = ng_send_data((hook), (m), (a)); \
(m) = NULL; \
(a) = NULL; \
} while (0)
/* Send queued data packet with meta-data */
#define NG_SEND_DATAQ(error, hook, m, a) \
do { \
(error) = ng_send_dataq((hook), (m), (a)); \
(m) = NULL; \
(a) = NULL; \
} while (0)
/* Free metadata */
#define NG_FREE_META(a) \
do { \
if ((a)) { \
FREE((a), M_NETGRAPH); \
a = NULL; \
} \
} while (0)
/* Free any data packet and/or meta-data */
#define NG_FREE_DATA(m, a) \
do { \
if ((m)) { \
m_freem((m)); \
m = NULL; \
} \
NG_FREE_META((a)); \
} while (0)
/*
* Use the NETGRAPH_INIT() macro to link a node type into the
* netgraph system. This works for types compiled into the kernel
* as well as KLD modules. The first argument should be the type
* name (eg, echo) and the second a pointer to the type struct.
*
* If a different link time is desired, e.g., a device driver that
* needs to install its netgraph type before probing, use the
* NETGRAPH_INIT_ORDERED() macro instead. Deivce drivers probably
* want to use SI_SUB_DRIVERS instead of SI_SUB_PSEUDO.
*/
#define NETGRAPH_INIT_ORDERED(typename, typestructp, sub, order) \
static moduledata_t ng_##typename##_mod = { \
"ng_" #typename, \
ng_mod_event, \
(typestructp) \
}; \
DECLARE_MODULE(ng_##typename, ng_##typename##_mod, sub, order)
#define NETGRAPH_INIT(tn, tp) \
NETGRAPH_INIT_ORDERED(tn, tp, SI_SUB_PSEUDO, SI_ORDER_ANY)
/* Special malloc() type for netgraph structs and ctrl messages */
MALLOC_DECLARE(M_NETGRAPH);
int ng_bypass(hook_p hook1, hook_p hook2);
void ng_cutlinks(node_p node);
int ng_con_nodes(node_p node,
const char *name, node_p node2, const char *name2);
void ng_destroy_hook(hook_p hook);
hook_p ng_findhook(node_p node, const char *name);
node_p ng_findname(node_p node, const char *name);
struct ng_type *ng_findtype(const char *type);
int ng_make_node(const char *type, node_p *nodepp);
int ng_make_node_common(struct ng_type *typep, node_p *nodep);
int ng_mkpeer(node_p node, const char *name, const char *name2, char *type);
int ng_mod_event(module_t mod, int what, void *arg);
int ng_name_node(node_p node, const char *name);
int ng_newtype(struct ng_type *tp);
ng_ID_t ng_node2ID(node_p node);
int ng_path2node(node_p here, const char *path, node_p *dest, char **rtnp);
int ng_path_parse(char *addr, char **node, char **path, char **hook);
int ng_queue_data(hook_p hook, struct mbuf *m, meta_p meta);
int ng_queue_msg(node_p here, struct ng_mesg *msg, int len,
const char *address);
void ng_release_node(node_p node);
void ng_rmnode(node_p node);
int ng_send_data(hook_p hook, struct mbuf *m, meta_p meta);
int ng_send_dataq(hook_p hook, struct mbuf *m, meta_p meta);
int ng_send_msg(node_p here, struct ng_mesg *msg,
const char *address, struct ng_mesg **resp);
void ng_unname(node_p node);
void ng_unref(node_p node);
int ng_wait_node(node_p node, char *msg);
#endif /* _NETGRAPH_NETGRAPH_H_ */
/*
* ng_ksocket.c
*
* Copyright (c) 1996-1999 Whistle Communications, Inc.
* All rights reserved.
*
* Subject to the following obligations and disclaimer of warranty, use and
* redistribution of this software, in source or object code forms, with or
* without modifications are expressly permitted by Whistle Communications;
* provided, however, that:
* 1. Any and all reproductions of the source or object code must include the
* copyright notice above and the following disclaimer of warranties; and
* 2. No rights are granted, in any manner or form, to use Whistle
* Communications, Inc. trademarks, including the mark "WHISTLE
* COMMUNICATIONS" on advertising, endorsements, or otherwise except as
* such appears in the above copyright notice or in the software.
*
* THIS SOFTWARE IS BEING PROVIDED BY WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS "AS IS", AND
* TO THE MAXIMUM EXTENT PERMITTED BY LAW, WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS MAKES NO
* REPRESENTATIONS OR WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, REGARDING THIS SOFTWARE,
* INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY AND ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
* MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR NON-INFRINGEMENT.
* WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS DOES NOT WARRANT, GUARANTEE, OR MAKE ANY
* REPRESENTATIONS REGARDING THE USE OF, OR THE RESULTS OF THE USE OF THIS
* SOFTWARE IN TERMS OF ITS CORRECTNESS, ACCURACY, RELIABILITY OR OTHERWISE.
* IN NO EVENT SHALL WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DAMAGES
* RESULTING FROM OR ARISING OUT OF ANY USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, INCLUDING
* WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY,
* PUNITIVE, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR
* SERVICES, LOSS OF USE, DATA OR PROFITS, HOWEVER CAUSED AND UNDER ANY
* THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
* (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF
* THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS IS ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY
* OF SUCH DAMAGE.
*
* Author: Archie Cobbs <archie@whistle.com>
*
* $FreeBSD: src/sys/netgraph/ng_ksocket.c,v 1.5 1999/12/07 05:50:47 julian Exp $
* $Whistle: ng_ksocket.c,v 1.1 1999/11/16 20:04:40 archie Exp $
*/
/*
* Kernel socket node type. This node type is basically a kernel-mode
* version of a socket... kindof like the reverse of the socket node type.
*/
#include <sys/param.h>
#include <sys/systm.h>
#include <sys/kernel.h>
#include <sys/mbuf.h>
#include <sys/proc.h>
#include <sys/malloc.h>
#include <sys/ctype.h>
#include <sys/protosw.h>
#include <sys/errno.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/socketvar.h>
#include <sys/uio.h>
#include <sys/un.h>
#include <netgraph/ng_message.h>
#include <netgraph/netgraph.h>
#include <netgraph/ng_parse.h>
#include <netgraph/ng_ksocket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <netatalk/at.h>
#define OFFSETOF(s, e) ((char *)&((s *)0)->e - (char *)((s *)0))
#define SADATA_OFFSET (OFFSETOF(struct sockaddr, sa_data))
/* Node private data */
struct ng_ksocket_private {
hook_p hook;
struct socket *so;
};
typedef struct ng_ksocket_private *priv_p;
/* Netgraph node methods */
static ng_constructor_t ng_ksocket_constructor;
static ng_rcvmsg_t ng_ksocket_rcvmsg;
static ng_shutdown_t ng_ksocket_rmnode;
static ng_newhook_t ng_ksocket_newhook;
static ng_rcvdata_t ng_ksocket_rcvdata;
static ng_disconnect_t ng_ksocket_disconnect;
/* Alias structure */
struct ng_ksocket_alias {
const char *name;
const int value;
const int family;
};
/* Protocol family aliases */
static const struct ng_ksocket_alias ng_ksocket_families[] = {
{ "local", PF_LOCAL },
{ "inet", PF_INET },
{ "inet6", PF_INET6 },
{ "atalk", PF_APPLETALK },
{ "ipx", PF_IPX },
{ "atm", PF_ATM },
{ NULL, -1 },
};
/* Socket type aliases */
static const struct ng_ksocket_alias ng_ksocket_types[] = {
{ "stream", SOCK_STREAM },
{ "dgram", SOCK_DGRAM },
{ "raw", SOCK_RAW },
{ "rdm", SOCK_RDM },
{ "seqpacket", SOCK_SEQPACKET },
{ NULL, -1 },
};
/* Protocol aliases */
static const struct ng_ksocket_alias ng_ksocket_protos[] = {
{ "ip", IPPROTO_IP, PF_INET },
{ "raw", IPPROTO_IP, PF_INET },
{ "icmp", IPPROTO_ICMP, PF_INET },
{ "igmp", IPPROTO_IGMP, PF_INET },
{ "tcp", IPPROTO_TCP, PF_INET },
{ "udp", IPPROTO_UDP, PF_INET },
{ "gre", IPPROTO_GRE, PF_INET },
{ "esp", IPPROTO_ESP, PF_INET },
{ "ah", IPPROTO_AH, PF_INET },
{ "swipe", IPPROTO_SWIPE, PF_INET },
{ "encap", IPPROTO_ENCAP, PF_INET },
{ "divert", IPPROTO_DIVERT, PF_INET },
{ "ddp", ATPROTO_DDP, PF_APPLETALK },
{ "aarp", ATPROTO_AARP, PF_APPLETALK },
{ NULL, -1 },
};
/* Helper functions */
static void ng_ksocket_incoming(struct socket *so, void *arg, int waitflag);
static int ng_ksocket_parse(const struct ng_ksocket_alias *aliases,
const char *s, int family);
/************************************************************************
STRUCT SOCKADDR PARSE TYPE
************************************************************************/
/* Get the length of the data portion of a generic struct sockaddr */
static int
ng_parse_generic_sockdata_getLength(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *start, const u_char *buf)
{
const struct sockaddr *sa;
sa = (const struct sockaddr *)(buf - SADATA_OFFSET);
return sa->sa_len - SADATA_OFFSET;
}
/* Type for the variable length data portion of a generic struct sockaddr */
static const struct ng_parse_type ng_ksocket_generic_sockdata_type = {
&ng_parse_bytearray_type,
&ng_parse_generic_sockdata_getLength
};
/* Type for a generic struct sockaddr */
static const struct ng_parse_struct_info ng_parse_generic_sockaddr_type_info = {
{
{ "len", &ng_parse_int8_type },
{ "family", &ng_parse_int8_type },
{ "data", &ng_ksocket_generic_sockdata_type },
{ NULL }
}
};
static const struct ng_parse_type ng_ksocket_generic_sockaddr_type = {
&ng_parse_struct_type,
&ng_parse_generic_sockaddr_type_info
};
/* Convert a struct sockaddr from ASCII to binary. If its a protocol
family that we specially handle, do that, otherwise defer to the
generic parse type ng_ksocket_generic_sockaddr_type. */
static int
ng_ksocket_sockaddr_parse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const char *s, int *off, const u_char *const start,
u_char *const buf, int *buflen)
{
struct sockaddr *const sa = (struct sockaddr *)buf;
enum ng_parse_token tok;
char fambuf[32];
int family, len;
char *t;
/* If next token is a left curly brace, use generic parse type */
if ((tok = ng_parse_get_token(s, off, &len)) == T_LBRACE) {
return (*ng_ksocket_generic_sockaddr_type.supertype->parse)
(&ng_ksocket_generic_sockaddr_type,
s, off, start, buf, buflen);
}
/* Get socket address family followed by a slash */
while (isspace(s[*off]))
(*off)++;
if ((t = index(s + *off, '/')) == NULL)
return (EINVAL);
if ((len = t - (s + *off)) > sizeof(fambuf) - 1)
return (EINVAL);
strncpy(fambuf, s + *off, len);
fambuf[len] = '\0';
*off += len + 1;
if ((family = ng_ksocket_parse(ng_ksocket_families, fambuf, 0)) == -1)
return (EINVAL);
/* Set family */
if (*buflen < SADATA_OFFSET)
return (ERANGE);
sa->sa_family = family;
/* Set family-specific data and length */
switch (sa->sa_family) {
case PF_LOCAL: /* Get pathname */
{
const int pathoff = OFFSETOF(struct sockaddr_un, sun_path);
struct sockaddr_un *const sun = (struct sockaddr_un *)sa;
int toklen, pathlen;
char *path;
if ((path = ng_get_string_token(s, off, &toklen)) == NULL)
return (EINVAL);
pathlen = strlen(path);
if (pathlen > SOCK_MAXADDRLEN) {
FREE(path, M_NETGRAPH);
return (E2BIG);
}
if (*buflen < pathoff + pathlen) {
FREE(path, M_NETGRAPH);
return (ERANGE);
}
*off += toklen;
bcopy(path, sun->sun_path, pathlen);
sun->sun_len = pathoff + pathlen;
FREE(path, M_NETGRAPH);
break;
}
case PF_INET: /* Get an IP address with optional port */
{
struct sockaddr_in *const sin = (struct sockaddr_in *)sa;
int i;
/* Parse this: <ipaddress>[:port] */
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
u_long val;
char *eptr;
val = strtoul(s + *off, &eptr, 10);
if (val > 0xff || eptr == s + *off)
return (EINVAL);
*off += (eptr - (s + *off));
((u_char *)&sin->sin_addr)[i] = (u_char)val;
if (i < 3) {
if (s[*off] != '.')
return (EINVAL);
(*off)++;
} else if (s[*off] == ':') {
(*off)++;
val = strtoul(s + *off, &eptr, 10);
if (val > 0xffff || eptr == s + *off)
return (EINVAL);
*off += (eptr - (s + *off));
sin->sin_port = htons(val);
} else
sin->sin_port = 0;
}
bzero(&sin->sin_zero, sizeof(sin->sin_zero));
sin->sin_len = sizeof(*sin);
break;
}
#if 0
case PF_APPLETALK: /* XXX implement these someday */
case PF_INET6:
case PF_IPX:
#endif
default:
return (EINVAL);
}
/* Done */
*buflen = sa->sa_len;
return (0);
}
/* Convert a struct sockaddr from binary to ASCII */
static int
ng_ksocket_sockaddr_unparse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *data, int *off, char *cbuf, int cbuflen)
{
const struct sockaddr *sa = (const struct sockaddr *)(data + *off);
int slen = 0;
/* Output socket address, either in special or generic format */
switch (sa->sa_family) {
case PF_LOCAL:
{
const int pathoff = OFFSETOF(struct sockaddr_un, sun_path);
const struct sockaddr_un *sun = (const struct sockaddr_un *)sa;
const int pathlen = sun->sun_len - pathoff;
char pathbuf[SOCK_MAXADDRLEN + 1];
char *pathtoken;
bcopy(sun->sun_path, pathbuf, pathlen);
pathbuf[pathlen] = '\0';
if ((pathtoken = ng_encode_string(pathbuf)) == NULL)
return (ENOMEM);
slen += snprintf(cbuf, cbuflen, "local/%s", pathtoken);
FREE(pathtoken, M_NETGRAPH);
if (slen >= cbuflen)
return (ERANGE);
*off += sun->sun_len;
return (0);
}
case PF_INET:
{
const struct sockaddr_in *sin = (const struct sockaddr_in *)sa;
slen += snprintf(cbuf, cbuflen, "inet/%d.%d.%d.%d",
((const u_char *)&sin->sin_addr)[0],
((const u_char *)&sin->sin_addr)[1],
((const u_char *)&sin->sin_addr)[2],
((const u_char *)&sin->sin_addr)[3]);
if (sin->sin_port != 0) {
slen += snprintf(cbuf + strlen(cbuf),
cbuflen - strlen(cbuf), ":%d",
(u_int)ntohs(sin->sin_port));
}
if (slen >= cbuflen)
return (ERANGE);
*off += sizeof(*sin);
return(0);
}
#if 0
case PF_APPLETALK: /* XXX implement these someday */
case PF_INET6:
case PF_IPX:
#endif
default:
return (*ng_ksocket_generic_sockaddr_type.supertype->unparse)
(&ng_ksocket_generic_sockaddr_type,
data, off, cbuf, cbuflen);
}
}
/* Parse type for struct sockaddr */
static const struct ng_parse_type ng_ksocket_sockaddr_type = {
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
&ng_ksocket_sockaddr_parse,
&ng_ksocket_sockaddr_unparse,
NULL /* no such thing as a default struct sockaddr */
};
/************************************************************************
STRUCT NG_KSOCKET_SOCKOPT PARSE TYPE
************************************************************************/
/* Get length of the struct ng_ksocket_sockopt value field, which is the
just the excess of the message argument portion over the length of
the struct ng_ksocket_sockopt. */
static int
ng_parse_sockoptval_getLength(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *start, const u_char *buf)
{
static const int offset = OFFSETOF(struct ng_ksocket_sockopt, value);
const struct ng_ksocket_sockopt *sopt;
const struct ng_mesg *msg;
sopt = (const struct ng_ksocket_sockopt *)(buf - offset);
msg = (const struct ng_mesg *)((const u_char *)sopt - sizeof(*msg));
return msg->header.arglen - sizeof(*sopt);
}
/* Parse type for the option value part of a struct ng_ksocket_sockopt
XXX Eventually, we should handle the different socket options specially.
XXX This would avoid byte order problems, eg an integer value of 1 is
XXX going to be "[1]" for little endian or "[3=1]" for big endian. */
static const struct ng_parse_type ng_ksocket_sockoptval_type = {
&ng_parse_bytearray_type,
&ng_parse_sockoptval_getLength
};
/* Parse type for struct ng_ksocket_sockopt */
static const struct ng_parse_struct_info ng_ksocket_sockopt_type_info
= NG_KSOCKET_SOCKOPT_INFO(&ng_ksocket_sockoptval_type);
static const struct ng_parse_type ng_ksocket_sockopt_type = {
&ng_parse_struct_type,
&ng_ksocket_sockopt_type_info,
};
/* List of commands and how to convert arguments to/from ASCII */
static const struct ng_cmdlist ng_ksocket_cmds[] = {
{
NGM_KSOCKET_COOKIE,
NGM_KSOCKET_BIND,
"bind",
&ng_ksocket_sockaddr_type,
NULL
},
{
NGM_KSOCKET_COOKIE,
NGM_KSOCKET_LISTEN,
"listen",
&ng_parse_int32_type,
NULL
},
{
NGM_KSOCKET_COOKIE,
NGM_KSOCKET_ACCEPT,
"accept",
NULL,
&ng_ksocket_sockaddr_type
},
{
NGM_KSOCKET_COOKIE,
NGM_KSOCKET_CONNECT,
"connect",
&ng_ksocket_sockaddr_type,
NULL
},
{
NGM_KSOCKET_COOKIE,
NGM_KSOCKET_GETNAME,
"getname",
NULL,
&ng_ksocket_sockaddr_type
},
{
NGM_KSOCKET_COOKIE,
NGM_KSOCKET_GETPEERNAME,
"getpeername",
NULL,
&ng_ksocket_sockaddr_type
},
{
NGM_KSOCKET_COOKIE,
NGM_KSOCKET_SETOPT,
"setopt",
&ng_ksocket_sockopt_type,
NULL
},
{
NGM_KSOCKET_COOKIE,
NGM_KSOCKET_GETOPT,
"getopt",
&ng_ksocket_sockopt_type,
&ng_ksocket_sockopt_type
},
{ 0 }
};
/* Node type descriptor */
static struct ng_type ng_ksocket_typestruct = {
NG_VERSION,
NG_KSOCKET_NODE_TYPE,
NULL,
ng_ksocket_constructor,
ng_ksocket_rcvmsg,
ng_ksocket_rmnode,
ng_ksocket_newhook,
NULL,
NULL,
ng_ksocket_rcvdata,
ng_ksocket_rcvdata,
ng_ksocket_disconnect,
ng_ksocket_cmds
};
NETGRAPH_INIT(ksocket, &ng_ksocket_typestruct);
#define ERROUT(x) do { error = (x); goto done; } while (0)
/************************************************************************
NETGRAPH NODE STUFF
************************************************************************/
/*
* Node type constructor
*/
static int
ng_ksocket_constructor(node_p *nodep)
{
priv_p priv;
int error;
/* Allocate private structure */
MALLOC(priv, priv_p, sizeof(*priv), M_NETGRAPH, M_WAITOK);
if (priv == NULL)
return (ENOMEM);
bzero(priv, sizeof(*priv));
/* Call generic node constructor */
if ((error = ng_make_node_common(&ng_ksocket_typestruct, nodep))) {
FREE(priv, M_NETGRAPH);
return (error);
}
(*nodep)->private = priv;
/* Done */
return (0);
}
/*
* Give our OK for a hook to be added. The hook name is of the
* form "<family>:<type>:<proto>" where the three components may
* be decimal numbers or else aliases from the above lists.
*
* Connecting a hook amounts to opening the socket. Disconnecting
* the hook closes the socket and destroys the node as well.
*/
static int
ng_ksocket_newhook(node_p node, hook_p hook, const char *name0)
{
struct proc *p = curproc ? curproc : &proc0; /* XXX broken */
const priv_p priv = node->private;
char *s1, *s2, name[NG_HOOKLEN+1];
int family, type, protocol, error;
/* Check if we're already connected */
if (priv->hook != NULL)
return (EISCONN);
/* Extract family, type, and protocol from hook name */
snprintf(name, sizeof(name), "%s", name0);
s1 = name;
if ((s2 = index(s1, '/')) == NULL)
return (EINVAL);
*s2++ = '\0';
if ((family = ng_ksocket_parse(ng_ksocket_families, s1, 0)) == -1)
return (EINVAL);
s1 = s2;
if ((s2 = index(s1, '/')) == NULL)
return (EINVAL);
*s2++ = '\0';
if ((type = ng_ksocket_parse(ng_ksocket_types, s1, 0)) == -1)
return (EINVAL);
s1 = s2;
if ((protocol = ng_ksocket_parse(ng_ksocket_protos, s1, family)) == -1)
return (EINVAL);
/* Create the socket */
if ((error = socreate(family, &priv->so, type, protocol, p)) != 0)
return (error);
/* XXX call soreserve() ? */
/* Add our hook for incoming data */
priv->so->so_upcallarg = (caddr_t)node;
priv->so->so_upcall = ng_ksocket_incoming;
priv->so->so_rcv.sb_flags |= SB_UPCALL;
/* OK */
priv->hook = hook;
return (0);
}
/*
* Receive a control message
*/
static int
ng_ksocket_rcvmsg(node_p node, struct ng_mesg *msg,
const char *raddr, struct ng_mesg **rptr)
{
struct proc *p = curproc ? curproc : &proc0; /* XXX broken */
const priv_p priv = node->private;
struct socket *const so = priv->so;
struct ng_mesg *resp = NULL;
int error = 0;
switch (msg->header.typecookie) {
case NGM_KSOCKET_COOKIE:
switch (msg->header.cmd) {
case NGM_KSOCKET_BIND:
{
struct sockaddr *const sa
= (struct sockaddr *)msg->data;
/* Sanity check */
if (msg->header.arglen < SADATA_OFFSET
|| msg->header.arglen < sa->sa_len)
ERROUT(EINVAL);
if (so == NULL)
ERROUT(ENXIO);
/* Bind */
error = sobind(so, sa, p);
break;
}
case NGM_KSOCKET_LISTEN:
{
/* Sanity check */
if (msg->header.arglen != sizeof(int))
ERROUT(EINVAL);
if (so == NULL)
ERROUT(ENXIO);
/* Listen */
if ((error = solisten(so, *((int *)msg->data), p)) != 0)
break;
/* Notify sender when we get a connection attempt */
/* XXX implement me */
error = ENODEV;
break;
}
case NGM_KSOCKET_ACCEPT:
{
/* Sanity check */
if (msg->header.arglen != 0)
ERROUT(EINVAL);
if (so == NULL)
ERROUT(ENXIO);
/* Accept on the socket in a non-blocking way */
/* Create a new ksocket node for the new connection */
/* Return a response with the peer's sockaddr and
the absolute name of the newly created node */
/* XXX implement me */
error = ENODEV;
break;
}
case NGM_KSOCKET_CONNECT:
{
struct sockaddr *const sa
= (struct sockaddr *)msg->data;
/* Sanity check */
if (msg->header.arglen < SADATA_OFFSET
|| msg->header.arglen < sa->sa_len)
ERROUT(EINVAL);
if (so == NULL)
ERROUT(ENXIO);
/* Do connect */
if ((so->so_state & SS_ISCONNECTING) != 0)
ERROUT(EALREADY);
if ((error = soconnect(so, sa, p)) != 0) {
so->so_state &= ~SS_ISCONNECTING;
ERROUT(error);
}
if ((so->so_state & SS_ISCONNECTING) != 0)
/* Notify sender when we connect */
/* XXX implement me */
ERROUT(EINPROGRESS);
break;
}
case NGM_KSOCKET_GETNAME:
case NGM_KSOCKET_GETPEERNAME:
{
int (*func)(struct socket *so, struct sockaddr **nam);
struct sockaddr *sa = NULL;
int len;
/* Sanity check */
if (msg->header.arglen != 0)
ERROUT(EINVAL);
if (so == NULL)
ERROUT(ENXIO);
/* Get function */
if (msg->header.cmd == NGM_KSOCKET_GETPEERNAME) {
if ((so->so_state
& (SS_ISCONNECTED|SS_ISCONFIRMING)) == 0)
ERROUT(ENOTCONN);
func = so->so_proto->pr_usrreqs->pru_peeraddr;
} else
func = so->so_proto->pr_usrreqs->pru_sockaddr;
/* Get local or peer address */
if ((error = (*func)(so, &sa)) != 0)
goto bail;
len = (sa == NULL) ? 0 : sa->sa_len;
/* Send it back in a response */
NG_MKRESPONSE(resp, msg, len, M_NOWAIT);
if (resp == NULL) {
error = ENOMEM;
goto bail;
}
bcopy(sa, resp->data, len);
bail:
/* Cleanup */
if (sa != NULL)
FREE(sa, M_SONAME);
break;
}
case NGM_KSOCKET_GETOPT:
{
struct ng_ksocket_sockopt *ksopt =
(struct ng_ksocket_sockopt *)msg->data;
struct sockopt sopt;
/* Sanity check */
if (msg->header.arglen != sizeof(*ksopt))
ERROUT(EINVAL);
if (so == NULL)
ERROUT(ENXIO);
/* Get response with room for option value */
NG_MKRESPONSE(resp, msg, sizeof(*ksopt)
+ NG_KSOCKET_MAX_OPTLEN, M_NOWAIT);
if (resp == NULL)
ERROUT(ENOMEM);
/* Get socket option, and put value in the response */
sopt.sopt_dir = SOPT_GET;
sopt.sopt_level = ksopt->level;
sopt.sopt_name = ksopt->name;
sopt.sopt_p = p;
sopt.sopt_valsize = NG_KSOCKET_MAX_OPTLEN;
ksopt = (struct ng_ksocket_sockopt *)resp->data;
sopt.sopt_val = ksopt->value;
if ((error = sogetopt(so, &sopt)) != 0) {
FREE(resp, M_NETGRAPH);
break;
}
/* Set actual value length */
resp->header.arglen = sizeof(*ksopt)
+ sopt.sopt_valsize;
break;
}
case NGM_KSOCKET_SETOPT:
{
struct ng_ksocket_sockopt *const ksopt =
(struct ng_ksocket_sockopt *)msg->data;
const int valsize = msg->header.arglen - sizeof(*ksopt);
struct sockopt sopt;
/* Sanity check */
if (valsize < 0)
ERROUT(EINVAL);
if (so == NULL)
ERROUT(ENXIO);
/* Set socket option */
sopt.sopt_dir = SOPT_SET;
sopt.sopt_level = ksopt->level;
sopt.sopt_name = ksopt->name;
sopt.sopt_val = ksopt->value;
sopt.sopt_valsize = valsize;
sopt.sopt_p = p;
error = sosetopt(so, &sopt);
break;
}
default:
error = EINVAL;
break;
}
break;
default:
error = EINVAL;
break;
}
if (rptr)
*rptr = resp;
else if (resp)
FREE(resp, M_NETGRAPH);
done:
FREE(msg, M_NETGRAPH);
return (error);
}
/*
* Receive incoming data on our hook. Send it out the socket.
*/
static int
ng_ksocket_rcvdata(hook_p hook, struct mbuf *m, meta_p meta)
{
struct proc *p = curproc ? curproc : &proc0; /* XXX broken */
const node_p node = hook->node;
const priv_p priv = node->private;
struct socket *const so = priv->so;
int error;
NG_FREE_META(meta);
error = (*so->so_proto->pr_usrreqs->pru_sosend)(so, 0, 0, m, 0, 0, p);
return (error);
}
/*
* Destroy node
*/
static int
ng_ksocket_rmnode(node_p node)
{
const priv_p priv = node->private;
/* Close our socket (if any) */
if (priv->so != NULL) {
priv->so->so_upcall = NULL;
priv->so->so_rcv.sb_flags &= ~SB_UPCALL;
soclose(priv->so);
priv->so = NULL;
}
/* Take down netgraph node */
node->flags |= NG_INVALID;
ng_cutlinks(node);
ng_unname(node);
bzero(priv, sizeof(*priv));
FREE(priv, M_NETGRAPH);
node->private = NULL;
ng_unref(node); /* let the node escape */
return (0);
}
/*
* Hook disconnection
*/
static int
ng_ksocket_disconnect(hook_p hook)
{
KASSERT(hook->node->numhooks == 0,
("%s: numhooks=%d?", __FUNCTION__, hook->node->numhooks));
ng_rmnode(hook->node);
return (0);
}
/************************************************************************
HELPER STUFF
************************************************************************/
/*
* When incoming data is appended to the socket, we get notified here.
*/
static void
ng_ksocket_incoming(struct socket *so, void *arg, int waitflag)
{
const node_p node = arg;
const priv_p priv = node->private;
meta_p meta = NULL;
struct sockaddr *nam;
struct mbuf *m;
struct uio auio;
int s, flags, error;
s = splnet();
/* Sanity check */
if ((node->flags & NG_INVALID) != 0) {
splx(s);
return;
}
KASSERT(so == priv->so, ("%s: wrong socket", __FUNCTION__));
KASSERT(priv->hook != NULL, ("%s: no hook", __FUNCTION__));
/* Read and forward available mbuf's */
auio.uio_procp = NULL;
auio.uio_resid = 1000000000;
flags = MSG_DONTWAIT;
do {
if ((error = (*so->so_proto->pr_usrreqs->pru_soreceive)
(so, &nam, &auio, &m, (struct mbuf **)0, &flags)) == 0
&& m != NULL) {
struct mbuf *n;
/* Don't trust the various socket layers to get the
packet header and length correct (eg. kern/15175) */
for (n = m, m->m_pkthdr.len = 0; n; n = n->m_next)
m->m_pkthdr.len += n->m_len;
NG_SEND_DATA(error, priv->hook, m, meta);
}
} while (error == 0 && m != NULL);
splx(s);
}
/*
* Parse out either an integer value or an alias.
*/
static int
ng_ksocket_parse(const struct ng_ksocket_alias *aliases,
const char *s, int family)
{
int k, val;
char *eptr;
/* Try aliases */
for (k = 0; aliases[k].name != NULL; k++) {
if (strcmp(s, aliases[k].name) == 0
&& aliases[k].family == family)
return aliases[k].value;
}
/* Try parsing as a number */
val = (int)strtoul(s, &eptr, 10);
if (val < 0 || *eptr != '\0')
return (-1);
return (val);
}
/*
* ng_ksocket.h
*
* Copyright (c) 1996-1999 Whistle Communications, Inc.
* All rights reserved.
*
* Subject to the following obligations and disclaimer of warranty, use and
* redistribution of this software, in source or object code forms, with or
* without modifications are expressly permitted by Whistle Communications;
* provided, however, that:
* 1. Any and all reproductions of the source or object code must include the
* copyright notice above and the following disclaimer of warranties; and
* 2. No rights are granted, in any manner or form, to use Whistle
* Communications, Inc. trademarks, including the mark "WHISTLE
* COMMUNICATIONS" on advertising, endorsements, or otherwise except as
* such appears in the above copyright notice or in the software.
*
* THIS SOFTWARE IS BEING PROVIDED BY WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS "AS IS", AND
* TO THE MAXIMUM EXTENT PERMITTED BY LAW, WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS MAKES NO
* REPRESENTATIONS OR WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, REGARDING THIS SOFTWARE,
* INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY AND ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
* MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR NON-INFRINGEMENT.
* WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS DOES NOT WARRANT, GUARANTEE, OR MAKE ANY
* REPRESENTATIONS REGARDING THE USE OF, OR THE RESULTS OF THE USE OF THIS
* SOFTWARE IN TERMS OF ITS CORRECTNESS, ACCURACY, RELIABILITY OR OTHERWISE.
* IN NO EVENT SHALL WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DAMAGES
* RESULTING FROM OR ARISING OUT OF ANY USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, INCLUDING
* WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY,
* PUNITIVE, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR
* SERVICES, LOSS OF USE, DATA OR PROFITS, HOWEVER CAUSED AND UNDER ANY
* THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
* (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF
* THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS IS ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY
* OF SUCH DAMAGE.
*
* Author: Archie Cobbs <archie@whistle.com>
*
* $FreeBSD: src/sys/netgraph/ng_ksocket.h,v 1.2 1999/11/30 02:45:21 archie Exp $
* $Whistle: ng_ksocket.h,v 1.1 1999/11/16 20:04:40 archie Exp $
*/
#ifndef _NETGRAPH_KSOCKET_H_
#define _NETGRAPH_KSOCKET_H_
/* Node type name and magic cookie */
#define NG_KSOCKET_NODE_TYPE "ksocket"
#define NGM_KSOCKET_COOKIE 942710669
/* For NGM_KSOCKET_SETOPT and NGM_KSOCKET_GETOPT control messages */
struct ng_ksocket_sockopt {
u_int32_t level; /* second arg of [gs]etsockopt() */
u_int32_t name; /* third arg of [gs]etsockopt() */
u_char value[0]; /* fourth arg of [gs]etsockopt() */
};
/* Max length socket option we can return via NGM_KSOCKET_GETOPT
XXX This should not be necessary, we should dynamically size
XXX the response. Until then.. */
#define NG_KSOCKET_MAX_OPTLEN 1024
/* Keep this in sync with the above structure definition */
#define NG_KSOCKET_SOCKOPT_INFO(svtype) { \
{ \
{ "level", &ng_parse_int32_type }, \
{ "name", &ng_parse_int32_type }, \
{ "value", (svtype) }, \
{ NULL }, \
} \
}
/* Netgraph commands */
enum {
NGM_KSOCKET_BIND = 1,
NGM_KSOCKET_LISTEN,
NGM_KSOCKET_ACCEPT,
NGM_KSOCKET_CONNECT,
NGM_KSOCKET_GETNAME,
NGM_KSOCKET_GETPEERNAME,
NGM_KSOCKET_SETOPT,
NGM_KSOCKET_GETOPT,
};
#endif /* _NETGRAPH_KSOCKET_H_ */
/*
* ng_message.h
*
* Copyright (c) 1996-1999 Whistle Communications, Inc.
* All rights reserved.
*
* Subject to the following obligations and disclaimer of warranty, use and
* redistribution of this software, in source or object code forms, with or
* without modifications are expressly permitted by Whistle Communications;
* provided, however, that:
* 1. Any and all reproductions of the source or object code must include the
* copyright notice above and the following disclaimer of warranties; and
* 2. No rights are granted, in any manner or form, to use Whistle
* Communications, Inc. trademarks, including the mark "WHISTLE
* COMMUNICATIONS" on advertising, endorsements, or otherwise except as
* such appears in the above copyright notice or in the software.
*
* THIS SOFTWARE IS BEING PROVIDED BY WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS "AS IS", AND
* TO THE MAXIMUM EXTENT PERMITTED BY LAW, WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS MAKES NO
* REPRESENTATIONS OR WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, REGARDING THIS SOFTWARE,
* INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY AND ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
* MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR NON-INFRINGEMENT.
* WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS DOES NOT WARRANT, GUARANTEE, OR MAKE ANY
* REPRESENTATIONS REGARDING THE USE OF, OR THE RESULTS OF THE USE OF THIS
* SOFTWARE IN TERMS OF ITS CORRECTNESS, ACCURACY, RELIABILITY OR OTHERWISE.
* IN NO EVENT SHALL WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DAMAGES
* RESULTING FROM OR ARISING OUT OF ANY USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, INCLUDING
* WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY,
* PUNITIVE, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR
* SERVICES, LOSS OF USE, DATA OR PROFITS, HOWEVER CAUSED AND UNDER ANY
* THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
* (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF
* THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS IS ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY
* OF SUCH DAMAGE.
*
* Author: Julian Elischer <julian@whistle.com>
*
* $FreeBSD: src/sys/netgraph/ng_message.h,v 1.4 1999/12/29 04:46:00 peter Exp $
* $Whistle: ng_message.h,v 1.12 1999/01/25 01:17:44 archie Exp $
*/
#ifndef _NETGRAPH_NG_MESSAGE_H_
#define _NETGRAPH_NG_MESSAGE_H_ 1
/* ASCII string size limits */
#define NG_TYPELEN 15 /* max type name len (16 with null) */
#define NG_HOOKLEN 15 /* max hook name len (16 with null) */
#define NG_NODELEN 15 /* max node name len (16 with null) */
#define NG_PATHLEN 511 /* max path len (512 with null) */
#define NG_CMDSTRLEN 15 /* max command string (16 with null) */
#define NG_TEXTRESPONSE 1024 /* allow this length for a text response */
/* A netgraph message */
struct ng_mesg {
struct ng_msghdr {
u_char version; /* must == NG_VERSION */
u_char spare; /* pad to 2 bytes */
u_int16_t arglen; /* length of data */
u_int32_t flags; /* message status */
u_int32_t token; /* match with reply */
u_int32_t typecookie; /* node's type cookie */
u_int32_t cmd; /* command identifier */
u_char cmdstr[NG_CMDSTRLEN+1]; /* cmd string + \0 */
} header;
char data[0]; /* placeholder for actual data */
};
/* Keep this in sync with the above structure definition */
#define NG_GENERIC_NG_MESG_INFO(dtype) { \
{ \
{ "version", &ng_parse_int8_type }, \
{ "spare", &ng_parse_int8_type }, \
{ "arglen", &ng_parse_int16_type }, \
{ "flags", &ng_parse_int32_type }, \
{ "token", &ng_parse_int32_type }, \
{ "typecookie", &ng_parse_int32_type }, \
{ "cmd", &ng_parse_int32_type }, \
{ "cmdstr", &ng_parse_cmdbuf_type }, \
{ "data", (dtype) }, \
{ NULL }, \
} \
}
/* Negraph type binary compatibility field */
#define NG_VERSION 2
/* Flags field flags */
#define NGF_ORIG 0x0000 /* the msg is the original request */
#define NGF_RESP 0x0001 /* the message is a response */
/* Type of a unique node ID */
#define ng_ID_t unsigned int
/*
* Here we describe the "generic" messages that all nodes inherently
* understand. With the exception of NGM_TEXT_STATUS, these are handled
* automatically by the base netgraph code.
*/
/* Generic message type cookie */
#define NGM_GENERIC_COOKIE 851672668
/* Generic messages defined for this type cookie */
#define NGM_SHUTDOWN 1 /* shut down node */
#define NGM_MKPEER 2 /* create and attach a peer node */
#define NGM_CONNECT 3 /* connect two nodes */
#define NGM_NAME 4 /* give a node a name */
#define NGM_RMHOOK 5 /* break a connection btw. two nodes */
#define NGM_NODEINFO 6 /* get nodeinfo for the target */
#define NGM_LISTHOOKS 7 /* get list of hooks on node */
#define NGM_LISTNAMES 8 /* list all globally named nodes */
#define NGM_LISTNODES 9 /* list all nodes, named and unnamed */
#define NGM_LISTTYPES 10 /* list all installed node types */
#define NGM_TEXT_STATUS 11 /* (optional) get text status report */
#define NGM_BINARY2ASCII 12 /* convert struct ng_mesg to ascii */
#define NGM_ASCII2BINARY 13 /* convert ascii to struct ng_mesg */
/* Structure used for NGM_MKPEER */
struct ngm_mkpeer {
char type[NG_TYPELEN + 1]; /* peer type */
char ourhook[NG_HOOKLEN + 1]; /* hook name */
char peerhook[NG_HOOKLEN + 1]; /* peer hook name */
};
/* Keep this in sync with the above structure definition */
#define NG_GENERIC_MKPEER_INFO() { \
{ \
{ "type", &ng_parse_typebuf_type }, \
{ "ourhook", &ng_parse_hookbuf_type }, \
{ "peerhook", &ng_parse_hookbuf_type }, \
{ NULL }, \
} \
}
/* Structure used for NGM_CONNECT */
struct ngm_connect {
char path[NG_PATHLEN + 1]; /* peer path */
char ourhook[NG_HOOKLEN + 1]; /* hook name */
char peerhook[NG_HOOKLEN + 1]; /* peer hook name */
};
/* Keep this in sync with the above structure definition */
#define NG_GENERIC_CONNECT_INFO() { \
{ \
{ "path", &ng_parse_pathbuf_type }, \
{ "ourhook", &ng_parse_hookbuf_type }, \
{ "peerhook", &ng_parse_hookbuf_type }, \
{ NULL }, \
} \
}
/* Structure used for NGM_NAME */
struct ngm_name {
char name[NG_NODELEN + 1]; /* node name */
};
/* Keep this in sync with the above structure definition */
#define NG_GENERIC_NAME_INFO() { \
{ \
{ "name", &ng_parse_nodebuf_type }, \
{ NULL }, \
} \
}
/* Structure used for NGM_RMHOOK */
struct ngm_rmhook {
char ourhook[NG_HOOKLEN + 1]; /* hook name */
};
/* Keep this in sync with the above structure definition */
#define NG_GENERIC_RMHOOK_INFO() { \
{ \
{ "hook", &ng_parse_hookbuf_type }, \
{ NULL }, \
} \
}
/* Structure used for NGM_NODEINFO */
struct nodeinfo {
char name[NG_NODELEN + 1]; /* node name (if any) */
char type[NG_TYPELEN + 1]; /* peer type */
ng_ID_t id; /* unique identifier */
u_int32_t hooks; /* number of active hooks */
};
/* Keep this in sync with the above structure definition */
#define NG_GENERIC_NODEINFO_INFO() { \
{ \
{ "name", &ng_parse_nodebuf_type }, \
{ "type", &ng_parse_typebuf_type }, \
{ "id", &ng_parse_int32_type }, \
{ "hooks", &ng_parse_int32_type }, \
{ NULL }, \
} \
}
/* Structure used for NGM_LISTHOOKS */
struct linkinfo {
char ourhook[NG_HOOKLEN + 1]; /* hook name */
char peerhook[NG_HOOKLEN + 1]; /* peer hook */
struct nodeinfo nodeinfo;
};
/* Keep this in sync with the above structure definition */
#define NG_GENERIC_LINKINFO_INFO(nitype) { \
{ \
{ "ourhook", &ng_parse_hookbuf_type }, \
{ "peerhook", &ng_parse_hookbuf_type }, \
{ "nodeinfo", (nitype) }, \
{ NULL }, \
} \
}
struct hooklist {
struct nodeinfo nodeinfo; /* node information */
struct linkinfo link[0]; /* info about each hook */
};
/* Keep this in sync with the above structure definition */
#define NG_GENERIC_HOOKLIST_INFO(nitype,litype) { \
{ \
{ "nodeinfo", (nitype) }, \
{ "linkinfo", (litype) }, \
{ NULL }, \
} \
}
/* Structure used for NGM_LISTNAMES/NGM_LISTNODES */
struct namelist {
u_int32_t numnames;
struct nodeinfo nodeinfo[0];
};
/* Keep this in sync with the above structure definition */
#define NG_GENERIC_LISTNODES_INFO(niarraytype) { \
{ \
{ "numnames", &ng_parse_int32_type }, \
{ "nodeinfo", (niarraytype) }, \
{ NULL }, \
} \
}
/* Structure used for NGM_LISTTYPES */
struct typeinfo {
char typename[NG_TYPELEN + 1]; /* name of type */
u_int32_t numnodes; /* number alive */
};
/* Keep this in sync with the above structure definition */
#define NG_GENERIC_TYPEINFO_INFO() { \
{ \
{ "typename", &ng_parse_typebuf_type }, \
{ "typeinfo", &ng_parse_int32_type }, \
{ NULL }, \
} \
}
struct typelist {
u_int32_t numtypes;
struct typeinfo typeinfo[0];
};
/* Keep this in sync with the above structure definition */
#define NG_GENERIC_TYPELIST_INFO(tiarraytype) { \
{ \
{ "numtypes", &ng_parse_int32_type }, \
{ "typeinfo", (tiarraytype) }, \
{ NULL }, \
} \
}
/*
* For netgraph nodes that are somehow associated with file descriptors
* (e.g., a device that has a /dev entry and is also a netgraph node),
* we define a generic ioctl for requesting the corresponding nodeinfo
* structure and for assigning a name (if there isn't one already).
*
* For these to you need to also #include <sys/ioccom.h>.
*/
#define NGIOCGINFO _IOR('N', 40, struct nodeinfo) /* get node info */
#define NGIOCSETNAME _IOW('N', 41, struct ngm_name) /* set node name */
#ifdef _KERNEL
/*
* Allocate and initialize a netgraph message "msg" with "len"
* extra bytes of argument. Sets "msg" to NULL if fails.
* Does not initialize token.
*/
#define NG_MKMESSAGE(msg, cookie, cmdid, len, how) \
do { \
MALLOC((msg), struct ng_mesg *, sizeof(struct ng_mesg) \
+ (len), M_NETGRAPH, (how)); \
if ((msg) == NULL) \
break; \
bzero((msg), sizeof(struct ng_mesg) + (len)); \
(msg)->header.version = NG_VERSION; \
(msg)->header.typecookie = (cookie); \
(msg)->header.cmd = (cmdid); \
(msg)->header.arglen = (len); \
strncpy((msg)->header.cmdstr, #cmdid, \
sizeof((msg)->header.cmdstr) - 1); \
} while (0)
/*
* Allocate and initialize a response "rsp" to a message "msg"
* with "len" extra bytes of argument. Sets "rsp" to NULL if fails.
*/
#define NG_MKRESPONSE(rsp, msg, len, how) \
do { \
MALLOC((rsp), struct ng_mesg *, sizeof(struct ng_mesg) \
+ (len), M_NETGRAPH, (how)); \
if ((rsp) == NULL) \
break; \
bzero((rsp), sizeof(struct ng_mesg) + (len)); \
(rsp)->header.version = NG_VERSION; \
(rsp)->header.arglen = (len); \
(rsp)->header.token = (msg)->header.token; \
(rsp)->header.typecookie = (msg)->header.typecookie; \
(rsp)->header.cmd = (msg)->header.cmd; \
bcopy((msg)->header.cmdstr, (rsp)->header.cmdstr, \
sizeof((rsp)->header.cmdstr)); \
(rsp)->header.flags |= NGF_RESP; \
} while (0)
#endif /* _KERNEL */
#endif /* _NETGRAPH_NG_MESSAGE_H_ */
/*
* ng_parse.c
*
* Copyright (c) 1999 Whistle Communications, Inc.
* All rights reserved.
*
* Subject to the following obligations and disclaimer of warranty, use and
* redistribution of this software, in source or object code forms, with or
* without modifications are expressly permitted by Whistle Communications;
* provided, however, that:
* 1. Any and all reproductions of the source or object code must include the
* copyright notice above and the following disclaimer of warranties; and
* 2. No rights are granted, in any manner or form, to use Whistle
* Communications, Inc. trademarks, including the mark "WHISTLE
* COMMUNICATIONS" on advertising, endorsements, or otherwise except as
* such appears in the above copyright notice or in the software.
*
* THIS SOFTWARE IS BEING PROVIDED BY WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS "AS IS", AND
* TO THE MAXIMUM EXTENT PERMITTED BY LAW, WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS MAKES NO
* REPRESENTATIONS OR WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, REGARDING THIS SOFTWARE,
* INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY AND ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
* MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR NON-INFRINGEMENT.
* WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS DOES NOT WARRANT, GUARANTEE, OR MAKE ANY
* REPRESENTATIONS REGARDING THE USE OF, OR THE RESULTS OF THE USE OF THIS
* SOFTWARE IN TERMS OF ITS CORRECTNESS, ACCURACY, RELIABILITY OR OTHERWISE.
* IN NO EVENT SHALL WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DAMAGES
* RESULTING FROM OR ARISING OUT OF ANY USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, INCLUDING
* WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY,
* PUNITIVE, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR
* SERVICES, LOSS OF USE, DATA OR PROFITS, HOWEVER CAUSED AND UNDER ANY
* THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
* (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF
* THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS IS ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY
* OF SUCH DAMAGE.
*
* Author: Archie Cobbs <archie@whistle.com>
*
* $Whistle: ng_parse.c,v 1.3 1999/11/29 01:43:48 archie Exp $
* $FreeBSD: src/sys/netgraph/ng_parse.c,v 1.3 1999/12/07 05:50:47 julian Exp $
*/
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/param.h>
#include <sys/systm.h>
#include <sys/errno.h>
#include <sys/malloc.h>
#include <sys/ctype.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <netgraph/ng_message.h>
#include <netgraph/netgraph.h>
#include <netgraph/ng_parse.h>
/* Compute alignment for primitive integral types */
struct int16_temp {
char x;
int16_t y;
};
struct int32_temp {
char x;
int32_t y;
};
struct int64_temp {
char x;
int64_t y;
};
#define INT8_ALIGNMENT 1
#define INT16_ALIGNMENT ((int)&((struct int16_temp *)0)->y)
#define INT32_ALIGNMENT ((int)&((struct int32_temp *)0)->y)
#define INT64_ALIGNMENT ((int)&((struct int64_temp *)0)->y)
/* Type of composite object: struct, array, or fixedarray */
enum comptype {
CT_STRUCT,
CT_ARRAY,
CT_FIXEDARRAY,
};
/* Composite types helper functions */
static int ng_parse_composite(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const char *s, int *off, const u_char *start,
u_char *const buf, int *buflen, enum comptype ctype);
static int ng_unparse_composite(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *data, int *off, char *cbuf, int cbuflen,
enum comptype ctype);
static int ng_get_composite_elem_default(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
int index, const u_char *start, u_char *buf,
int *buflen, enum comptype ctype);
static int ng_get_composite_len(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *start, const u_char *buf,
enum comptype ctype);
static const struct ng_parse_type *ng_get_composite_etype(const struct
ng_parse_type *type, int index, enum comptype ctype);
static int ng_parse_get_elem_pad(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
int index, enum comptype ctype, int posn);
/* Parsing helper functions */
static int ng_parse_skip_value(const char *s, int off, int *lenp);
/* Poor man's virtual method calls */
#define METHOD(t,m) (ng_get_ ## m ## _method(t))
#define INVOKE(t,m) (*METHOD(t,m))
static ng_parse_t *ng_get_parse_method(const struct ng_parse_type *t);
static ng_unparse_t *ng_get_unparse_method(const struct ng_parse_type *t);
static ng_getDefault_t *ng_get_getDefault_method(const
struct ng_parse_type *t);
static ng_getAlign_t *ng_get_getAlign_method(const struct ng_parse_type *t);
#define ALIGNMENT(t) (METHOD(t, getAlign) == NULL ? \
0 : INVOKE(t, getAlign)(t))
/* For converting binary to string */
#define NG_PARSE_APPEND(fmt, args...) \
do { \
int len; \
\
len = snprintf((cbuf), (cbuflen), \
fmt , ## args); \
if (len >= (cbuflen)) \
return (ERANGE); \
(cbuf) += len; \
(cbuflen) -= len; \
} while (0)
/************************************************************************
PUBLIC FUNCTIONS
************************************************************************/
/*
* Convert an ASCII string to binary according to the supplied type descriptor
*/
int
ng_parse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const char *string, int *off, u_char *buf, int *buflen)
{
return INVOKE(type, parse)(type, string, off, buf, buf, buflen);
}
/*
* Convert binary to an ASCII string according to the supplied type descriptor
*/
int
ng_unparse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *data, char *cbuf, int cbuflen)
{
int off = 0;
return INVOKE(type, unparse)(type, data, &off, cbuf, cbuflen);
}
/*
* Fill in the default value according to the supplied type descriptor
*/
int
ng_parse_getDefault(const struct ng_parse_type *type, u_char *buf, int *buflen)
{
ng_getDefault_t *const func = METHOD(type, getDefault);
if (func == NULL)
return (EOPNOTSUPP);
return (*func)(type, buf, buf, buflen);
}
/************************************************************************
STRUCTURE TYPE
************************************************************************/
static int
ng_struct_parse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const char *s, int *off, const u_char *const start,
u_char *const buf, int *buflen)
{
return ng_parse_composite(type, s, off, start, buf, buflen, CT_STRUCT);
}
static int
ng_struct_unparse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *data, int *off, char *cbuf, int cbuflen)
{
return ng_unparse_composite(type, data, off, cbuf, cbuflen, CT_STRUCT);
}
static int
ng_struct_getDefault(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *const start, u_char *buf, int *buflen)
{
int off = 0;
return ng_parse_composite(type,
"{}", &off, start, buf, buflen, CT_STRUCT);
}
static int
ng_struct_getAlign(const struct ng_parse_type *type)
{
const struct ng_parse_struct_info *si = type->info;
const struct ng_parse_struct_field *field;
int align = 0;
for (field = si->fields; field->name != NULL; field++) {
int falign = ALIGNMENT(field->type);
if (falign > align)
align = falign;
}
return align;
}
const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_struct_type = {
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
ng_struct_parse,
ng_struct_unparse,
ng_struct_getDefault,
ng_struct_getAlign
};
/************************************************************************
FIXED LENGTH ARRAY TYPE
************************************************************************/
static int
ng_fixedarray_parse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const char *s, int *off, const u_char *const start,
u_char *const buf, int *buflen)
{
return ng_parse_composite(type,
s, off, start, buf, buflen, CT_FIXEDARRAY);
}
static int
ng_fixedarray_unparse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *data, int *off, char *cbuf, int cbuflen)
{
return ng_unparse_composite(type,
data, off, cbuf, cbuflen, CT_FIXEDARRAY);
}
static int
ng_fixedarray_getDefault(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *const start, u_char *buf, int *buflen)
{
int off = 0;
return ng_parse_composite(type,
"[]", &off, start, buf, buflen, CT_FIXEDARRAY);
}
static int
ng_fixedarray_getAlign(const struct ng_parse_type *type)
{
const struct ng_parse_fixedarray_info *fi = type->info;
return ALIGNMENT(fi->elementType);
}
const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_fixedarray_type = {
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
ng_fixedarray_parse,
ng_fixedarray_unparse,
ng_fixedarray_getDefault,
ng_fixedarray_getAlign
};
/************************************************************************
VARIABLE LENGTH ARRAY TYPE
************************************************************************/
static int
ng_array_parse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const char *s, int *off, const u_char *const start,
u_char *const buf, int *buflen)
{
return ng_parse_composite(type, s, off, start, buf, buflen, CT_ARRAY);
}
static int
ng_array_unparse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *data, int *off, char *cbuf, int cbuflen)
{
return ng_unparse_composite(type, data, off, cbuf, cbuflen, CT_ARRAY);
}
static int
ng_array_getDefault(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *const start, u_char *buf, int *buflen)
{
int off = 0;
return ng_parse_composite(type,
"[]", &off, start, buf, buflen, CT_ARRAY);
}
static int
ng_array_getAlign(const struct ng_parse_type *type)
{
const struct ng_parse_array_info *ai = type->info;
return ALIGNMENT(ai->elementType);
}
const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_array_type = {
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
ng_array_parse,
ng_array_unparse,
ng_array_getDefault,
ng_array_getAlign
};
/************************************************************************
INT8 TYPE
************************************************************************/
static int
ng_int8_parse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const char *s, int *off, const u_char *const start,
u_char *const buf, int *buflen)
{
long val;
int8_t val8;
char *eptr;
val = strtol(s + *off, &eptr, 0);
if (val < -0x80 || val > 0xff || eptr == s + *off)
return (EINVAL);
*off = eptr - s;
val8 = (int8_t)val;
bcopy(&val8, buf, sizeof(int8_t));
*buflen = sizeof(int8_t);
return (0);
}
static int
ng_int8_unparse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *data, int *off, char *cbuf, int cbuflen)
{
int8_t val;
bcopy(data + *off, &val, sizeof(int8_t));
NG_PARSE_APPEND("%d", (int)val);
*off += sizeof(int8_t);
return (0);
}
static int
ng_int8_getDefault(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *const start, u_char *buf, int *buflen)
{
int8_t val;
if (*buflen < sizeof(int8_t))
return (ERANGE);
val = 0;
bcopy(&val, buf, sizeof(int8_t));
*buflen = sizeof(int8_t);
return (0);
}
static int
ng_int8_getAlign(const struct ng_parse_type *type)
{
return INT8_ALIGNMENT;
}
const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_int8_type = {
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
ng_int8_parse,
ng_int8_unparse,
ng_int8_getDefault,
ng_int8_getAlign
};
/************************************************************************
INT16 TYPE
************************************************************************/
static int
ng_int16_parse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const char *s, int *off, const u_char *const start,
u_char *const buf, int *buflen)
{
long val;
int16_t val16;
char *eptr;
val = strtol(s + *off, &eptr, 0);
if (val < -0x8000 || val > 0xffff || eptr == s + *off)
return (EINVAL);
*off = eptr - s;
val16 = (int16_t)val;
bcopy(&val16, buf, sizeof(int16_t));
*buflen = sizeof(int16_t);
return (0);
}
static int
ng_int16_unparse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *data, int *off, char *cbuf, int cbuflen)
{
int16_t val;
bcopy(data + *off, &val, sizeof(int16_t));
NG_PARSE_APPEND("%d", (int)val);
*off += sizeof(int16_t);
return (0);
}
static int
ng_int16_getDefault(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *const start, u_char *buf, int *buflen)
{
int16_t val;
if (*buflen < sizeof(int16_t))
return (ERANGE);
val = 0;
bcopy(&val, buf, sizeof(int16_t));
*buflen = sizeof(int16_t);
return (0);
}
static int
ng_int16_getAlign(const struct ng_parse_type *type)
{
return INT16_ALIGNMENT;
}
const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_int16_type = {
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
ng_int16_parse,
ng_int16_unparse,
ng_int16_getDefault,
ng_int16_getAlign
};
/************************************************************************
INT32 TYPE
************************************************************************/
static int
ng_int32_parse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const char *s, int *off, const u_char *const start,
u_char *const buf, int *buflen)
{
long val; /* assumes long is at least 32 bits */
int32_t val32;
char *eptr;
val = strtol(s + *off, &eptr, 0);
if (val < (long)-0x80000000
|| val > (u_long)0xffffffff || eptr == s + *off)
return (EINVAL);
*off = eptr - s;
val32 = (int32_t)val;
bcopy(&val32, buf, sizeof(int32_t));
*buflen = sizeof(int32_t);
return (0);
}
static int
ng_int32_unparse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *data, int *off, char *cbuf, int cbuflen)
{
int32_t val;
bcopy(data + *off, &val, sizeof(int32_t));
NG_PARSE_APPEND("%ld", (long)val);
*off += sizeof(int32_t);
return (0);
}
static int
ng_int32_getDefault(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *const start, u_char *buf, int *buflen)
{
int32_t val;
if (*buflen < sizeof(int32_t))
return (ERANGE);
val = 0;
bcopy(&val, buf, sizeof(int32_t));
*buflen = sizeof(int32_t);
return (0);
}
static int
ng_int32_getAlign(const struct ng_parse_type *type)
{
return INT32_ALIGNMENT;
}
const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_int32_type = {
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
ng_int32_parse,
ng_int32_unparse,
ng_int32_getDefault,
ng_int32_getAlign
};
/************************************************************************
INT64 TYPE
************************************************************************/
static int
ng_int64_parse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const char *s, int *off, const u_char *const start,
u_char *const buf, int *buflen)
{
quad_t val;
int64_t val64;
char *eptr;
val = strtoq(s + *off, &eptr, 0);
if (eptr == s + *off)
return (EINVAL);
*off = eptr - s;
val64 = (int64_t)val;
bcopy(&val64, buf, sizeof(int64_t));
*buflen = sizeof(int64_t);
return (0);
}
static int
ng_int64_unparse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *data, int *off, char *cbuf, int cbuflen)
{
int64_t val;
bcopy(data + *off, &val, sizeof(int64_t));
NG_PARSE_APPEND("%lld", (long long)val);
*off += sizeof(int64_t);
return (0);
}
static int
ng_int64_getDefault(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *const start, u_char *buf, int *buflen)
{
int64_t val;
if (*buflen < sizeof(int64_t))
return (ERANGE);
val = 0;
bcopy(&val, buf, sizeof(int64_t));
*buflen = sizeof(int64_t);
return (0);
}
static int
ng_int64_getAlign(const struct ng_parse_type *type)
{
return INT64_ALIGNMENT;
}
const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_int64_type = {
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
ng_int64_parse,
ng_int64_unparse,
ng_int64_getDefault,
ng_int64_getAlign
};
/************************************************************************
STRING TYPE
************************************************************************/
static int
ng_string_parse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const char *s, int *off, const u_char *const start,
u_char *const buf, int *buflen)
{
char *sval;
int len;
if ((sval = ng_get_string_token(s, off, &len)) == NULL)
return (EINVAL);
*off += len;
len = strlen(sval) + 1;
bcopy(sval, buf, len);
FREE(sval, M_NETGRAPH);
*buflen = len;
return (0);
}
static int
ng_string_unparse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *data, int *off, char *cbuf, int cbuflen)
{
const char *const raw = (const char *)data + *off;
char *const s = ng_encode_string(raw);
if (s == NULL)
return (ENOMEM);
NG_PARSE_APPEND("%s", s);
*off += strlen(raw) + 1;
FREE(s, M_NETGRAPH);
return (0);
}
static int
ng_string_getDefault(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *const start, u_char *buf, int *buflen)
{
if (*buflen < 1)
return (ERANGE);
buf[0] = (u_char)'\0';
*buflen = 1;
return (0);
}
const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_string_type = {
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
ng_string_parse,
ng_string_unparse,
ng_string_getDefault,
NULL
};
/************************************************************************
FIXED BUFFER STRING TYPE
************************************************************************/
static int
ng_fixedstring_parse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const char *s, int *off, const u_char *const start,
u_char *const buf, int *buflen)
{
const struct ng_parse_fixedsstring_info *const fi = type->info;
char *sval;
int len;
if ((sval = ng_get_string_token(s, off, &len)) == NULL)
return (EINVAL);
if (strlen(sval) + 1 > fi->bufSize)
return (E2BIG);
*off += len;
len = strlen(sval) + 1;
bcopy(sval, buf, len);
FREE(sval, M_NETGRAPH);
bzero(buf + len, fi->bufSize - len);
*buflen = fi->bufSize;
return (0);
}
static int
ng_fixedstring_unparse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *data, int *off, char *cbuf, int cbuflen)
{
const struct ng_parse_fixedsstring_info *const fi = type->info;
int error, temp = *off;
if ((error = ng_string_unparse(type, data, &temp, cbuf, cbuflen)) != 0)
return (error);
*off += fi->bufSize;
return (0);
}
static int
ng_fixedstring_getDefault(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *const start, u_char *buf, int *buflen)
{
const struct ng_parse_fixedsstring_info *const fi = type->info;
if (*buflen < fi->bufSize)
return (ERANGE);
bzero(buf, fi->bufSize);
*buflen = fi->bufSize;
return (0);
}
const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_fixedstring_type = {
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
ng_fixedstring_parse,
ng_fixedstring_unparse,
ng_fixedstring_getDefault,
NULL
};
const struct ng_parse_fixedsstring_info ng_parse_nodebuf_info = {
NG_NODELEN + 1
};
const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_nodebuf_type = {
&ng_parse_fixedstring_type,
&ng_parse_nodebuf_info
};
const struct ng_parse_fixedsstring_info ng_parse_hookbuf_info = {
NG_HOOKLEN + 1
};
const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_hookbuf_type = {
&ng_parse_fixedstring_type,
&ng_parse_hookbuf_info
};
const struct ng_parse_fixedsstring_info ng_parse_pathbuf_info = {
NG_PATHLEN + 1
};
const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_pathbuf_type = {
&ng_parse_fixedstring_type,
&ng_parse_pathbuf_info
};
const struct ng_parse_fixedsstring_info ng_parse_typebuf_info = {
NG_TYPELEN + 1
};
const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_typebuf_type = {
&ng_parse_fixedstring_type,
&ng_parse_typebuf_info
};
const struct ng_parse_fixedsstring_info ng_parse_cmdbuf_info = {
NG_CMDSTRLEN + 1
};
const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_cmdbuf_type = {
&ng_parse_fixedstring_type,
&ng_parse_cmdbuf_info
};
/************************************************************************
IP ADDRESS TYPE
************************************************************************/
static int
ng_ipaddr_parse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const char *s, int *off, const u_char *const start,
u_char *const buf, int *buflen)
{
int i, error;
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
if ((error = ng_int8_parse(&ng_parse_int8_type,
s, off, start, buf + i, buflen)) != 0)
return (error);
if (i < 3 && s[*off] != '.')
return (EINVAL);
(*off)++;
}
*buflen = 4;
return (0);
}
static int
ng_ipaddr_unparse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *data, int *off, char *cbuf, int cbuflen)
{
struct in_addr ip;
bcopy(data + *off, &ip, sizeof(ip));
NG_PARSE_APPEND("%d.%d.%d.%d", ((u_char *)&ip)[0],
((u_char *)&ip)[1], ((u_char *)&ip)[2], ((u_char *)&ip)[3]);
*off += sizeof(ip);
return (0);
}
static int
ng_ipaddr_getDefault(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *const start, u_char *buf, int *buflen)
{
struct in_addr ip = { 0 };
if (*buflen < sizeof(ip))
return (ERANGE);
bcopy(&ip, buf, sizeof(ip));
*buflen = sizeof(ip);
return (0);
}
const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_ipaddr_type = {
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
ng_ipaddr_parse,
ng_ipaddr_unparse,
ng_ipaddr_getDefault,
ng_int32_getAlign
};
/************************************************************************
BYTE ARRAY TYPE
************************************************************************/
/* Get the length of a byte array */
static int
ng_parse_bytearray_subtype_getLength(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *start, const u_char *buf)
{
ng_parse_array_getLength_t *const getLength = type->private;
return (*getLength)(type, start, buf);
}
static int
ng_bytearray_elem_unparse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *data, int *off, char *cbuf, int cbuflen)
{
int8_t val;
bcopy(data + *off, &val, sizeof(int8_t));
NG_PARSE_APPEND("0x%02x", (int)val & 0xff); /* always hex format */
*off += sizeof(int8_t);
return (0);
}
/* Byte array element type is int8, but always output in hex format */
const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_bytearray_elem_type = {
&ng_parse_int8_type,
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
ng_bytearray_elem_unparse,
NULL,
NULL
};
static const struct ng_parse_array_info ng_parse_bytearray_subtype_info = {
&ng_parse_bytearray_elem_type,
&ng_parse_bytearray_subtype_getLength,
NULL
};
static const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_bytearray_subtype = {
&ng_parse_array_type,
&ng_parse_bytearray_subtype_info
};
static int
ng_bytearray_parse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const char *s, int *off, const u_char *const start,
u_char *const buf, int *buflen)
{
char *str;
int toklen;
/* We accept either an array of bytes or a string constant */
if ((str = ng_get_string_token(s, off, &toklen)) != NULL) {
ng_parse_array_getLength_t *const getLength = type->info;
int arraylen, slen;
arraylen = (*getLength)(type, start, buf);
if (arraylen > *buflen) {
FREE(str, M_NETGRAPH);
return (ERANGE);
}
slen = strlen(str) + 1;
if (slen > arraylen) {
FREE(str, M_NETGRAPH);
return (E2BIG);
}
bcopy(str, buf, slen);
bzero(buf + slen, arraylen - slen);
FREE(str, M_NETGRAPH);
*off += toklen;
*buflen = arraylen;
return (0);
} else {
struct ng_parse_type subtype;
subtype = ng_parse_bytearray_subtype;
(const void *)subtype.private = type->info;
return ng_array_parse(&subtype, s, off, start, buf, buflen);
}
}
static int
ng_bytearray_unparse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *data, int *off, char *cbuf, int cbuflen)
{
struct ng_parse_type subtype;
subtype = ng_parse_bytearray_subtype;
(const void *)subtype.private = type->info;
return ng_array_unparse(&subtype, data, off, cbuf, cbuflen);
}
static int
ng_bytearray_getDefault(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *const start, u_char *buf, int *buflen)
{
struct ng_parse_type subtype;
subtype = ng_parse_bytearray_subtype;
(const void *)subtype.private = type->info;
return ng_array_getDefault(&subtype, start, buf, buflen);
}
const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_bytearray_type = {
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
ng_bytearray_parse,
ng_bytearray_unparse,
ng_bytearray_getDefault,
NULL
};
/************************************************************************
STRUCT NG_MESG TYPE
************************************************************************/
/* Get msg->header.arglen when "buf" is pointing to msg->data */
static int
ng_parse_ng_mesg_getLength(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *start, const u_char *buf)
{
const struct ng_mesg *msg;
msg = (const struct ng_mesg *)(buf - sizeof(*msg));
return msg->header.arglen;
}
/* Type for the variable length data portion of a struct ng_mesg */
static const struct ng_parse_type ng_msg_data_type = {
&ng_parse_bytearray_type,
&ng_parse_ng_mesg_getLength
};
/* Type for the entire struct ng_mesg header with data section */
static const struct ng_parse_struct_info
ng_parse_ng_mesg_type_info = NG_GENERIC_NG_MESG_INFO(&ng_msg_data_type);
const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_ng_mesg_type = {
&ng_parse_struct_type,
&ng_parse_ng_mesg_type_info,
};
/************************************************************************
COMPOSITE HELPER ROUTINES
************************************************************************/
/*
* Convert a structure or array from ASCII to binary
*/
static int
ng_parse_composite(const struct ng_parse_type *type, const char *s,
int *off, const u_char *const start, u_char *const buf, int *buflen,
const enum comptype ctype)
{
const int num = ng_get_composite_len(type, start, buf, ctype);
int nextIndex = 0; /* next implicit array index */
u_int index; /* field or element index */
int *foff; /* field value offsets in string */
int align, len, blen, error = 0;
/* Initialize */
MALLOC(foff, int *, num * sizeof(*foff), M_NETGRAPH, M_NOWAIT);
if (foff == NULL) {
error = ENOMEM;
goto done;
}
bzero(foff, num * sizeof(*foff));
/* Get opening brace/bracket */
if (ng_parse_get_token(s, off, &len)
!= (ctype == CT_STRUCT ? T_LBRACE : T_LBRACKET)) {
error = EINVAL;
goto done;
}
*off += len;
/* Get individual element value positions in the string */
for (;;) {
enum ng_parse_token tok;
/* Check for closing brace/bracket */
tok = ng_parse_get_token(s, off, &len);
if (tok == (ctype == CT_STRUCT ? T_RBRACE : T_RBRACKET)) {
*off += len;
break;
}
/* For arrays, the 'name' (ie, index) is optional, so
distinguish name from values by seeing if the next
token is an equals sign */
if (ctype != CT_STRUCT) {
int len2, off2;
char *eptr;
/* If an opening brace/bracket, index is implied */
if (tok == T_LBRACE || tok == T_LBRACKET) {
index = nextIndex++;
goto gotIndex;
}
/* Might be an index, might be a value, either way... */
if (tok != T_WORD) {
error = EINVAL;
goto done;
}
/* If no equals sign follows, index is implied */
off2 = *off + len;
if (ng_parse_get_token(s, &off2, &len2) != T_EQUALS) {
index = nextIndex++;
goto gotIndex;
}
/* Index was specified explicitly; parse it */
index = (u_int)strtoul(s + *off, &eptr, 0);
if (index < 0 || eptr - (s + *off) != len) {
error = EINVAL;
goto done;
}
nextIndex = index + 1;
*off += len + len2;
gotIndex:
} else { /* a structure field */
const struct ng_parse_struct_field *field = NULL;
const struct ng_parse_struct_info *si = type->info;
/* Find the field by name (required) in field list */
if (tok != T_WORD) {
error = EINVAL;
goto done;
}
for (index = 0; index < num; index++) {
field = &si->fields[index];
if (strncmp(&s[*off], field->name, len) == 0
&& field->name[len] == '\0')
break;
}
if (index == num) {
error = ENOENT;
goto done;
}
*off += len;
/* Get equals sign */
if (ng_parse_get_token(s, off, &len) != T_EQUALS) {
error = EINVAL;
goto done;
}
*off += len;
}
/* Check array index */
if (index >= num) {
error = E2BIG;
goto done;
}
/* Save value's position and skip over it for now */
if (foff[index] != 0) {
error = EALREADY; /* duplicate */
goto done;
}
while (isspace(s[*off]))
(*off)++;
foff[index] = *off;
if ((error = ng_parse_skip_value(s, *off, &len)) != 0)
goto done;
*off += len;
}
/* Now build binary structure from supplied values and defaults */
for (blen = index = 0; index < num; index++) {
const struct ng_parse_type *const
etype = ng_get_composite_etype(type, index, ctype);
int k, pad, vlen;
/* Zero-pad any alignment bytes */
pad = ng_parse_get_elem_pad(type, index, ctype, blen);
for (k = 0; k < pad; k++) {
if (blen >= *buflen) {
error = ERANGE;
goto done;
}
buf[blen++] = 0;
}
/* Get value */
vlen = *buflen - blen;
if (foff[index] == 0) { /* use default value */
error = ng_get_composite_elem_default(type, index,
start, buf + blen, &vlen, ctype);
} else { /* parse given value */
*off = foff[index];
error = INVOKE(etype, parse)(etype,
s, off, start, buf + blen, &vlen);
}
if (error != 0)
goto done;
blen += vlen;
}
/* Make total composite structure size a multiple of its alignment */
if ((align = ALIGNMENT(type)) != 0) {
while (blen % align != 0) {
if (blen >= *buflen) {
error = ERANGE;
goto done;
}
buf[blen++] = 0;
}
}
/* Done */
*buflen = blen;
done:
FREE(foff, M_NETGRAPH);
return (error);
}
/*
* Convert an array or structure from binary to ASCII
*/
static int
ng_unparse_composite(const struct ng_parse_type *type, const u_char *data,
int *off, char *cbuf, int cbuflen, const enum comptype ctype)
{
const int num = ng_get_composite_len(type, data, data + *off, ctype);
int nextIndex = 0, didOne = 0;
int error, index;
/* Opening brace/bracket */
NG_PARSE_APPEND("%c", (ctype == CT_STRUCT) ? '{' : '[');
/* Do each item */
for (index = 0; index < num; index++) {
const struct ng_parse_type *const
etype = ng_get_composite_etype(type, index, ctype);
u_char temp[1024];
/* Skip any alignment pad bytes */
*off += ng_parse_get_elem_pad(type, index, ctype, *off);
/* See if element is equal to its default value; skip if so */
if (*off < sizeof(temp)) {
int tempsize = sizeof(temp) - *off;
bcopy(data, temp, *off);
if (ng_get_composite_elem_default(type, index, temp,
temp + *off, &tempsize, ctype) == 0
&& bcmp(temp + *off, data + *off, tempsize) == 0) {
*off += tempsize;
continue;
}
}
/* Print name= */
NG_PARSE_APPEND(" ");
if (ctype != CT_STRUCT) {
if (index != nextIndex) {
nextIndex = index;
NG_PARSE_APPEND("%d=", index);
}
nextIndex++;
} else {
const struct ng_parse_struct_info *si = type->info;
NG_PARSE_APPEND("%s=", si->fields[index].name);
}
/* Print value */
if ((error = INVOKE(etype, unparse)
(etype, data, off, cbuf, cbuflen)) != 0)
return (error);
cbuflen -= strlen(cbuf);
cbuf += strlen(cbuf);
didOne = 1;
}
/* Closing brace/bracket */
NG_PARSE_APPEND("%s%c",
didOne ? " " : "", (ctype == CT_STRUCT) ? '}' : ']');
return (0);
}
/*
* Generate the default value for an element of an array or structure
* Returns EOPNOTSUPP if default value is unspecified.
*/
static int
ng_get_composite_elem_default(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
int index, const u_char *const start, u_char *buf, int *buflen,
const enum comptype ctype)
{
const struct ng_parse_type *etype;
ng_getDefault_t *func;
switch (ctype) {
case CT_STRUCT:
break;
case CT_ARRAY:
{
const struct ng_parse_array_info *const ai = type->info;
if (ai->getDefault != NULL) {
return (*ai->getDefault)(type,
index, start, buf, buflen);
}
break;
}
case CT_FIXEDARRAY:
{
const struct ng_parse_fixedarray_info *const fi = type->info;
if (*fi->getDefault != NULL) {
return (*fi->getDefault)(type,
index, start, buf, buflen);
}
break;
}
default:
panic("%s", __FUNCTION__);
}
/* Default to element type default */
etype = ng_get_composite_etype(type, index, ctype);
func = METHOD(etype, getDefault);
if (func == NULL)
return (EOPNOTSUPP);
return (*func)(etype, start, buf, buflen);
}
/*
* Get the number of elements in a struct, variable or fixed array.
*/
static int
ng_get_composite_len(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *const start, const u_char *buf,
const enum comptype ctype)
{
switch (ctype) {
case CT_STRUCT:
{
const struct ng_parse_struct_info *const si = type->info;
int numFields = 0;
for (numFields = 0; ; numFields++) {
const struct ng_parse_struct_field *const
fi = &si->fields[numFields];
if (fi->name == NULL)
break;
}
return (numFields);
}
case CT_ARRAY:
{
const struct ng_parse_array_info *const ai = type->info;
return (*ai->getLength)(type, start, buf);
}
case CT_FIXEDARRAY:
{
const struct ng_parse_fixedarray_info *const fi = type->info;
return fi->length;
}
default:
panic("%s", __FUNCTION__);
}
return (0);
}
/*
* Return the type of the index'th element of a composite structure
*/
static const struct ng_parse_type *
ng_get_composite_etype(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
int index, const enum comptype ctype)
{
const struct ng_parse_type *etype = NULL;
switch (ctype) {
case CT_STRUCT:
{
const struct ng_parse_struct_info *const si = type->info;
etype = si->fields[index].type;
break;
}
case CT_ARRAY:
{
const struct ng_parse_array_info *const ai = type->info;
etype = ai->elementType;
break;
}
case CT_FIXEDARRAY:
{
const struct ng_parse_fixedarray_info *const fi = type->info;
etype = fi->elementType;
break;
}
default:
panic("%s", __FUNCTION__);
}
return (etype);
}
/*
* Get the number of bytes to skip to align for the next
* element in a composite structure.
*/
static int
ng_parse_get_elem_pad(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
int index, enum comptype ctype, int posn)
{
const struct ng_parse_type *const
etype = ng_get_composite_etype(type, index, ctype);
int align;
/* Get element's alignment, and possibly override */
align = ALIGNMENT(etype);
if (ctype == CT_STRUCT) {
const struct ng_parse_struct_info *si = type->info;
if (si->fields[index].alignment != 0)
align = si->fields[index].alignment;
}
/* Return number of bytes to skip to align */
return (align ? (align - (posn % align)) % align : 0);
}
/************************************************************************
PARSING HELPER ROUTINES
************************************************************************/
/*
* Skip over a value
*/
static int
ng_parse_skip_value(const char *s, int off0, int *lenp)
{
int len, nbracket, nbrace;
int off = off0;
len = nbracket = nbrace = 0;
do {
switch (ng_parse_get_token(s, &off, &len)) {
case T_LBRACKET:
nbracket++;
break;
case T_LBRACE:
nbrace++;
break;
case T_RBRACKET:
if (nbracket-- == 0)
return (EINVAL);
break;
case T_RBRACE:
if (nbrace-- == 0)
return (EINVAL);
break;
case T_EOF:
return (EINVAL);
default:
break;
}
off += len;
} while (nbracket > 0 || nbrace > 0);
*lenp = off - off0;
return (0);
}
/*
* Find the next token in the string, starting at offset *startp.
* Returns the token type, with *startp pointing to the first char
* and *lenp the length.
*/
enum ng_parse_token
ng_parse_get_token(const char *s, int *startp, int *lenp)
{
char *t;
int i;
while (isspace(s[*startp]))
(*startp)++;
switch (s[*startp]) {
case '\0':
*lenp = 0;
return T_EOF;
case '{':
*lenp = 1;
return T_LBRACE;
case '}':
*lenp = 1;
return T_RBRACE;
case '[':
*lenp = 1;
return T_LBRACKET;
case ']':
*lenp = 1;
return T_RBRACKET;
case '=':
*lenp = 1;
return T_EQUALS;
case '"':
if ((t = ng_get_string_token(s, startp, lenp)) == NULL)
return T_ERROR;
FREE(t, M_NETGRAPH);
return T_STRING;
default:
for (i = *startp + 1; s[i] != '\0' && !isspace(s[i])
&& s[i] != '{' && s[i] != '}' && s[i] != '['
&& s[i] != ']' && s[i] != '=' && s[i] != '"'; i++)
;
*lenp = i - *startp;
return T_WORD;
}
}
/*
* Get a string token, which must be enclosed in double quotes.
* The normal C backslash escapes are recognized.
*/
char *
ng_get_string_token(const char *s, int *startp, int *lenp)
{
char *cbuf, *p;
int start, off;
while (isspace(s[*startp]))
(*startp)++;
start = *startp;
if (s[*startp] != '"')
return (NULL);
MALLOC(cbuf, char *, strlen(s + start), M_NETGRAPH, M_NOWAIT);
if (cbuf == NULL)
return (NULL);
strcpy(cbuf, s + start + 1);
for (off = 1, p = cbuf; *p != '\0'; off++, p++) {
if (*p == '"') {
*p = '\0';
*lenp = off + 1;
return (cbuf);
} else if (p[0] == '\\' && p[1] != '\0') {
int x, k;
char *v;
strcpy(p, p + 1);
v = p;
switch (*p) {
case 't':
*v = '\t';
off++;
continue;
case 'n':
*v = '\n';
off++;
continue;
case 'r':
*v = '\r';
off++;
continue;
case 'v':
*v = '\v';
off++;
continue;
case 'f':
*v = '\f';
off++;
continue;
case '"':
*v = '"';
off++;
continue;
case '0': case '1': case '2': case '3':
case '4': case '5': case '6': case '7':
for (x = k = 0;
k < 3 && *v >= '0' && *v <= '7'; v++) {
x = (x << 3) + (*v - '0');
off++;
}
*--v = (char)x;
break;
case 'x':
for (v++, x = k = 0;
k < 2 && isxdigit(*v); v++) {
x = (x << 4) + (isdigit(*v) ?
(*v - '0') :
(tolower(*v) - 'a' + 10));
off++;
}
*--v = (char)x;
break;
default:
continue;
}
strcpy(p, v);
}
}
return (NULL); /* no closing quote */
}
/*
* Encode a string so it can be safely put in double quotes.
* Caller must free the result.
*/
char *
ng_encode_string(const char *raw)
{
char *cbuf;
int off = 0;
MALLOC(cbuf, char *, strlen(raw) * 4 + 3, M_NETGRAPH, M_NOWAIT);
if (cbuf == NULL)
return (NULL);
cbuf[off++] = '"';
for ( ; *raw != '\0'; raw++) {
switch (*raw) {
case '\t':
cbuf[off++] = '\\';
cbuf[off++] = 't';
break;
case '\f':
cbuf[off++] = '\\';
cbuf[off++] = 'f';
break;
case '\n':
cbuf[off++] = '\\';
cbuf[off++] = 'n';
break;
case '\r':
cbuf[off++] = '\\';
cbuf[off++] = 'r';
break;
case '\v':
cbuf[off++] = '\\';
cbuf[off++] = 'v';
break;
case '"':
case '\\':
cbuf[off++] = '\\';
cbuf[off++] = *raw;
break;
default:
if (*raw < 0x20 || *raw > 0x7e) {
off += sprintf(cbuf + off,
"\\x%02x", (u_char)*raw);
break;
}
cbuf[off++] = *raw;
break;
}
}
cbuf[off++] = '"';
cbuf[off] = '\0';
return (cbuf);
}
/************************************************************************
VIRTUAL METHOD LOOKUP
************************************************************************/
static ng_parse_t *
ng_get_parse_method(const struct ng_parse_type *t)
{
while (t != NULL && t->parse == NULL)
t = t->supertype;
return (t ? t->parse : NULL);
}
static ng_unparse_t *
ng_get_unparse_method(const struct ng_parse_type *t)
{
while (t != NULL && t->unparse == NULL)
t = t->supertype;
return (t ? t->unparse : NULL);
}
static ng_getDefault_t *
ng_get_getDefault_method(const struct ng_parse_type *t)
{
while (t != NULL && t->getDefault == NULL)
t = t->supertype;
return (t ? t->getDefault : NULL);
}
static ng_getAlign_t *
ng_get_getAlign_method(const struct ng_parse_type *t)
{
while (t != NULL && t->getAlign == NULL)
t = t->supertype;
return (t ? t->getAlign : NULL);
}
/*
* ng_parse.h
*
* Copyright (c) 1999 Whistle Communications, Inc.
* All rights reserved.
*
* Subject to the following obligations and disclaimer of warranty, use and
* redistribution of this software, in source or object code forms, with or
* without modifications are expressly permitted by Whistle Communications;
* provided, however, that:
* 1. Any and all reproductions of the source or object code must include the
* copyright notice above and the following disclaimer of warranties; and
* 2. No rights are granted, in any manner or form, to use Whistle
* Communications, Inc. trademarks, including the mark "WHISTLE
* COMMUNICATIONS" on advertising, endorsements, or otherwise except as
* such appears in the above copyright notice or in the software.
*
* THIS SOFTWARE IS BEING PROVIDED BY WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS "AS IS", AND
* TO THE MAXIMUM EXTENT PERMITTED BY LAW, WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS MAKES NO
* REPRESENTATIONS OR WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, REGARDING THIS SOFTWARE,
* INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY AND ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
* MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR NON-INFRINGEMENT.
* WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS DOES NOT WARRANT, GUARANTEE, OR MAKE ANY
* REPRESENTATIONS REGARDING THE USE OF, OR THE RESULTS OF THE USE OF THIS
* SOFTWARE IN TERMS OF ITS CORRECTNESS, ACCURACY, RELIABILITY OR OTHERWISE.
* IN NO EVENT SHALL WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DAMAGES
* RESULTING FROM OR ARISING OUT OF ANY USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, INCLUDING
* WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY,
* PUNITIVE, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR
* SERVICES, LOSS OF USE, DATA OR PROFITS, HOWEVER CAUSED AND UNDER ANY
* THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
* (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF
* THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS IS ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY
* OF SUCH DAMAGE.
*
* Author: Archie Cobbs <archie@whistle.com>
*
* $Whistle: ng_parse.h,v 1.2 1999/11/29 01:43:48 archie Exp $
* $FreeBSD: src/sys/netgraph/ng_parse.h,v 1.2 1999/12/01 19:41:15 archie Exp $
*/
#ifndef _NETGRAPH_PARSE_H_
#define _NETGRAPH_PARSE_H_
/*
This defines a library of routines for converting between various C
language types in binary form and ASCII strings. Types are user
definable. Several pre-defined types are supplied, for some common
C types: structures, variable and fixed length arrays, integer types,
variable and fixed length strings, IP addresses, etc.
A netgraph node type may provide a list of types that correspond to
the structures it expects to send and receive in the arguments field
of a control message. This allows these messages to be converted
between their native binary form and the corresponding ASCII form.
A future use of the ASCII form may be for inter-machine communication
of control messages, because the ASCII form is machine independent
whereas the native binary form is not.
Syntax
------
Structures:
'{' [ <name>=<value> ... ] '}'
Omitted fields have their default values by implication.
The order in which the fields are specified does not matter.
Arrays:
'[' [ [index=]<value> ... ] ']'
Element value may be specified with or without the "<index>=" prefix;
If omitted, the index after the previous element is used.
Omitted fields have their default values by implication.
Strings:
"foo bar blah\r\n"
That is, strings are specified just like C strings. The usual
backslash escapes are accepted.
Other simple types (integers, IP addresses) have their obvious forms.
Example
-------
Suppose we have a netgraph command that takes as an argument
a 'struct foo' shown below. Here is an example of a possible
value for the structure, and the corresponding ASCII encoding
of that value:
Structure Binary value
--------- ------------
struct foo {
struct in_addr ip; 01 02 03 04
int bar; 00 00 00 00
char label[8]; 61 62 63 0a 00 00 00 00
u_char alen; 03 00
short ary[0]; 05 00 00 00 0a 00
};
ASCII value
-----------
{ ip=1.2.3.4 label="abc\n" alen=3 ary=[ 5 2=10 ] }
Note that omitted fields and array elements get their default
values ("bar" and ary[2]), and that the alignment is handled
automatically (the extra 00 byte after "num"). Also, since byte
order and alignment are inherently machine dependent, so is this
conversion process. The above example shows an x86 (little
endian) encoding. Also the above example is tricky because the
structure is variable length, depending on 'alen', the number of
elements in the array 'ary'.
Here is how one would define a parse type for the above structure,
subclassing the pre-defined types below. We construct the type in
a 'bottom up' fashion, defining each field's type first, then the
type for the whole structure ('//' comments used to avoid breakage).
// Super-type info for 'label' field
struct ng_parse_fixedsstring_info foo_label_info = { 8 };
// Parse type for 'label' field
struct ng_parse_type foo_label_type = {
&ng_parse_fixedstring_type // super-type
&foo_label_info // super-type info
};
#define OFFSETOF(s, e) ((char *)&((s *)0)->e - (char *)((s *)0))
// Function to compute the length of the array 'ary', which
// is variable length, depending on the previous field 'alen'.
// Upon entry 'buf' will be pointing at &ary[0].
int
foo_ary_getLength(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *start, const u_char *buf)
{
const struct foo *f;
f = (const struct foo *)(buf - OFFSETOF(struct foo, ary));
return f->alen;
}
// Super-type info for 'ary' field
struct ng_parse_array_info foo_ary_info = {
&ng_parse_int16_type, // element type
&foo_ary_getLength // func to get array length
}
// Parse type for 'ary' field
struct ng_parse_type foo_ary_type = {
&ng_parse_array_type, // super-type
&foo_ary_info // super-type info
};
// Super-type info for struct foo
struct ng_parse_struct_info foo_fields = {
{ "ip", &ng_parse_ipaddr_type },
{ "bar", &ng_parse_int32_type },
{ "label", &foo_label_type },
{ "alen", &ng_parse_int8_type },
{ "ary", &foo_ary_type },
{ NULL }
};
// Parse type for struct foo
struct ng_parse_type foo_type = {
&ng_parse_struct_type, // super-type
&foo_fields // super-type info
};
To define a type, you can define it as a sub-type of a predefined
type as shown above, possibly overriding some of the predefined
type's methods, or define an entirely new syntax, with the restriction
that the ASCII representation of your type's value must not contain
any whitespace or any of these characters: { } [ ] = "
See ng_ksocket.c for an example of how to do this for 'struct sockaddr'.
See ng_parse.c to see implementations of the pre-defined types below.
*/
/************************************************************************
METHODS REQUIRED BY A TYPE
************************************************************************/
/*
* Three methods are required for a type. These may be given explicitly
* or, if NULL, inherited from the super-type. The 'getDefault' method
* is always optional; the others are required if there is no super-type.
*/
struct ng_parse_type;
/*
* Convert ASCII to binary according to the supplied type.
*
* The ASCII characters begin at offset *off in 'string'. The binary
* representation is put into 'buf', which has at least *buflen bytes.
* 'start' points to the first byte output by ng_parse() (ie, start <= buf).
*
* Upon return, *buflen contains the length of the new binary data, and
* *off is updated to point just past the end of the parsed range of
* characters, or, in the case of an error, to the offending character(s).
*
* Return values:
* 0 Success; *buflen holds the length of the data
* and *off points just past the last char parsed.
* EALREADY Field specified twice
* ENOENT Unknown field
* E2BIG Array or character string overflow
* ERANGE Output was longer than *buflen bytes
* EINVAL Parse failure or other invalid content
* ENOMEM Out of memory
* EOPNOTSUPP Mandatory array/structure element missing
*/
typedef int ng_parse_t(const struct ng_parse_type *type, const char *string,
int *off, const u_char *start,
u_char *buf, int *buflen);
/*
* Convert binary to ASCII according to the supplied type.
*
* The results are put into 'buf', which is at least buflen bytes long.
* *off points to the current byte in 'data' and should be updated
* before return to point just past the last byte unparsed.
*
* Returns:
* 0 Success
* ERANGE Output was longer than buflen bytes
*/
typedef int ng_unparse_t(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *data, int *off, char *buf, int buflen);
/*
* Compute the default value according to the supplied type.
*
* Store the result in 'buf', which is at least *buflen bytes long.
* Upon return *buflen contains the length of the output.
*
* Returns:
* 0 Success
* ERANGE Output was longer than *buflen bytes
* EOPNOTSUPP Default value is not specified for this type
*/
typedef int ng_getDefault_t(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *start, u_char *buf, int *buflen);
/*
* Return the alignment requirement of this type. Zero is same as one.
*/
typedef int ng_getAlign_t(const struct ng_parse_type *type);
/************************************************************************
TYPE DEFINITION
************************************************************************/
/*
* This structure describes a type, which may be a sub-type of another
* type by pointing to it with 'supertype' and possibly omitting methods.
* Typically the super-type requires some type-specific info, which is
* supplied by the 'info' field.
*
* The 'private' field is ignored by all of the pre-defined types.
* Sub-types may use it as they see fit.
*
* The 'getDefault' method may always be omitted (even if there is no
* super-type), which means the value for any item of this type must
* always be explicitly given.
*/
struct ng_parse_type {
const struct ng_parse_type *supertype; /* super-type, if any */
const void *info; /* type-specific info */
void *private; /* client private info */
ng_parse_t *parse; /* parse method */
ng_unparse_t *unparse; /* unparse method */
ng_getDefault_t *getDefault; /* get default value method */
ng_getAlign_t *getAlign; /* get alignment */
};
/************************************************************************
PRE-DEFINED TYPES
************************************************************************/
/*
* STRUCTURE TYPE
*
* This type supports arbitrary C structures. The normal field alignment
* rules for the local machine are applied. Fields are always parsed in
* field order, no matter what order they are listed in the ASCII string.
*
* Default value: Determined on a per-field basis
* Additional info: struct ng_parse_struct_info *
*/
extern const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_struct_type;
/* Each field has a name, type, and optional alignment override. If the
override is non-zero, the alignment is determined from the field type.
Note: add an extra struct ng_parse_struct_field with name == NULL
to indicate the end of the list. */
struct ng_parse_struct_info {
struct ng_parse_struct_field {
const char *name; /* field name */
const struct ng_parse_type
*type; /* field type */
int alignment; /* override alignment */
} fields[0];
};
/*
* FIXED LENGTH ARRAY TYPE
*
* This type supports fixed length arrays, having any element type.
*
* Default value: As returned by getDefault for each index
* Additional info: struct ng_parse_fixedarray_info *
*/
extern const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_fixedarray_type;
/*
* Get the default value for the element at index 'index'. This method
* may be NULL, in which case the default value is computed from the
* element type. Otherwise, it should fill in the default value at *buf
* (having size *buflen) and update *buflen to the length of the filled-in
* value before return. If there is not enough routine return ERANGE.
*/
typedef int ng_parse_array_getDefault_t(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
int index, const u_char *start,
u_char *buf, int *buflen);
struct ng_parse_fixedarray_info {
const struct ng_parse_type *elementType;
int length;
ng_parse_array_getDefault_t *getDefault;
};
/*
* VARIABLE LENGTH ARRAY TYPE
*
* Same as fixed length arrays, except that the length is determined
* by a function instead of a constant value.
*
* Default value: Same as with fixed length arrays
* Additional info: struct ng_parse_array_info *
*/
extern const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_array_type;
/*
* Return the length of the array. If the array is a field in a structure,
* all prior fields are guaranteed to be filled in already. Upon entry,
* 'start' is equal to the first byte parsed in this run, while 'buf' points
* to the first element of the array to be filled in.
*/
typedef int ng_parse_array_getLength_t(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *start, const u_char *buf);
struct ng_parse_array_info {
const struct ng_parse_type *elementType;
ng_parse_array_getLength_t *getLength;
ng_parse_array_getDefault_t *getDefault;
};
/*
* ARBITRARY LENGTH STRING TYPE
*
* For arbirary length, NUL-terminated strings.
*
* Default value: Empty string
* Additional info: None required
*/
extern const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_string_type;
/*
* BOUNDED LENGTH STRING TYPE
*
* These are strings that have a fixed-size buffer, and always include
* a terminating NUL character.
*
* Default value: Empty string
* Additional info: struct ng_parse_fixedsstring_info *
*/
extern const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_fixedstring_type;
struct ng_parse_fixedsstring_info {
int bufSize; /* size of buffer (including NUL) */
};
/*
* COMMONLY USED BOUNDED LENGTH STRING TYPES
*/
extern const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_nodebuf_type; /* NG_NODELEN + 1 */
extern const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_hookbuf_type; /* NG_HOOKLEN + 1 */
extern const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_pathbuf_type; /* NG_PATHLEN + 1 */
extern const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_typebuf_type; /* NG_TYPELEN + 1 */
extern const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_cmdbuf_type; /* NG_CMDSTRLEN + 1 */
/*
* INTEGER TYPES
*
* Default value: 0
* Additional info: None required
*/
extern const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_int8_type;
extern const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_int16_type;
extern const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_int32_type;
extern const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_int64_type;
/*
* IP ADDRESS TYPE
*
* Default value: 0.0.0.0
* Additional info: None required
*/
extern const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_ipaddr_type;
/*
* VARIABLE LENGTH BYTE ARRAY TYPE
*
* The bytes are displayed in hex. The ASCII form may be either an
* array of bytes or a string constant, in which case the array is
* zero-filled after the string bytes.
*
* Default value: All bytes are zero
* Additional info: ng_parse_array_getLength_t *
*/
extern const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_bytearray_type;
/*
* NETGRAPH CONTROL MESSAGE TYPE
*
* This is the parse type for a struct ng_mesg.
*
* Default value: All fields zero
* Additional info: None required
*/
extern const struct ng_parse_type ng_parse_ng_mesg_type;
/************************************************************************
CONVERSTION AND PARSING ROUTINES
************************************************************************/
/* Tokens for parsing structs and arrays */
enum ng_parse_token {
T_LBRACE, /* '{' */
T_RBRACE, /* '}' */
T_LBRACKET, /* '[' */
T_RBRACKET, /* ']' */
T_EQUALS, /* '=' */
T_STRING, /* string in double quotes */
T_ERROR, /* error parsing string in double quotes */
T_WORD, /* anything else containing no whitespace */
T_EOF, /* end of string reached */
};
/*
* See typedef ng_parse_t for definition
*/
extern int ng_parse(const struct ng_parse_type *type, const char *string,
int *off, u_char *buf, int *buflen);
/*
* See typedef ng_unparse_t for definition (*off assumed to be zero).
*/
extern int ng_unparse(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
const u_char *data, char *buf, int buflen);
/*
* See typedef ng_getDefault_t for definition
*/
extern int ng_parse_getDefault(const struct ng_parse_type *type,
u_char *buf, int *buflen);
/*
* Parse a token: '*startp' is the offset to start looking. Upon
* successful return, '*startp' equals the beginning of the token
* and '*lenp' the length. If error, '*startp' points at the
* offending character(s).
*/
extern enum ng_parse_token ng_parse_get_token(const char *s,
int *startp, int *lenp);
/*
* Like above, but specifically for getting a string token and returning
* the string value. The string token must be enclosed in double quotes
* and the normal C backslash escapes are recognized. The caller must
* eventually free() the returned result. Returns NULL if token is
* not a string token, or parse or other error.
*/
extern char *ng_get_string_token(const char *s, int *startp, int *lenp);
/*
* Convert a raw string into a doubly-quoted string including any
* necessary backslash escapes. Caller must free the result.
* Returns NULL if ENOMEM.
*/
extern char *ng_encode_string(const char *s);
#endif /* _NETGRAPH_PARSE_H_ */
/*
* ng_tee.c
*
* Copyright (c) 1996-1999 Whistle Communications, Inc.
* All rights reserved.
*
* Subject to the following obligations and disclaimer of warranty, use and
* redistribution of this software, in source or object code forms, with or
* without modifications are expressly permitted by Whistle Communications;
* provided, however, that:
* 1. Any and all reproductions of the source or object code must include the
* copyright notice above and the following disclaimer of warranties; and
* 2. No rights are granted, in any manner or form, to use Whistle
* Communications, Inc. trademarks, including the mark "WHISTLE
* COMMUNICATIONS" on advertising, endorsements, or otherwise except as
* such appears in the above copyright notice or in the software.
*
* THIS SOFTWARE IS BEING PROVIDED BY WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS "AS IS", AND
* TO THE MAXIMUM EXTENT PERMITTED BY LAW, WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS MAKES NO
* REPRESENTATIONS OR WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, REGARDING THIS SOFTWARE,
* INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY AND ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
* MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR NON-INFRINGEMENT.
* WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS DOES NOT WARRANT, GUARANTEE, OR MAKE ANY
* REPRESENTATIONS REGARDING THE USE OF, OR THE RESULTS OF THE USE OF THIS
* SOFTWARE IN TERMS OF ITS CORRECTNESS, ACCURACY, RELIABILITY OR OTHERWISE.
* IN NO EVENT SHALL WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DAMAGES
* RESULTING FROM OR ARISING OUT OF ANY USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, INCLUDING
* WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY,
* PUNITIVE, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR
* SERVICES, LOSS OF USE, DATA OR PROFITS, HOWEVER CAUSED AND UNDER ANY
* THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
* (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF
* THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS IS ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY
* OF SUCH DAMAGE.
*
* Author: Julian Elischer <julian@whistle.com>
*
* $FreeBSD: src/sys/netgraph/ng_tee.c,v 1.7 2000/01/27 01:32:53 archie Exp $
* $Whistle: ng_tee.c,v 1.18 1999/11/01 09:24:52 julian Exp $
*/
/*
* This node is like the tee(1) command and is useful for ``snooping.''
* It has 4 hooks: left, right, left2right, and right2left. Data
* entering from the right is passed to the left and duplicated on
* right2left, and data entering from the left is passed to the right
* and duplicated on left2right. Data entering from left2right is
* sent to right, and data from right2left to left.
*/
#include <sys/param.h>
#include <sys/systm.h>
#include <sys/errno.h>
#include <sys/kernel.h>
#include <sys/malloc.h>
#include <sys/mbuf.h>
#include <netgraph/ng_message.h>
#include <netgraph/netgraph.h>
#include <netgraph/ng_parse.h>
#include <netgraph/ng_tee.h>
/* Per hook info */
struct hookinfo {
hook_p hook;
struct ng_tee_hookstat stats;
};
/* Per node info */
struct privdata {
node_p node;
struct hookinfo left;
struct hookinfo right;
struct hookinfo left2right;
struct hookinfo right2left;
};
typedef struct privdata *sc_p;
/* Netgraph methods */
static ng_constructor_t ngt_constructor;
static ng_rcvmsg_t ngt_rcvmsg;
static ng_shutdown_t ngt_rmnode;
static ng_newhook_t ngt_newhook;
static ng_rcvdata_t ngt_rcvdata;
static ng_disconnect_t ngt_disconnect;
/* Parse type for struct ng_tee_hookstat */
static const struct ng_parse_struct_info
ng_tee_hookstat_type_info = NG_TEE_HOOKSTAT_INFO;
static const struct ng_parse_type ng_tee_hookstat_type = {
&ng_parse_struct_type,
&ng_tee_hookstat_type_info,
};
/* Parse type for struct ng_tee_stats */
static const struct ng_parse_struct_info
ng_tee_stats_type_info = NG_TEE_STATS_INFO(&ng_tee_hookstat_type);
static const struct ng_parse_type ng_tee_stats_type = {
&ng_parse_struct_type,
&ng_tee_stats_type_info,
};
/* List of commands and how to convert arguments to/from ASCII */
static const struct ng_cmdlist ng_tee_cmds[] = {
{
NGM_TEE_COOKIE,
NGM_TEE_GET_STATS,
"getstats",
NULL,
&ng_tee_stats_type
},
{
NGM_TEE_COOKIE,
NGM_TEE_CLR_STATS,
"clrstats",
NULL,
NULL
},
{ 0 }
};
/* Netgraph type descriptor */
static struct ng_type ng_tee_typestruct = {
NG_VERSION,
NG_TEE_NODE_TYPE,
NULL,
ngt_constructor,
ngt_rcvmsg,
ngt_rmnode,
ngt_newhook,
NULL,
NULL,
ngt_rcvdata,
ngt_rcvdata,
ngt_disconnect,
ng_tee_cmds
};
NETGRAPH_INIT(tee, &ng_tee_typestruct);
/*
* Node constructor
*/
static int
ngt_constructor(node_p *nodep)
{
sc_p privdata;
int error = 0;
MALLOC(privdata, sc_p, sizeof(*privdata), M_NETGRAPH, M_WAITOK);
if (privdata == NULL)
return (ENOMEM);
bzero(privdata, sizeof(*privdata));
if ((error = ng_make_node_common(&ng_tee_typestruct, nodep))) {
FREE(privdata, M_NETGRAPH);
return (error);
}
(*nodep)->private = privdata;
privdata->node = *nodep;
return (0);
}
/*
* Add a hook
*/
static int
ngt_newhook(node_p node, hook_p hook, const char *name)
{
const sc_p sc = node->private;
if (strcmp(name, NG_TEE_HOOK_RIGHT) == 0) {
sc->right.hook = hook;
bzero(&sc->right.stats, sizeof(sc->right.stats));
hook->private = &sc->right;
} else if (strcmp(name, NG_TEE_HOOK_LEFT) == 0) {
sc->left.hook = hook;
bzero(&sc->left.stats, sizeof(sc->left.stats));
hook->private = &sc->left;
} else if (strcmp(name, NG_TEE_HOOK_RIGHT2LEFT) == 0) {
sc->right2left.hook = hook;
bzero(&sc->right2left.stats, sizeof(sc->right2left.stats));
hook->private = &sc->right2left;
} else if (strcmp(name, NG_TEE_HOOK_LEFT2RIGHT) == 0) {
sc->left2right.hook = hook;
bzero(&sc->left2right.stats, sizeof(sc->left2right.stats));
hook->private = &sc->left2right;
} else
return (EINVAL);
return (0);
}
/*
* Receive a control message
*/
static int
ngt_rcvmsg(node_p node, struct ng_mesg *msg, const char *retaddr,
struct ng_mesg **rptr)
{
const sc_p sc = node->private;
struct ng_mesg *resp = NULL;
int error = 0;
switch (msg->header.typecookie) {
case NGM_TEE_COOKIE:
switch (msg->header.cmd) {
case NGM_TEE_GET_STATS:
{
struct ng_tee_stats *stats;
NG_MKRESPONSE(resp, msg,
sizeof(struct ng_tee_stats), M_NOWAIT);
if (resp == NULL) {
error = ENOMEM;
goto done;
}
stats = (struct ng_tee_stats *) resp->data;
bcopy(&sc->right.stats,
&stats->right, sizeof(stats->right));
bcopy(&sc->left.stats,
&stats->left, sizeof(stats->left));
bcopy(&sc->right2left.stats,
&stats->right2left, sizeof(stats->right2left));
bcopy(&sc->left2right.stats,
&stats->left2right, sizeof(stats->left2right));
break;
}
case NGM_TEE_CLR_STATS:
bzero(&sc->right.stats, sizeof(sc->right.stats));
bzero(&sc->left.stats, sizeof(sc->left.stats));
bzero(&sc->right2left.stats,
sizeof(sc->right2left.stats));
bzero(&sc->left2right.stats,
sizeof(sc->left2right.stats));
break;
default:
error = EINVAL;
break;
}
break;
default:
error = EINVAL;
break;
}
if (rptr)
*rptr = resp;
else if (resp)
FREE(resp, M_NETGRAPH);
done:
FREE(msg, M_NETGRAPH);
return (error);
}
/*
* Receive data on a hook
*
* If data comes in the right link send a copy out right2left, and then
* send the original onwards out through the left link.
* Do the opposite for data coming in from the left link.
* Data coming in right2left or left2right is forwarded
* on through the appropriate destination hook as if it had come
* from the other side.
*/
static int
ngt_rcvdata(hook_p hook, struct mbuf *m, meta_p meta)
{
const sc_p sc = hook->node->private;
struct hookinfo *const hinfo = (struct hookinfo *) hook->private;
struct hookinfo *dest;
struct hookinfo *dup;
int error = 0;
/* Which hook? */
if (hinfo == &sc->left) {
dup = &sc->left2right;
dest = &sc->right;
} else if (hinfo == &sc->right) {
dup = &sc->right2left;
dest = &sc->left;
} else if (hinfo == &sc->right2left) {
dup = NULL;
dest = &sc->left;
} else if (hinfo == &sc->left2right) {
dup = NULL;
dest = &sc->right;
} else
panic("%s: no hook!", __FUNCTION__);
/* Update stats on incoming hook */
hinfo->stats.inOctets += m->m_pkthdr.len;
hinfo->stats.inFrames++;
/* Duplicate packet and meta info if requried */
if (dup != NULL) {
struct mbuf *m2;
meta_p meta2;
/* Copy packet */
m2 = m_dup(m, M_NOWAIT);
if (m2 == NULL) {
NG_FREE_DATA(m, meta);
return (ENOBUFS);
}
/* Copy meta info */
if (meta != NULL) {
MALLOC(meta2, meta_p,
meta->used_len, M_NETGRAPH, M_NOWAIT);
if (meta2 == NULL) {
m_freem(m2);
NG_FREE_DATA(m, meta);
return (ENOMEM);
}
bcopy(meta, meta2, meta->used_len);
meta2->allocated_len = meta->used_len;
} else
meta2 = NULL;
/* Deliver duplicate */
dup->stats.outOctets += m->m_pkthdr.len;
dup->stats.outFrames++;
NG_SEND_DATA(error, dup->hook, m2, meta2);
}
/* Deliver frame out destination hook */
dest->stats.outOctets += m->m_pkthdr.len;
dest->stats.outFrames++;
NG_SEND_DATA(error, dest->hook, m, meta);
return (0);
}
/*
* Shutdown processing
*
* This is tricky. If we have both a left and right hook, then we
* probably want to extricate ourselves and leave the two peers
* still linked to each other. Otherwise we should just shut down as
* a normal node would.
*
* To keep the scope of info correct the routine to "extract" a node
* from two links is in ng_base.c.
*/
static int
ngt_rmnode(node_p node)
{
const sc_p privdata = node->private;
node->flags |= NG_INVALID;
if (privdata->left.hook && privdata->right.hook)
ng_bypass(privdata->left.hook, privdata->right.hook);
ng_cutlinks(node);
ng_unname(node);
node->private = NULL;
ng_unref(privdata->node);
FREE(privdata, M_NETGRAPH);
return (0);
}
/*
* Hook disconnection
*/
static int
ngt_disconnect(hook_p hook)
{
struct hookinfo *const hinfo = (struct hookinfo *) hook->private;
KASSERT(hinfo != NULL, ("%s: null info", __FUNCTION__));
hinfo->hook = NULL;
if (hook->node->numhooks == 0)
ng_rmnode(hook->node);
return (0);
}
/*
* ng_tee.h
*
* Copyright (c) 1996-1999 Whistle Communications, Inc.
* All rights reserved.
*
* Subject to the following obligations and disclaimer of warranty, use and
* redistribution of this software, in source or object code forms, with or
* without modifications are expressly permitted by Whistle Communications;
* provided, however, that:
* 1. Any and all reproductions of the source or object code must include the
* copyright notice above and the following disclaimer of warranties; and
* 2. No rights are granted, in any manner or form, to use Whistle
* Communications, Inc. trademarks, including the mark "WHISTLE
* COMMUNICATIONS" on advertising, endorsements, or otherwise except as
* such appears in the above copyright notice or in the software.
*
* THIS SOFTWARE IS BEING PROVIDED BY WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS "AS IS", AND
* TO THE MAXIMUM EXTENT PERMITTED BY LAW, WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS MAKES NO
* REPRESENTATIONS OR WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, REGARDING THIS SOFTWARE,
* INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY AND ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
* MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR NON-INFRINGEMENT.
* WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS DOES NOT WARRANT, GUARANTEE, OR MAKE ANY
* REPRESENTATIONS REGARDING THE USE OF, OR THE RESULTS OF THE USE OF THIS
* SOFTWARE IN TERMS OF ITS CORRECTNESS, ACCURACY, RELIABILITY OR OTHERWISE.
* IN NO EVENT SHALL WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DAMAGES
* RESULTING FROM OR ARISING OUT OF ANY USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, INCLUDING
* WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY,
* PUNITIVE, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR
* SERVICES, LOSS OF USE, DATA OR PROFITS, HOWEVER CAUSED AND UNDER ANY
* THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
* (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF
* THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF WHISTLE COMMUNICATIONS IS ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY
* OF SUCH DAMAGE.
*
* Author: Archie Cobbs <archie@whistle.com>
*
* $FreeBSD: src/sys/netgraph/ng_tee.h,v 1.3 2000/01/27 01:32:53 archie Exp $
* $Whistle: ng_tee.h,v 1.2 1999/01/20 00:22:14 archie Exp $
*/
#ifndef _NETGRAPH_TEE_H_
#define _NETGRAPH_TEE_H_
/* Node type name and magic cookie */
#define NG_TEE_NODE_TYPE "tee"
#define NGM_TEE_COOKIE 916107047
/* Hook names */
#define NG_TEE_HOOK_RIGHT "right"
#define NG_TEE_HOOK_LEFT "left"
#define NG_TEE_HOOK_RIGHT2LEFT "right2left"
#define NG_TEE_HOOK_LEFT2RIGHT "left2right"
/* Statistics structure for one hook */
struct ng_tee_hookstat {
u_int64_t inOctets;
u_int64_t inFrames;
u_int64_t outOctets;
u_int64_t outFrames;
};
/* Keep this in sync with the above structure definition */
#define NG_TEE_HOOKSTAT_INFO { \
{ \
{ "inOctets", &ng_parse_int64_type }, \
{ "inFrames", &ng_parse_int64_type }, \
{ "outOctets", &ng_parse_int64_type }, \
{ "outFrames", &ng_parse_int64_type }, \
{ NULL }, \
} \
}
/* Statistics structure returned by NGM_TEE_GET_STATS */
struct ng_tee_stats {
struct ng_tee_hookstat right;
struct ng_tee_hookstat left;
struct ng_tee_hookstat right2left;
struct ng_tee_hookstat left2right;
};
/* Keep this in sync with the above structure definition */
#define NG_TEE_STATS_INFO(hstype) { \
{ \
{ "right", (hstype) }, \
{ "left", (hstype) }, \
{ "right2left", (hstype) }, \
{ "left2right", (hstype) }, \
{ NULL }, \
} \
}
/* Netgraph commands */
enum {
NGM_TEE_GET_STATS = 1, /* get stats */
NGM_TEE_CLR_STATS, /* clear stats */
};
#endif /* _NETGRAPH_TEE_H_ */